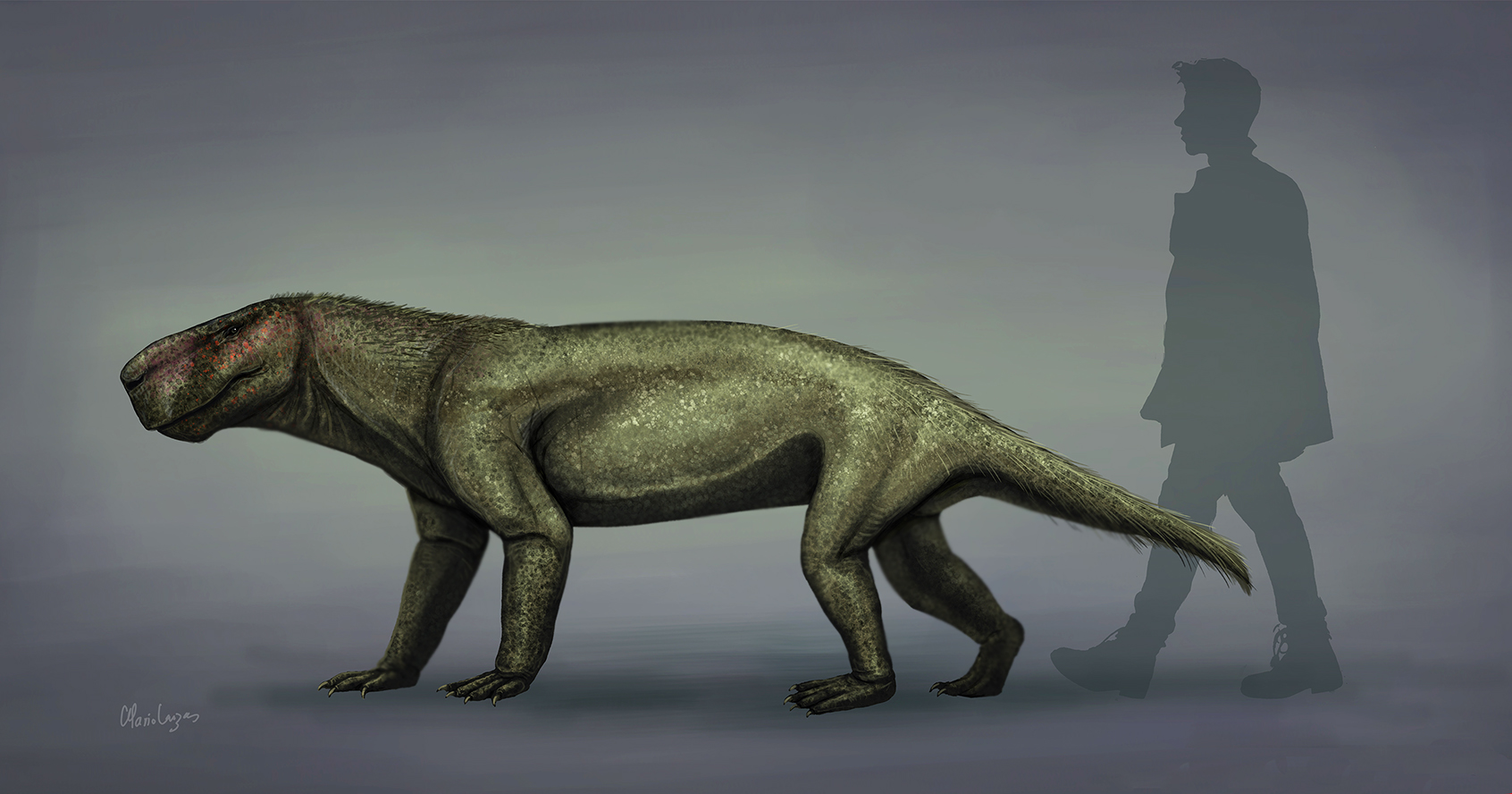|
Clelandina
''Clelandina'' is an extinct genus of rubidgeine gorgonopsian from the Late Permian of ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa. It was first named by Broom in 1948. The type and only species is ''C. rubidgei''. It is relatively rare, with only four known specimens. Description ''Clelandina rubidgei'' has an extraordinarily small sclerotic ring relative to the size of its orbit, which implies that it was diurnal. It is the only rubidgeine with a preserved sclerotic ring, so it is unknown whether this trait was shared by other members of the subfamily. Like all rubidgeines, it was relatively large, with a skull up to 36 cm long. It had reduced dentition, with the teeth posterior to the canines being absent and replaced with a bony ridge. The skull has heavily pachyostosed, with massive rugose bosses. Classification ''Clelandina'' shares many characteristics with the contemporary ''Rubidgea'', and is currently recognized as the sister taxon of this genus. Toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clelandina Rubidgei
''Clelandina'' is an extinct genus of rubidgeine gorgonopsian from the Late Permian of ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa. It was first named by Broom in 1948. The type and only species is ''C. rubidgei''. It is relatively rare, with only four known specimens. Description ''Clelandina rubidgei'' has an extraordinarily small sclerotic ring relative to the size of its orbit, which implies that it was diurnal. It is the only rubidgeine with a preserved sclerotic ring, so it is unknown whether this trait was shared by other members of the subfamily. Like all rubidgeines, it was relatively large, with a skull up to 36 cm long. It had reduced dentition, with the teeth posterior to the canines being absent and replaced with a bony ridge. The skull has heavily pachyostosed, with massive rugose bosses. Classification ''Clelandina'' shares many characteristics with the contemporary ''Rubidgea'', and is currently recognized as the sister taxon of this genus. Toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigrisaurus Pricei
''Clelandina'' is an extinct genus of rubidgeine gorgonopsian from the Late Permian of ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa. It was first named by Broom in 1948. The type and only species is ''C. rubidgei''. It is relatively rare, with only four known specimens. Description ''Clelandina rubidgei'' has an extraordinarily small sclerotic ring relative to the size of its orbit, which implies that it was diurnal. It is the only rubidgeine with a preserved sclerotic ring, so it is unknown whether this trait was shared by other members of the subfamily. Like all rubidgeines, it was relatively large, with a skull up to 36 cm long. It had reduced dentition, with the teeth posterior to the canines being absent and replaced with a bony ridge. The skull has heavily pachyostosed, with massive rugose bosses. Classification ''Clelandina'' shares many characteristics with the contemporary ''Rubidgea'', and is currently recognized as the sister taxon of this genus. Toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsia
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonopsia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsia
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonopsia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidgeini
Rubidgeinae is an extinct subfamily of gorgonopsid therapsids known only from Africa. They were among the largest gorgonopsians, and their fossils are common in the Cistecephalus and Daptocephalus assemblage zones of the Karoo Basin. They lived during the Late Permian, and became extinct at the end of the Permian. Description Rubidgeines were large, quadrupedal carnivores of the family Gorgonopsidae. Their largest teeth are their upper canines, which were blade-like and had well-developed serrations. Their postcanine teeth were small and conical, but were also frequently serrated. Tooth replacement was rapid relative to basal therocephalians. Rubidgeines can be distinguished from other gorgonopsians by the absence of a blade-like parasphenoid bone and reduced or absent preparietal bone. The jugal bone, while narrow in most gorgonopsians, was often broadly expanded in rubidgeines. The largest rubidgeins were ''Dinogorgon'' and ''Rubidgea''. Paleobiology Rubidgeines were among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidgeinae
Rubidgeinae is an extinct subfamily of gorgonopsid therapsids known only from Africa. They were among the largest gorgonopsians, and their fossils are common in the Cistecephalus and Daptocephalus assemblage zones of the Karoo Basin. They lived during the Late Permian, and became extinct at the end of the Permian. Description Rubidgeines were large, quadrupedal carnivores of the family Gorgonopsidae. Their largest teeth are their upper canines, which were blade-like and had well-developed serrations. Their postcanine teeth were small and conical, but were also frequently serrated. Tooth replacement was rapid relative to basal therocephalians. Rubidgeines can be distinguished from other gorgonopsians by the absence of a blade-like parasphenoid bone and reduced or absent preparietal bone. The jugal bone, while narrow in most gorgonopsians, was often broadly expanded in rubidgeines. The largest rubidgeins were ''Dinogorgon'' and ''Rubidgea''. Paleobiology Rubidgeines were among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Therapsids
This list of therapsids is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the Therapsida excluding mammals and purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered therapsids. The list currently contains 510 generic names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synonym, and all other instances are junior synonyms. Senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinogorgon Rubidgei
''Dinogorgon'' is a genus of gorgonopsid from the Late Permian of South Africa and Tanzania. The generic name ''Dinogorgon'' is derived from Greek, meaning "terrible gorgon", while its species name ''rubidgei'' is taken from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Basin. The type species of the genus is ''D. rubidgei''. ''Dinogorgon'' is part of the gorgonopsian subfamily Rubidgeinae, a derived group of large-bodied gorgonopsians restricted to the Late Permian (Lopingian). The Rubidgeinae subfamily first appeared in the ''Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone, and reached their highest diversity in the ''Cistecephalus'' and ''Daptocephalus'' assemblage zones of the Beaufort Group in South Africa. History of discovery The type species of ''Dinogorgon rubidgei'' was discovered on Wellwood farm, a farm owned by the grandfather of Bruce Rubidge, Sidney H. Rubidge, outside of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinogorgon
''Dinogorgon'' is a genus of gorgonopsid from the Late Permian of South Africa and Tanzania. The generic name ''Dinogorgon'' is derived from Greek, meaning "terrible gorgon", while its species name ''rubidgei'' is taken from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Basin. The type species of the genus is ''D. rubidgei''. ''Dinogorgon'' is part of the gorgonopsian subfamily Rubidgeinae, a derived group of large-bodied gorgonopsians restricted to the Late Permian (Lopingian). The Rubidgeinae subfamily first appeared in the ''Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone, and reached their highest diversity in the ''Cistecephalus'' and ''Daptocephalus'' assemblage zones of the Beaufort Group in South Africa. History of discovery The type species of ''Dinogorgon rubidgei'' was discovered on Wellwood farm, a farm owned by the grandfather of Bruce Rubidge, Sidney H. Rubidge, outside of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidgea
''Rubidgea'' is a genus of Gorgonopsia, gorgonopsid from the upper Permian of South Africa and Tanzania, containing the species ''Rubidgea atrox''. The generic name ''Rubidgea'' is sometimes believed to be derived from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Supergroup, Karoo Basin. However, this generic name was actually erected in honor of Rubidge's paternal grandfather, Sydney Rubidge, who was a renowned fossil hunter. Its species name ''atrox'' is derived from Latin, meaning “fierce, savage, terrible”. ''Rubidgea'' is part of the gorgonopsian subfamily Rubidgeinae, a Derived (phylogenetics), derived group of large-bodied gorgonopsians restricted to the Late Permian (Lopingian). The subfamily Rubidgeinae first appeared in the Tropidostoma Assemblage Zone, ''Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone. They reached their highest diversity in the ''Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidgea Atrox
''Rubidgea'' is a genus of Gorgonopsia, gorgonopsid from the upper Permian of South Africa and Tanzania, containing the species ''Rubidgea atrox''. The generic name ''Rubidgea'' is sometimes believed to be derived from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Supergroup, Karoo Basin. However, this generic name was actually erected in honor of Rubidge's paternal grandfather, Sydney Rubidge, who was a renowned fossil hunter. Its species name ''atrox'' is derived from Latin, meaning “fierce, savage, terrible”. ''Rubidgea'' is part of the gorgonopsian subfamily Rubidgeinae, a Derived (phylogenetics), derived group of large-bodied gorgonopsians restricted to the Late Permian (Lopingian). The subfamily Rubidgeinae first appeared in the Tropidostoma Assemblage Zone, ''Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone. They reached their highest diversity in the ''Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smilesaurus Ferox
''Smilesaurus'' is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian known from Africa. It lived during the Late Permian. It contains the single species ''S. ferox''. Description ''Smilesaurus'' was a large gorgonopsian, with a skull length of up to 31 centimeters. It is characterized by extremely long canine teeth, and has the proportionally longest canines of any gorgonopsian. Unlike other gorgonopsians, which probably hunted similarly to predatory reptiles, ''Smilesaurus'' probably was a true saber-toothed predator which hunted using similar tactics to saber-toothed cats. It can be distinguished by other rubidgeines by its lack of cranial pachyostosis and rugosoties, and by its relatively small orbits. Classification The classification of ''Smilesaurus'' has been disputed. It has often been included in Rubidgeinae, but it differs from other members of the clade considerably. Instead, it may be more closely related to '' Arctops'', a position supported by a phylogenetic analysis in 2018. Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |