|
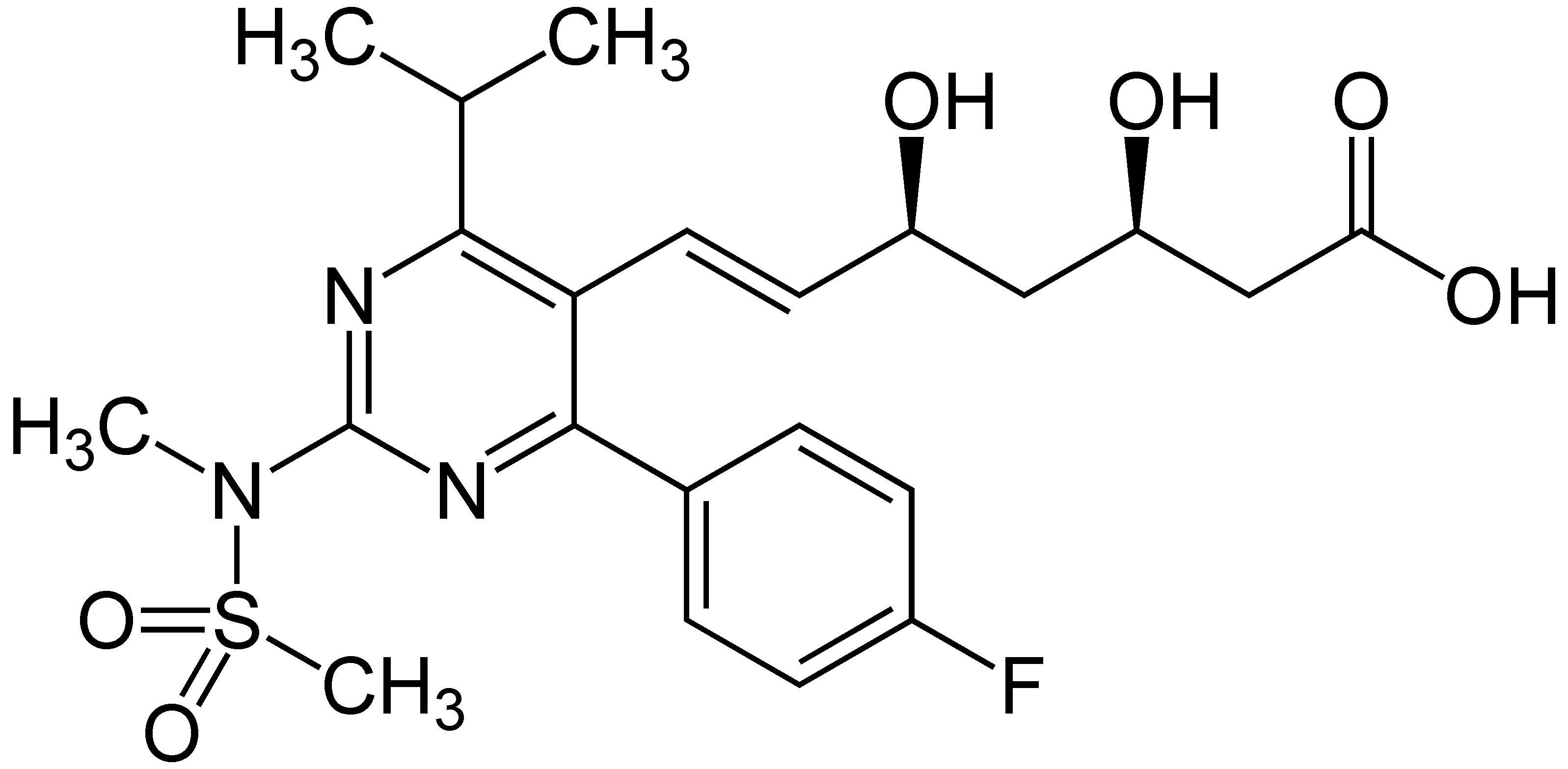
Ranirestat
Ranirestat (also known as AS-3201) is an aldose reductase inhibitor being developed for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma and PharmaKyorin. It has been granted orphan drug status. The drug is to be used orally. Trials A Canadian Phase III clinical trial has been completed. Phase III trials in Europe and the US started in June 2009 and are expected to complete in April 2013. Mechanism of action Ranirestat is aldose reductase inhibitor that acts by reducing sorbitol accumulation in cells. Aldose reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes one of the steps in sorbitol (polyol) pathway which is responsible for formation of fructose from glucose. Aldose reductase activity is increased, parallel to glucose blood levels, in tissues that are not insulin sensitive, including lenses, peripheral nerves and renal glomeruli. Sorbitol does not diffuse through cell membranes easily and therefore accumulates in these tissues, causing osmotic damage, leading to retinopat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldose Reductase Inhibitor
Aldose reductase inhibitors are a class of drugs being studied as a way to prevent eye and nerve damage in people with diabetes. Mechanism Their target, aldose reductase, is an enzyme that is normally present in many other parts of the body, and catalyzes one of the steps in the polyol pathway, sorbitol(polyol) pathway that is responsible for fructose formation from glucose. Aldose reductase activity increases as the glucose concentration rises in diabetes Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ... in those tissues that are not insulin sensitive, which include the lens (anatomy), lenses, peripheral nerves and glomerulus. Sorbitol does not diffuse through cell membranes easily and therefore accumulates, causing osmotic damage which leads to retinopathy and neuropathy. Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is various types of nerve damage associated with diabetes mellitus. Symptoms depend on the site of nerve damage and can include motor changes such as weakness; sensory symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain; or autonomic changes such as urinary symptoms. These changes are thought to result from microvascular injury involving small blood vessels that supply nerves (vasa nervorum). Relatively common conditions which may be associated with diabetic neuropathy include distal symmetric polyneuropathy; third, fourth, or sixth cranial nerve palsy; mononeuropathy; mononeuropathy multiplex; diabetic amyotrophy; and autonomic neuropathy. Signs and symptoms Diabetic neuropathy can affect any peripheral nerves including sensory neurons, motor neurons, and the autonomic nervous system. Therefore, diabetic neuropathy has the potential to affect essentially any organ system and can cause a range of symptoms. There are several distinct syndromes based on the organ syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma
is a pharmaceutical company based in Japan. Its headquarters are in Chuo-ku, Osaka. The original Dainippon Pharmaceuticals (Dainippon Seiyaku) was established in 1885 by Nagayo Sensai, a graduate of Tekijuku – the first private medical school in Japan established by Ogata Kōan. It was set up as a wholly privately-owned company funded by individuals from Tokyo and Osaka, with the land and buildings lent by the government. Technical expertise for the enterprise was provided by Shibata Shokei and Nagai Nagayoshi. The company started its operation in 1885 with equipment imported from Germany. The main products were tincture and other similar drugs listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. Among them was ephedrine, an anti-asthma drug invented by Nagai. In 1893, however, Nagai left the company and the business started to post operating losses. In 1898 it was acquired by Osaka Seiyaku (Osaka Pharmaceutical). Another origin of the company began as Sumitomo Pharmaceuticals, incorporate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyol
In organic chemistry, a polyol is an organic compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups (). The term "polyol" can have slightly different meanings depending on whether it is used in food science or polymer chemistry. Polyols containing two, three and four hydroxyl groups are diols, triols, and tetrols, respectively. Classification Polyols may be classified according to their chemistry. Some of these chemistries are polyether, polyester, polycarbonate and also acrylic polyols. Polyether polyols may be further subdivided and classified as polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol (PEG), polypropylene glycol (PPG) and Polytetrahydrofuran or PTMEG. These have 2, 3 and 4 carbons respectively per oxygen atom in the repeat unit. Polycaprolactone polyols are also commercially available. There is also an increasing trend to use biobased (and hence renewable) polyols. Uses Polyether polyols have numerous uses. As an example, polyurethane foam is a big user of polyether polyols. Polye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolrestat
Tolrestat (INN) (AY-27773) is an aldose reductase inhibitor which was approved for the control of certain diabetic complications. While it was approved for marketed in several countries, it failed a Phase III trial in the U.S. due to toxicity and never received FDA approval. It was discontinued by Wyeth Wyeth, LLC was an American pharmaceutical company. The company was founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1860 as ''John Wyeth and Brother''. It was later known, in the early 1930s, as American Home Products, before being renamed to Wyeth in ... in 1997 because of the risk of severe liver toxicity and death. It was sold under the tradename Alredase. References Aldose reductase inhibitors Acetic acids Hepatotoxins Naphthol ethers Trifluoromethyl compounds Thioamides Withdrawn drugs {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldose Reductase Inhibitors
Aldose reductase inhibitors are a class of drugs being studied as a way to prevent eye and nerve damage in people with diabetes. Mechanism Their target, aldose reductase, is an enzyme that is normally present in many other parts of the body, and catalyzes one of the steps in the sorbitol(polyol) pathway that is responsible for fructose formation from glucose. Aldose reductase activity increases as the glucose concentration rises in diabetes in those tissues that are not insulin sensitive, which include the lenses, peripheral nerves and glomerulus. Sorbitol does not diffuse through cell membranes easily and therefore accumulates, causing osmotic damage which leads to retinopathy and neuropathy. Examples File:Alrestatin.svg, Alrestatin File:Epalrestat.svg, Epalrestat File:Fidarestat structure.svg, Fidarestat File:Imirestat.svg, Imirestat File:Lidorestat.svg, Lidorestat File:Minalrestat.svg, Minalrestat File:Ponalrestat.svg, Ponalrestat File:Ranirestat.svg, Ranirestat File:Salfr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drugs
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
