|
Rock Blasting
Drilling and blasting is the controlled use of explosives and other methods, such as gas pressure blasting pyrotechnics, to break rock for excavation. It is practiced most often in mining, quarrying and civil engineering such as dam, tunnel or road construction. The result of rock blasting is often known as a rock cut. Drilling and blasting currently utilizes many different varieties of explosives with different compositions and performance properties. Higher velocity explosives are used for relatively hard rock in order to shatter and break the rock, while low velocity explosives are used in soft rocks to generate more gas pressure and a greater heaving effect. For instance, an early 20th-century blasting manual compared the effects of black powder to that of a wedge, and dynamite to that of a hammer. The most commonly used explosives in mining today are ANFO based blends due to lower cost than dynamite. Before the advent of tunnel boring machines (TBMs), drilling and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blasting Honkanummi 4-6
{{disambiguation ...
Blasting may refer to: * Abrasive blasting * Blast furnace * Rock blasting See also * Blast (other) * Blaster (other) Blaster may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional entities * Raygun, or blaster, a science-fiction directed-energy weapon ** Blaster (Star Wars), Blaster (''Star Wars'') * Blaster, ''G.I. Joe'' comic book character, a member of the G.I. Joe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , hosting a population exceeding 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of the present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. From the late 6th century, parts of modern Slovakia were incorporated into the Pannonian Avars, Avar Khaghanate. In the 7th century, the Slavs played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. When the Avar Khaghanate dissolved in the 9th century, the Slavs established the Principality of Nitra before it was annexed by the Great Moravia, Principality of Moravia, which later became Great Moravia. When Great Moravia fell in the 10th century, the territory was integrated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a drill bit for making holes, or a screwdriver bit for securing fasteners. Historically, they were powered by hand, and later mains power, but cordless battery-powered drills are proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use. Drills are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, construction, machine tool fabrication, and utility projects. Specially designed versions are made for surgery, dentistry, miniatures, and other applications. History Around 35,000 BC, ''Homo sapiens'' discovered the benefits of the application of rotary tools. This would have rudimentarily consisted of a pointed rock being spun between the hands to bore a hole through another material. This led to the hand drill, a smooth stick, that was sometimes attached to flint point, and was rubbed between the palms. This was used by many ancient civilizations around the world including the Mayans. The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances. The potential energy stored in an explosive material may, for example, be: * chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or grain dust * pressurized gas, such as a gas cylinder, aerosol can, or boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion * nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239 Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand. Materials that detonate (the front of the chemical reaction moves faster through the material than the speed of sound) are said to be "high explosives" and materials that deflagrate ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Ridge Tunnel
The Blue Ridge Tunnel (also known as the Crozet Tunnel) is a historic railroad tunnel built during the construction of the Blue Ridge Railroad in the 1850s. The tunnel was the westernmost and longest of four tunnels engineered by Claudius Crozet to cross the Blue Ridge Mountains at Rockfish Gap in central Virginia. At in length, the tunnel was the longest tunnel in the United States at the time of its completion. The tunnel was used by the Virginia Central Railroad from its opening to 1858, when the line was reorganized as the Chesapeake and Ohio Railroad (renamed Chesapeake and Ohio Railway in 1878). The Chesapeake and Ohio routed trains through the tunnel until it was abandoned and replaced by a new tunnel in 1944. The new tunnel was named the "Blue Ridge Tunnel" as well, although the original tunnel still remains abandoned nearby. The old Blue Ridge Tunnel has since been named a Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers in 1976. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern Railway (UK)
The South Eastern Railway (SER) was a railway company in south-eastern England from 1836 until 1922. The company was formed to construct a route from London to Dover. Branch lines were later opened to Tunbridge Wells, Hastings, Canterbury and other places in Kent. The absorbed or leased other railways, some older than itself, including the London and Greenwich Railway and the Canterbury and Whitstable Railway. Most of the company's routes were in Kent, eastern Sussex and the London suburbs, with a long cross-country route from in Surrey to Reading, Berkshire. Much of the company's early history saw attempts at expansion and feuding with its neighbours; the London Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR) in the west and the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) to the north-east. However, in 1899 the agreed with the to share operation of the two railways, work them as a single system (marketed as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway) and pool receipts: but it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
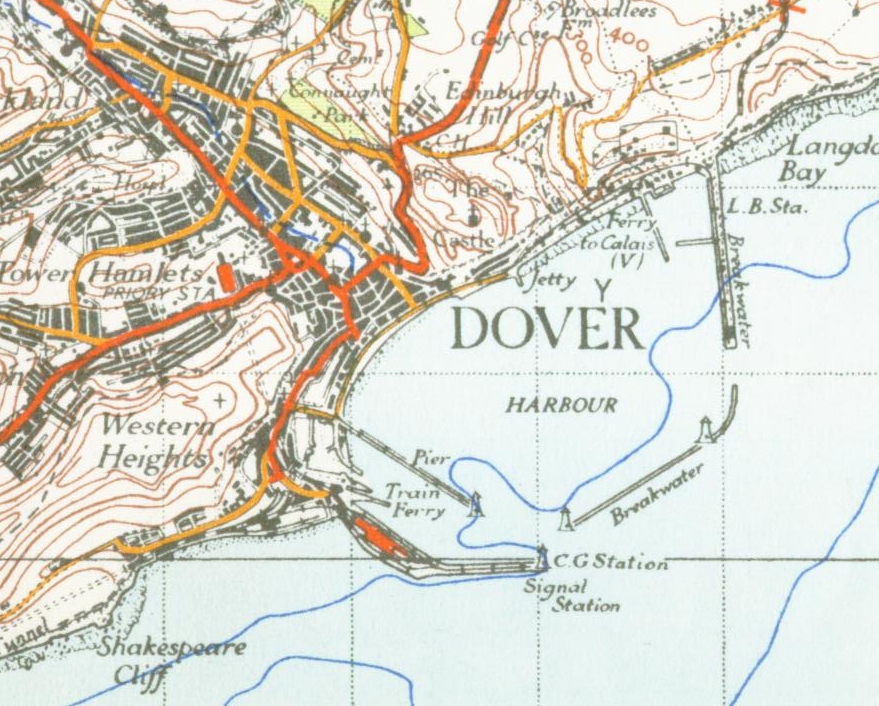
Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Great Britain, Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many English Channel migrant crossings (2018-present), illegal migrant crossings. The Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Cubitt
Sir William Cubitt FRS (bapt. 9 October 1785 – 13 October 1861) was an English civil engineer and millwright. Born in Norfolk, England, he was employed in many of the great engineering undertakings of his time. He invented a type of windmill sail and the prison treadwheel, and was employed as chief engineer, at Ransomes of Ipswich, before moving to London. He worked on canals, docks, and railways, including the South Eastern Railway and the Great Northern Railway. He was the chief engineer of Crystal Palace erected at Hyde Park in 1851. He was president of the Institution of Civil Engineers between 1850 and 1851. Early life Cubitt was born in Dilham, Norfolk, the son of Joseph Cubitt of Bacton Wood, a miller, and Hannah Lubbock. He attended the village school. His father moved to Southrepps, and William at an early age was employed in the mill, but in 1800 was apprenticed to James Lyon, a cabinet-maker at Stalham, from whom he parted after four years. At Bacton W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spithead
Spithead is an eastern area of the Solent and a roadstead for vessels off Gilkicker Point in Hampshire, England. It is protected from all winds except those from the southeast, with the Isle of Wight lying to the south-west. Spithead and the channel to the north is the main approach for shipping to Portsmouth Harbour and onwards to Southampton. Spithead itself is an important naval Anchorage (maritime), anchorage. Historically, Spithead was used for assembling Royal Navy ships, including as a formation area for squadrons or fleets at anchor, as well as for the resupply of ships. Geography It receives its name from the Spit (landform), Spit, a Shoal, sandbank stretching south from the Hampshire shore for . Spithead is long by about in average breadth. Horse and Dean Sand lie to the NE side and Ryde Sand and No Man's Land to the South side. As of 2004, the main channel was reported as being maintained at a dredged depth of 9.5m. History There are evidence of submerged prehis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
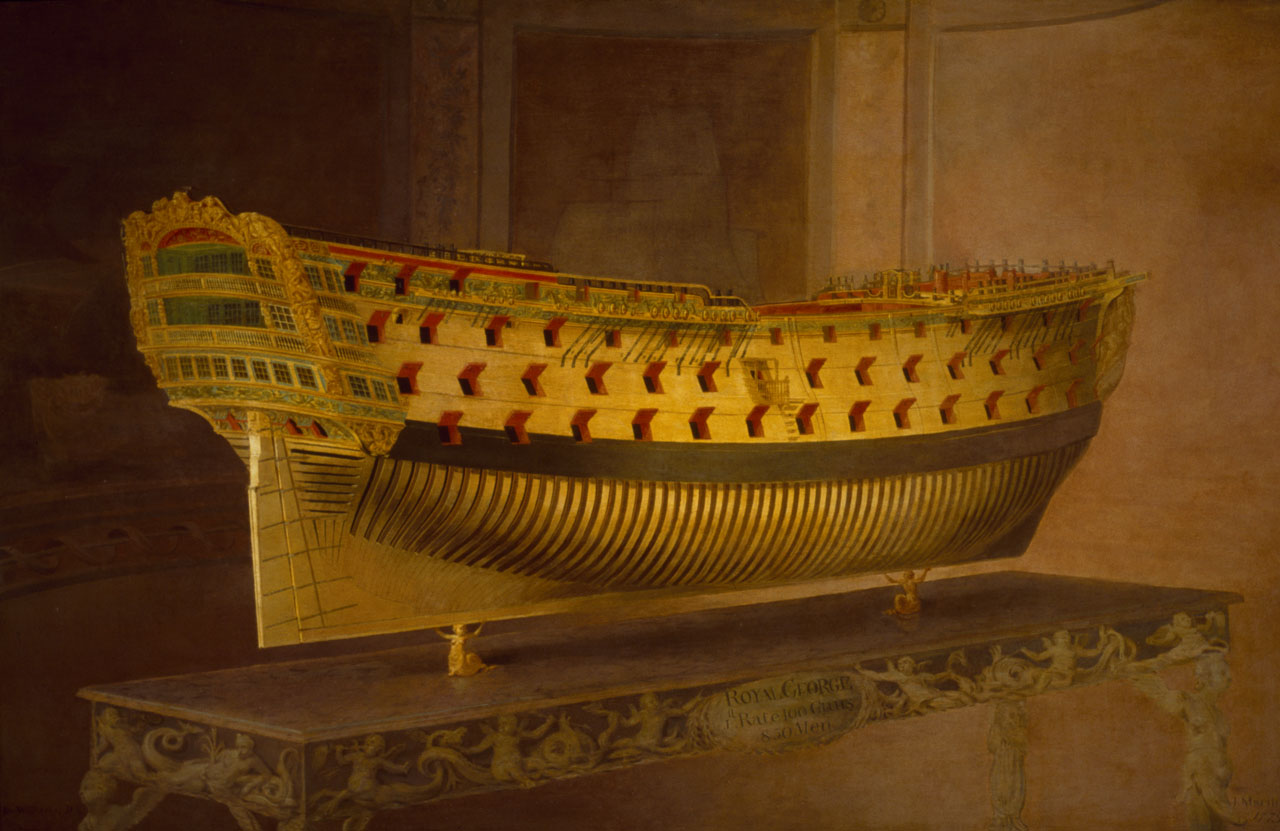
HMS Royal George (1756)
HMS ''Royal George'' was a ship of the line of the Royal Navy. A first-rate with 100 guns on three decks, she was the largest warship in the world at the time of her launch on 18 February 1756. Construction at Woolwich Dockyard had taken ten years. The ship saw immediate service during the Seven Years' War, including the Raid on Rochefort in 1757. She was Admiral Sir Edward Hawke's flagship at the Battle of Quiberon Bay in 1759. The ship was laid up following the conclusion of the war in 1763, but was reactivated in 1777 for the American Revolutionary War. She then served as Rear Admiral Robert Digby's flagship at the Battle of Cape St Vincent in 1780. ''Royal George'' sank on 29 August 1782 whilst anchored at Spithead off Portsmouth. The ship was intentionally rolled (a 'parliamentary heel') so maintenance could be performed on the hull, but the roll became unstable and out of control; the ship took on water and sank. More than 800 people died, making it one of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Pasley
General Sir Charles William Pasley (8 September 1780 – 19 April 1861) was a British soldier and military engineer who wrote the defining text on the role of the post-American Revolution British Empire: ''An Essay on the Military Policy and Institutions of the British Empire'', published in 1810. This text changed how Britons thought their empire should relate to the rest of the world. He warned that Britain could not keep its Empire by its "splendid isolation". Britain would need to fight to gain its empire, and by using the colonies as a resource for soldiers and sailors it grew by an average of per year between the Battle of Waterloo and the American Civil War. Serving in the Royal Engineers in the Napoleonic Wars, he was Europe's leading demolitions expert and siege warfare specialist. Life Pasley was born at Eskdale Muir, Dumfriesshire, on 8 September 1780. He was highly intelligent, capable of translating the New Testament from Greek at the age of eight. In 1796, he e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
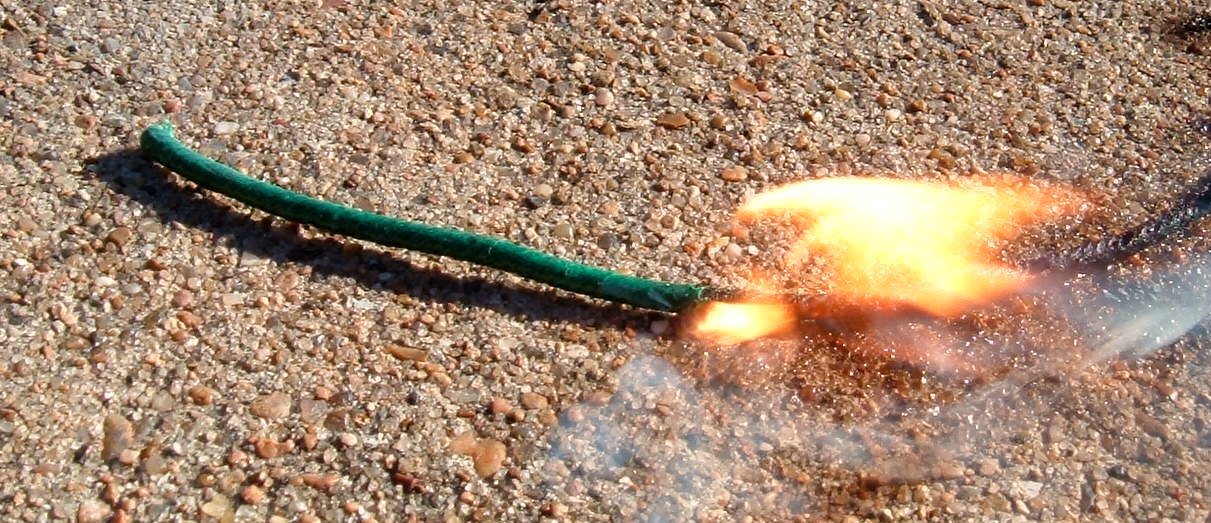
Safety Fuse
The safety fuse is a type of fuse (explosive), fuse invented and patented by English inventor William Bickford (1774–1834), William Bickford in 1831. Originally it consisted of a "tube" of gunpowder surrounded by a waterproofed varnished jute "rope." It replaced earlier and less reliable methods of igniting gunpowder blasting charges which had caused many injuries and deaths in the mining industry. The safety fuse burns at a rate of typically about 30 seconds per foot (1 second per cm). History Documented evidence suggests that the earliest fuse (explosive), fuses were first used by the Chinese between the 10th and 12th centuries. After the Chinese had invented gunpowder, they began adapting its explosive properties for use in military technology. By 1044 they were using gunpowder in simple grenades, bombs, and flamethrowers. Gunpowder did not reach Europe until the early 13th century, carried over from China by Middle Eastern traders and merchants along the old Silk Road. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |