|
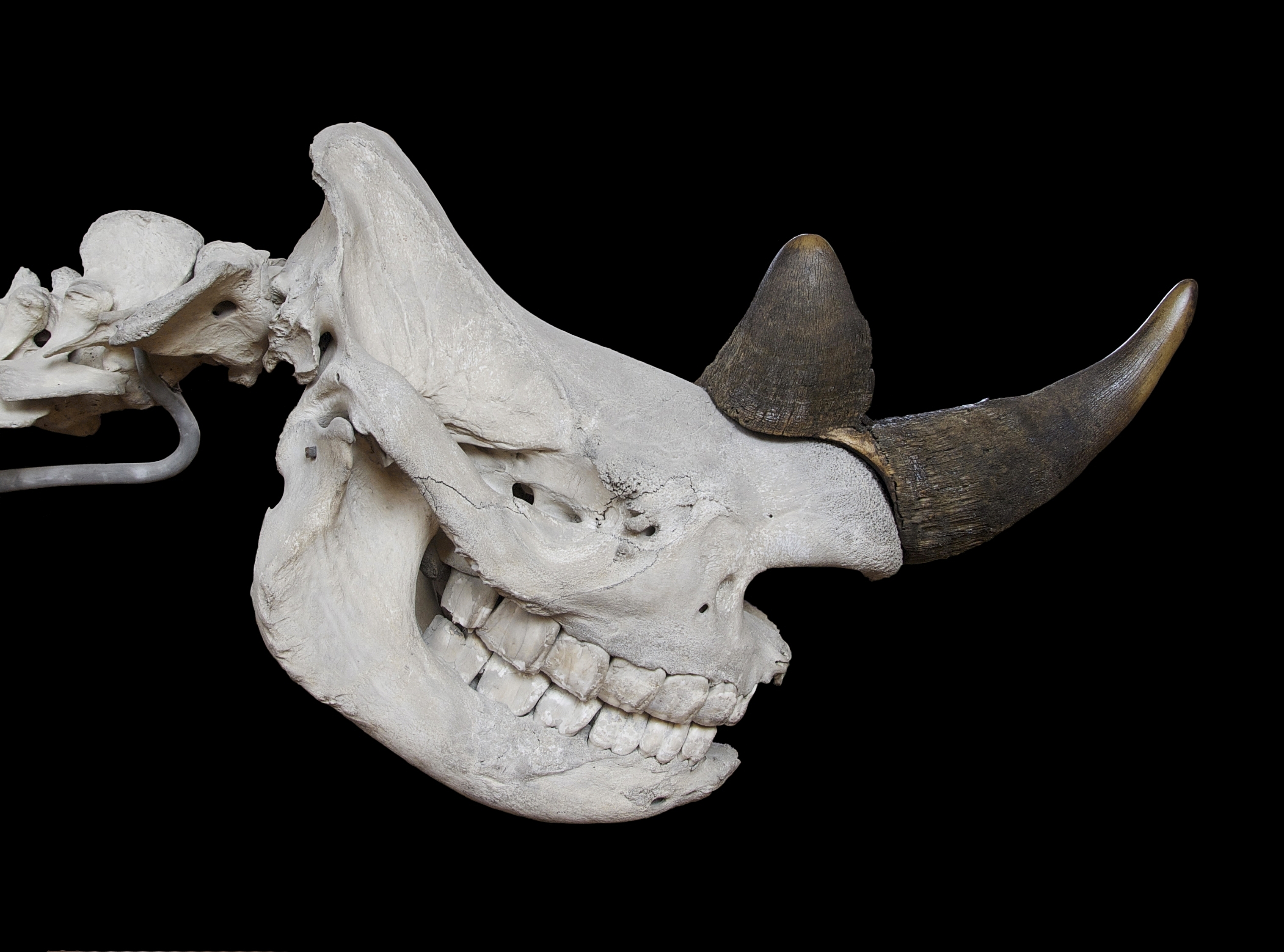
Rhinocerotidae
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South and Southeast Asia. Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen positioned in a lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their hindgut allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of rhinoceros lack teeth at the front of their mouths; they rely instead on their lips t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhino Horn
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family (biology), family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South Asia, South and Southeast Asia. Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivore, herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen positioned in a crystal structure, lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their colon (anatomy), hindgut allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephanorhinus
''Stephanorhinus'' is an extinct genus of two-horned rhinoceros native to Eurasia and North Africa that lived during the Pliocene to Late Pleistocene. Species of ''Stephanorhinus'' were the predominant and often only species of rhinoceros in much of temperate Eurasia, especially Europe, for most of the Pleistocene. Two species of ''Stephanorhinus'' – Merck's rhinoceros (''S. kirchbergensis'') and the narrow-nosed rhinoceros (''S. hemitoechus'') – persisted into the last glacial period. Etymology The first part of the name, ''Stephano-'', honours Stephen I, the first king of Hungary. (The genus name was coined by Kretzoi, a Hungarian.) The second part is from (Greek for "nose"), a typical suffix of rhinoceros genus names. Taxonomy The taxonomic history of ''Stephanorhinus'' is long and convoluted, as many species are known by numerous synonyms and different genera – typically ''Rhinoceros'' and ''Dicerorhinus'' – for the 19th and most of the early 20th century. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmotherium
''Elasmotherium'' is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during Late Miocene through the Pleistocene, existing at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. A more recent date of 26,000 BP is considered less reliable. It was the last surviving member of Elasmotheriinae, a distinctive group of rhinoceroses separate from the group that contains living rhinoceros (Rhinocerotinae). The two groups are estimated to have split at least 35 million years ago according to fossils and molecular evidence. Five species are recognised. The genus first appeared in the Late Miocene in China, likely having evolved from ''Sinotherium'', before spreading to the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Caucasus and Central Asia. The best known, ''E. sibiricum'', sometimes called the Siberian unicorn, was the size of a mammoth and is thought to have borne a large, thick horn on its forehead (though see below). Like all rhinoceroses, elasmotheres were herbivorous. Unlik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perissodactyl
Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Perissodactyla (, ), are animals—ungulates—who have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three (rhinoceroses and tapirs, with tapirs still using four toes on the front legs) or one (equines, third toe) of the five original toes. The non-weight-bearing toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or positioned posteriorly. By contrast, the even-toed ungulates bear most of their weight equally on four or two (an even number) of the five toes: their third and fourth toes. Another difference between the two is that odd-toed ungulates digest plant cellulose in their intestines rather than in one or more stomach chambers as even-toed ungulates, with the exception of Suina, do. The order includes about 17 species divided into three families: Equidae (horses, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). Despite their very different appearances, they were recognized as related families in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odd-toed Ungulate
Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Perissodactyla (, ), are animals—ungulates—who have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three (rhinoceroses and tapirs, with tapirs still using four toes on the front legs) or one (equines, third toe) of the five original toes. The non-weight-bearing toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or positioned posteriorly. By contrast, the even-toed ungulates bear most of their weight equally on four or two (an even number) of the five toes: their third and fourth toes. Another difference between the two is that odd-toed ungulates digest plant cellulose in their intestines rather than in one or more stomach chambers as even-toed ungulates, with the exception of Suina, do. The order includes about 17 species divided into three families: Equidae (horses, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). Despite their very different appearances, they were recognized as related families in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatran Rhinoceros
The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis''), also known as the Sumatran rhino, hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros. It is the only extant species of the genus ''Dicerorhinus''. It is the smallest rhinoceros, although it is still a large mammal; it stands high at the shoulder, with a head-and-body length of and a tail of . The weight is reported to range from , averaging . Like both African species, it has two horns; the larger is the nasal horn, typically , while the other horn is typically a stub. A coat of reddish-brown hair covers most of the Sumatran rhino's body. The Sumatran rhinoceros once inhabited rainforests, swamps and cloud forests in India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and southwestern China, particularly in Sichuan. It is now critically endangered, with only five substantial populations in the wild: four in Suma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum'') is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing (behaviour), grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists of two subspecies: the southern white rhinoceros, with an estimated 19,682–21,077 wild-living animals in the year 2015, and the much rarer northern white rhinoceros. The northern subspecies has very few remaining individuals, with only two confirmed left in 2018 (two females: Fatu, 18 and Najin, 29), both in captivity. Sudan (rhinoceros), Sudan, the world's last known male Northern white rhinoceros, died in Kenya on 19 March 2018 at age 45. Naming A popular albeit widely discredited theory of the origins of the name "white rhinoceros" is a mistranslation from Dutch to English. The English word "white" is said to have been derived by mistranslation of the Dutch word "wijd", which means "wide" in English. The word " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Rhinoceros
} The Indian rhinoceros (''Rhinoceros unicornis''), also called the Indian rhino, greater one-horned rhinoceros or great Indian rhinoceros, is a rhinoceros species native to the Indian subcontinent. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, as populations are fragmented and restricted to less than . Moreover, the extent and quality of the rhino's most important habitat, the alluvial Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands and riverine forest, is considered to be in decline due to human and livestock encroachment. As of August 2018, the global population was estimated to comprise 3,588 individuals, including 2,939 individuals in India and 649 in Nepal. Kaziranga National Park alone had an estimated population of 2,048 rhinos in 2009. Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary in Assam has the highest density of Indian rhinos in the world with 84 individuals in an area of in 2009. Indian rhinos once ranged throughout the entire stretch of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, but excessive hunting and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicerorhinus
''Dicerorhinus'' (Greek: "two" (dio), "horn" (keratos), "nose" (rhinos)) is a genus of the family Rhinocerotidae, consisting of a single extant species, the two-horned Sumatran rhinoceros (''D. sumatrensis''), and several extinct species. The genus likely originated in the Mid to Late Pliocene of Northern Indochina and South China. Many species attributed to the genus probably actually belong in ''Stephanorhinus.'' Taxonomy Historically, ''Dicerorhinus'' was a wastebasket taxon. Revisions by several authors over the years have removed many species: Transferred to ''Stephanorhinus'' *''Dicerorhinus merckii'' *''Dicerorhinus hemitoechus'' *''Dicerorhinus etruscus'' *''Dicerorhinus yunchuchenensis'' *''Dicerorhinus jeanvireti'' *''Dicerorhinus choukoutienensis'' (synonym of Merck's rhinoceros) *''Dicerorhinus orientalis'' (synonym of Merck's rhinoceros) *''Dicerorhinus nipponicus'' Transferred to ''Dihoplus'' *''Dicerorhinus megarhinus'' *''Dicerorhinus schleiermacheri'' *''Dicero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratotherium
''Ceratotherium'' (Greek: "horn" (keratos), "beast" (therion)) is a genus of the family Rhinocerotidae, consisting of a single extant species, the white rhinoceros The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum'') is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists ..., and its extinct relatives, ''Ceratotherium neumayri'' and ''Ceratotherium mauritanicum'', of which ''Ceratotherium efficax'' is considered a synonym. Another species known as ''Ceratotherium praecox'' is now considered a member of the related '' Diceros''. References Mammal genera with one living species Taxa named by John Edward Gray Rhinoceroses Mammal genera Extant Tortonian first appearances {{oddtoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinocerotoidea
Rhinocerotoidea is a superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily consisting of three family groups of odd-toed ungulates, three of which, the Amynodontidae, Hyracodontidae, and Paraceratheriidae, are extinct. The only extant family group is the Rhinocerotidae (true rhinoceroses), which survives as five living species. The extinct members of this superfamily are often called "rhinoceroses" alongside members of the family Rhinocerotidae, though they include genera, such as ''Paraceratherium'', which do not closely resemble modern rhinoceroses. Taxonomy The cladogram below follows a phylogenetic analysis by Bai ''et al.'' (2020): References {{Taxonbar, from=Q15487229 Odd-toed ungulates Mammal superfamilies Taxa named by John Edward Gray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rhinoceros
The black rhinoceros, black rhino or hook-lipped rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis'') is a species of rhinoceros, native to eastern and southern Africa including Angola, Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the rhinoceros is referred to as ''black'', its colours vary from brown to grey. The other African rhinoceros is the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word ' (Dutch ') meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros. The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-western black rhinoceros is classified as near threatened). Three subspecies have been declared extinct, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)