|
Retinitis
Retinitis is inflammation of the retina in the eye, which can permanently damage the retina and lead to blindness. The retina is the eye's "sensing" tissue. Retinitis may be caused by a number of different infectious agents. Its most common form, called retinitis pigmentosa, has a prevalence of one in every 2,500–7,000 people. This condition is one of the leading causes that leads to blindness in patients in the age range of 20–60 years old. Retinitis may be caused by several infectious agents, including toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus and candida. Cytomegalovirus retinitis is an important cause of blindness in AIDS patients. Candida spreading to the retina from the bloodstream usually results in the production of several retinal abscesses An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of rednes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
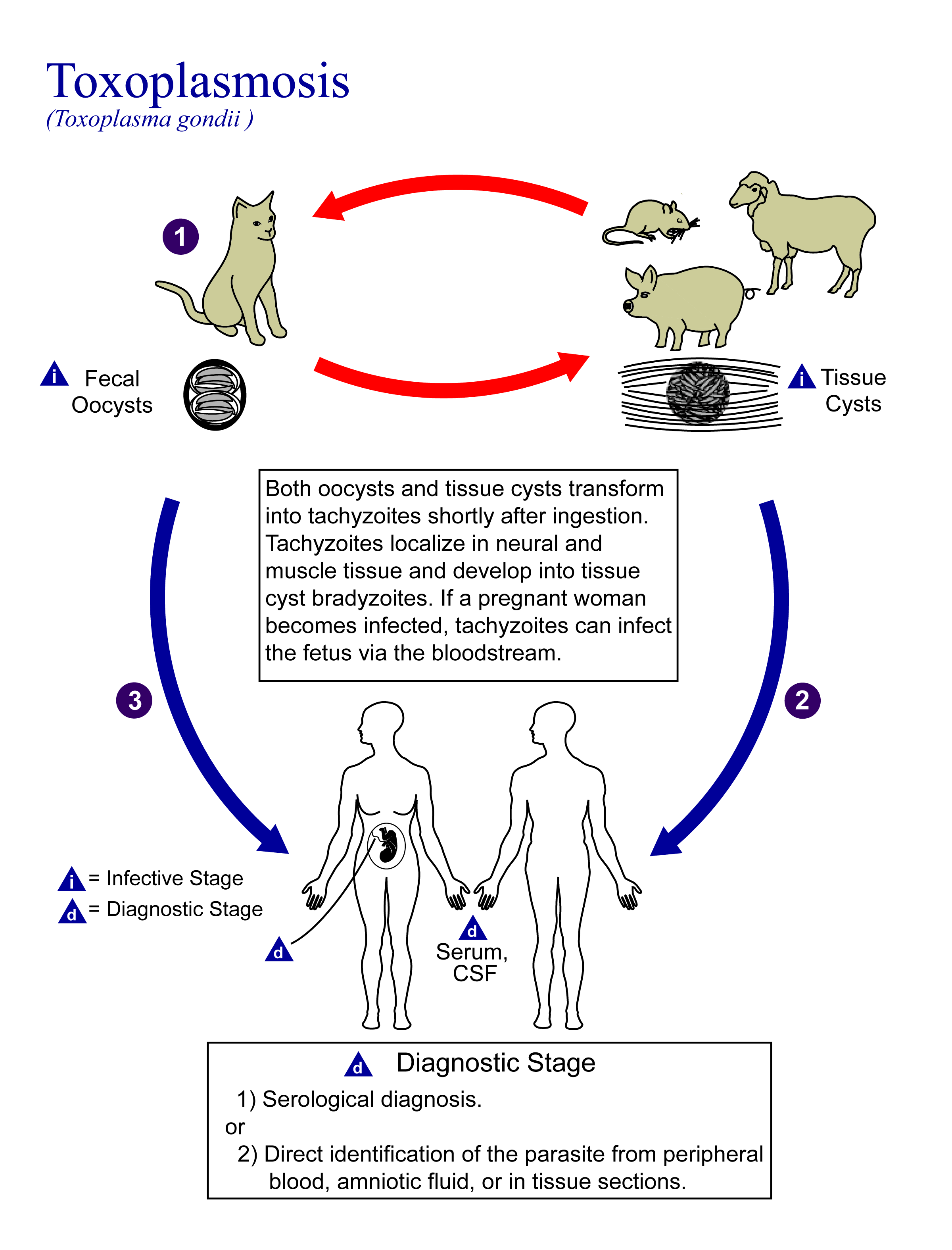
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If a person becomes infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child. Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected woman to their baby during pregnancy. Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people. The parasite is known to reproduce sexually only in the cat family. However, it can infect most types of warm-blooded animals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rods and cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible for the perception of colour through the use of a range of opsins, as well as high-acuity vision used f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (''CMV'') (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherpesvirinae''. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include '' human betaherpesvirus 5'' (HCMV, human cytomegalovirus, HHV-5), which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia. In the medical literature, most mentions of CMV without further specification refer implicitly to human CMV. Human CMV is the most studied of all cytomegaloviruses. MX2/MXB was identified as a restriction factor for herpesviruses, which acts at a very early stage of the replication cycle and MX2/MXB restriction of herpesvirus requires GTPase activity. Taxonomy Within the '' Herpesviridae'', CMV belongs to the '' Betaherpesvirinae'' subfamily, which also include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved. More than 20 types of ''Candida'' can cause infection with ''Candida albicans'' being the most common. Infections of the mouth are most common among children less than one month old, the elderly, and those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual may not notice any symptoms, or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged incubation period with no symptoms. If the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors which are rare in people who have normal immune function. These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss. HIV is spread primarily by unprotected sex (including anal and vaginal sex), contaminated blood transfusions, hypodermic needles, and from mother to ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscesses
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. They are usually caused by a bacterial infection. Often many different types of bacteria are involved in a single infection. In many areas of the world, the most common bacteria present is ''methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus''. Rarely, parasites can cause abscesses; this is more common in the developing world. Diagnosis of a skin abscess is usually made based on what it looks like and is confirmed by cutting it open. Ultrasound imaging may be useful in cases in which the diagnosis is not clear. In abscesses around the anus, computer tomography (CT) may be important to look for deeper infection. Standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |