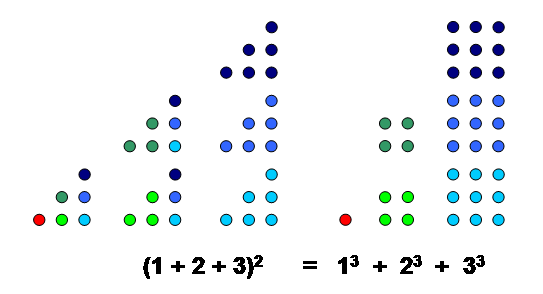|
Prime Signature
In mathematics, the prime signature of a number is the multiset of (nonzero) exponents of its prime factorization. The prime signature of a number having prime factorization p_1^p_2^ \dots p_n^ is the multiset \left \. For example, all prime numbers have a prime signature of , the squares of primes have a prime signature of , the products of 2 distinct primes have a prime signature of and the products of a square of a prime and a different prime (e.g. 12, 18, 20, ...) have a prime signature of . Properties The divisor function τ(''n''), the Möbius function ''μ''(''n''), the number of distinct prime divisors ω(''n'') of ''n'', the number of prime divisors Ω(''n'') of ''n'', the indicator function of the squarefree integers, and many other important functions in number theory, are functions of the prime signature of ''n''. In particular, τ(''n'') equals the product of the incremented by 1 exponents from the prime signature of ''n''. For example, 20 has prime signature an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube (algebra)
In arithmetic and algebra, the cube of a number is its third power, that is, the result of multiplying three instances of together. The cube of a number or any other mathematical expression is denoted by a superscript 3, for example or . The cube is also the number multiplied by its square: :. The ''cube function'' is the function (often denoted ) that maps a number to its cube. It is an odd function, as :. The volume of a geometric cube is the cube of its side length, giving rise to the name. The inverse operation that consists of finding a number whose cube is is called extracting the cube root of . It determines the side of the cube of a given volume. It is also raised to the one-third power. The graph of the cube function is known as the cubic parabola. Because the cube function is an odd function, this curve has a center of symmetry at the origin, but no axis of symmetry. In integers A cube number, or a perfect cube, or sometimes just a cube, is a number wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
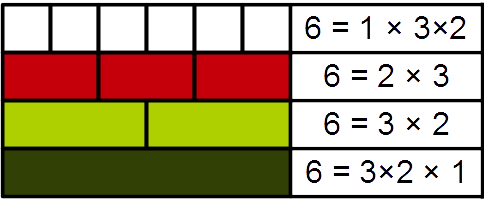
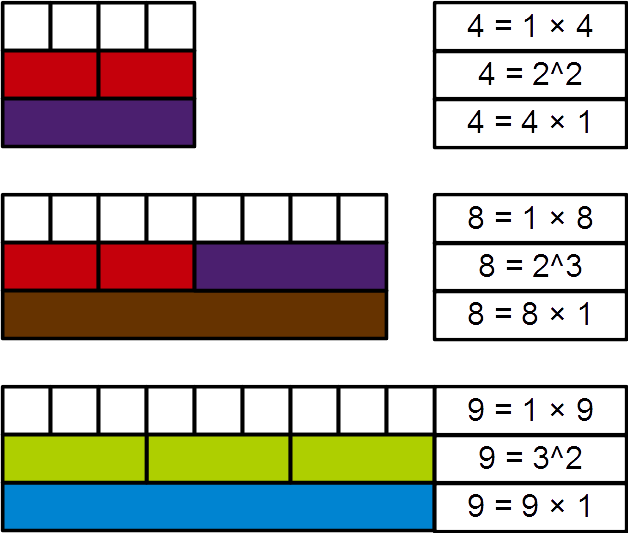
Canonical Representation Of A Positive Integer
In mathematics, the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, also called the unique factorization theorem and prime factorization theorem, states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, up to the order of the factors. For example, : 1200 = 2^4 \cdot 3^1 \cdot 5^2 = (2 \cdot 2 \cdot 2 \cdot 2) \cdot 3 \cdot (5 \cdot 5) = 5 \cdot 2 \cdot 5 \cdot 2 \cdot 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 2 = \ldots The theorem says two things about this example: first, that 1200 be represented as a product of primes, and second, that no matter how this is done, there will always be exactly four 2s, one 3, two 5s, and no other primes in the product. The requirement that the factors be prime is necessary: factorizations containing composite numbers may not be unique (for example, 12 = 2 \cdot 6 = 3 \cdot 4). This theorem is one of the main reasons why 1 is not considered a prime number: if 1 were prime, then factorization into primes would not be unique; for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almost Prime
In number theory, a natural number is called ''k''-almost prime if it has ''k'' prime factors. More formally, a number ''n'' is ''k''-almost prime if and only if Ω(''n'') = ''k'', where Ω(''n'') is the total number of primes in the prime factorization of ''n'' (can be also seen as the sum of all the primes' exponents): :\Omega(n) := \sum a_i \qquad\mbox\qquad n = \prod p_i^. A natural number is thus prime if and only if it is 1-almost prime, and semiprime if and only if it is 2-almost prime. The set of ''k''-almost primes is usually denoted by ''P''''k''. The smallest ''k''-almost prime is 2''k''. The first few ''k''-almost primes are: : The number π''k''(''n'') of positive integers less than or equal to ''n'' with exactly ''k'' prime divisors (not necessarily distinct) is asymptotic to: : \pi_k(n) \sim \left( \frac \right) \frac, a result of Landau. See also the Hardy–Ramanujan theorem In mathematics, the Hardy–Ramanujan theorem, proved by , states that the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achilles Number
An Achilles number is a number that is powerful but not a perfect power. A positive integer is a powerful number if, for every prime factor of , is also a divisor. In other words, every prime factor appears at least squared in the factorization. All Achilles numbers are powerful. However, not all powerful numbers are Achilles numbers: only those that cannot be represented as , where and are positive integers greater than 1. Achilles numbers were named by Henry Bottomley after Achilles, a hero of the Trojan war, who was also powerful but imperfect. ''Strong Achilles numbers'' are Achilles numbers whose Euler totients are also Achilles numbers. Sequence of Achilles numbers A number is powerful if . If in addition the number is an Achilles number. The Achilles numbers up to 5000 are: :72, 108, 200, 288, 392, 432, 500, 648, 675, 800, 864, 968, 972, 1125, 1152, 1323, 1352, 1372, 1568, 1800, 1944, 2000, 2312, 2592, 2700, 2888, 3087, 3200, 3267, 3456, 3528, 3872, 3888, 4000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Power
In mathematics, a perfect power is a natural number that is a product of equal natural factors, or, in other words, an integer that can be expressed as a square or a higher integer power of another integer greater than one. More formally, ''n'' is a perfect power if there exist natural numbers ''m'' > 1, and ''k'' > 1 such that ''mk'' = ''n''. In this case, ''n'' may be called a perfect ''k''th power. If ''k'' = 2 or ''k'' = 3, then ''n'' is called a perfect square or perfect cube, respectively. Sometimes 0 and 1 are also considered perfect powers (0''k'' = 0 for any ''k'' > 0, 1''k'' = 1 for any ''k''). Examples and sums A sequence of perfect powers can be generated by iterating through the possible values for ''m'' and ''k''. The first few ascending perfect powers in numerical order (showing duplicate powers) are : : 2^2 = 4,\ 2^3 = 8,\ 3^2 = 9,\ 2^4 = 16,\ 4^2 = 16,\ 5^2 = 25,\ 3^3 = 27, 2^5 = 32,\ 6^2 = 36,\ 7^2 = 49,\ 2^6 = 64,\ 4^3 = 64,\ 8^2 = 64, \dots The sum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powerful Number
A powerful number is a positive integer ''m'' such that for every prime number ''p'' dividing ''m'', ''p''2 also divides ''m''. Equivalently, a powerful number is the product of a square and a cube, that is, a number ''m'' of the form ''m'' = ''a''2''b''3, where ''a'' and ''b'' are positive integers. Powerful numbers are also known as squareful, square-full, or 2-full. Paul Erdős and George Szekeres studied such numbers and Solomon W. Golomb named such numbers ''powerful''. The following is a list of all powerful numbers between 1 and 1000: :1, 4, 8, 9, 16, 25, 27, 32, 36, 49, 64, 72, 81, 100, 108, 121, 125, 128, 144, 169, 196, 200, 216, 225, 243, 256, 288, 289, 324, 343, 361, 392, 400, 432, 441, 484, 500, 512, 529, 576, 625, 648, 675, 676, 729, 784, 800, 841, 864, 900, 961, 968, 972, 1000, ... . Equivalence of the two definitions If ''m'' = ''a''2''b''3, then every prime in the prime factorization of ''a'' appears in the prime factorization of ''m'' with an exponent of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube-free Integer
In mathematics, a square-free integer (or squarefree integer) is an integer which is divisible by no square number other than 1. That is, its prime factorization has exactly one factor for each prime that appears in it. For example, is square-free, but is not, because 18 is divisible by . The smallest positive square-free numbers are Square-free factorization Every positive integer n can be factored in a unique way as n=\prod_^k q_i^i, where the q_i different from one are square-free integers that are pairwise coprime. This is called the ''square-free factorization'' of . To construct the square-free factorization, let n=\prod_^h p_j^ be the prime factorization of n, where the p_j are distinct prime numbers. Then the factors of the square-free factorization are defined as q_i=\prod_p_j. An integer is square-free if and only if q_i=1 for all i > 1. An integer greater than one is the kth power of another integer if and only if k is a divisor of all i such that q_i\neq 1. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square-free Integer
In mathematics, a square-free integer (or squarefree integer) is an integer which is divisible by no square number other than 1. That is, its prime factorization has exactly one factor for each prime that appears in it. For example, is square-free, but is not, because 18 is divisible by . The smallest positive square-free numbers are Square-free factorization Every positive integer n can be factored in a unique way as n=\prod_^k q_i^i, where the q_i different from one are square-free integers that are pairwise coprime. This is called the ''square-free factorization'' of . To construct the square-free factorization, let n=\prod_^h p_j^ be the prime factorization of n, where the p_j are distinct prime numbers. Then the factors of the square-free factorization are defined as q_i=\prod_p_j. An integer is square-free if and only if q_i=1 for all i > 1. An integer greater than one is the kth power of another integer if and only if k is a divisor of all i such that q_i\neq 1. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube (algebra)
In arithmetic and algebra, the cube of a number is its third power, that is, the result of multiplying three instances of together. The cube of a number or any other mathematical expression is denoted by a superscript 3, for example or . The cube is also the number multiplied by its square: :. The ''cube function'' is the function (often denoted ) that maps a number to its cube. It is an odd function, as :. The volume of a geometric cube is the cube of its side length, giving rise to the name. The inverse operation that consists of finding a number whose cube is is called extracting the cube root of . It determines the side of the cube of a given volume. It is also raised to the one-third power. The graph of the cube function is known as the cubic parabola. Because the cube function is an odd function, this curve has a center of symmetry at the origin, but no axis of symmetry. In integers A cube number, or a perfect cube, or sometimes just a cube, is a number wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parity (mathematics)
In mathematics, parity is the property of an integer of whether it is even or odd. An integer is even if it is a multiple of two, and odd if it is not.. For example, −4, 0, 82 are even because \begin -2 \cdot 2 &= -4 \\ 0 \cdot 2 &= 0 \\ 41 \cdot 2 &= 82 \end By contrast, −3, 5, 7, 21 are odd numbers. The above definition of parity applies only to integer numbers, hence it cannot be applied to numbers like 1/2 or 4.201. See the section "Higher mathematics" below for some extensions of the notion of parity to a larger class of "numbers" or in other more general settings. Even and odd numbers have opposite parities, e.g., 22 (even number) and 13 (odd number) have opposite parities. In particular, the parity of zero is even. Any two consecutive integers have opposite parity. A number (i.e., integer) expressed in the decimal numeral system is even or odd according to whether its last digit is even or odd. That is, if the last digit is 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9, then it is odd; otherwis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greatest Common Divisor
In mathematics, the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers. For two integers ''x'', ''y'', the greatest common divisor of ''x'' and ''y'' is denoted \gcd (x,y). For example, the GCD of 8 and 12 is 4, that is, \gcd (8, 12) = 4. In the name "greatest common divisor", the adjective "greatest" may be replaced by "highest", and the word "divisor" may be replaced by "factor", so that other names include highest common factor (hcf), etc. Historically, other names for the same concept have included greatest common measure. This notion can be extended to polynomials (see Polynomial greatest common divisor) and other commutative rings (see below). Overview Definition The ''greatest common divisor'' (GCD) of two nonzero integers and is the greatest positive integer such that is a divisor of both and ; that is, there are integers and such that and , and is the largest s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |