|
Pramiconazole
Pramiconazole is a triazole antifungal An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as crypto ... which was under development by Barrier Therapeutics for the treatment of acute skin and mucosal fungal infections but was never marketed. References Dioxolanes Imidazolidinones Isopropyl compounds Lanosterol 14α-demethylase inhibitors Organofluorides Phenol ethers para-Methoxyphenylpiperazines Phenylethanolamine ethers Triazole antifungals Ureas {{Antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triazole
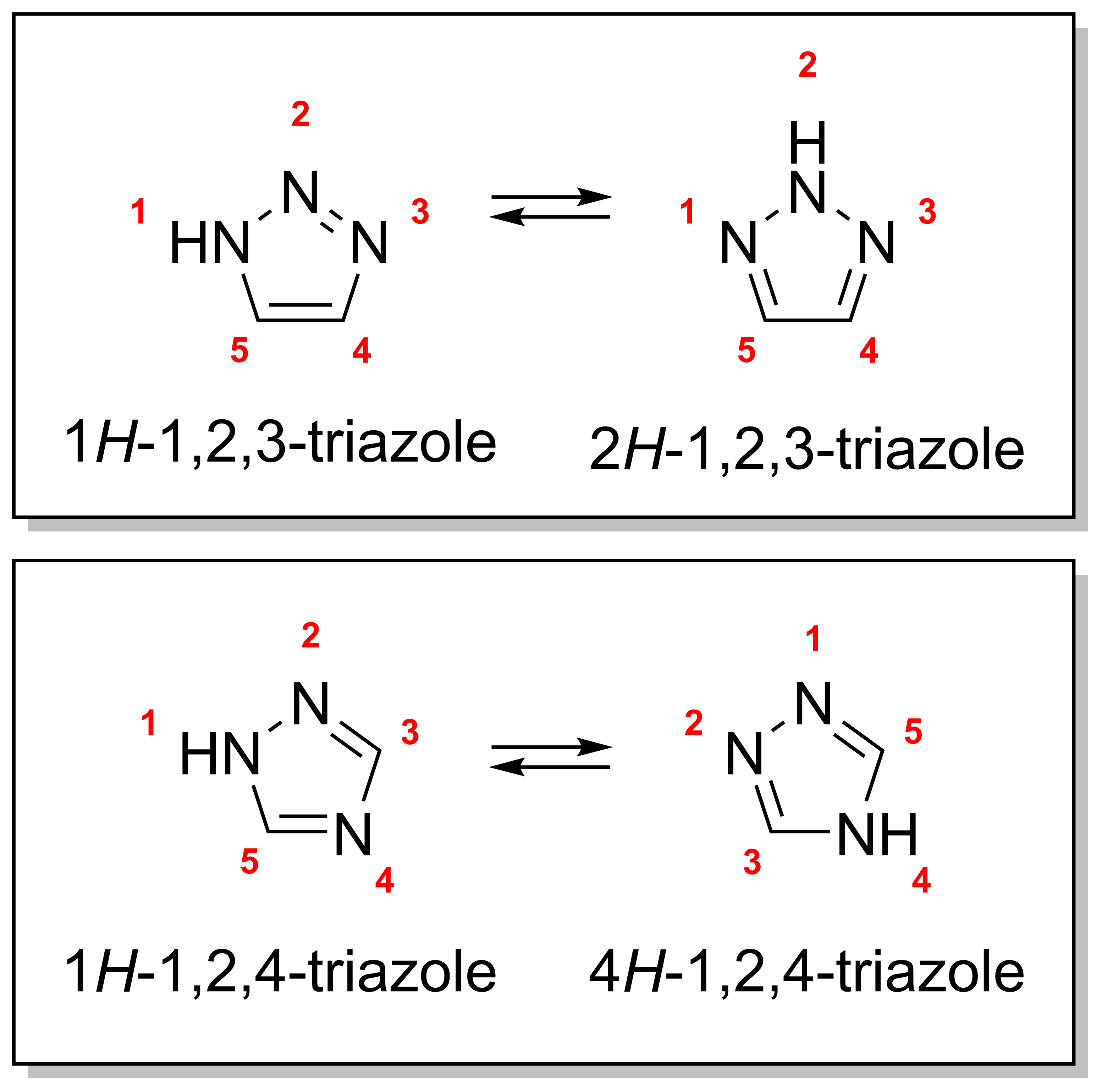
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triazole Antifungals
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple conjugated do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioxolanes
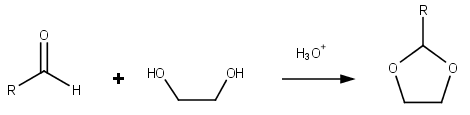
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran by interchange of one oxygen for a CH2 group. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals. As a class of compounds Dioxolanes are a group of organic compounds containing the dioxolane ring. Dioxolanes can be prepared by acetalization of aldehydes and ketalization of ketones with ethylene glycol. (+)-''cis''-Dioxolane is the trivial name for which is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. Protecting groups Organic compounds containing carbonyl groups sometimes need protection so that they do not undergo reactions during transformations of other functional groups that may be present. A variety of approaches to protection and deprotection of carbonyls including as dioxolanes are known. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, propyl is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is often represented in organic chemistry with the symbol Pr (not to be confused with the element praseodymium). An isomeric form of propyl is obtained by moving the point of attachment from a terminal carbon atom to the central carbon atom, named 1-methylethyl or isopropyl. To maintain four substituents on each carbon atom, one hydrogen atom has to be moved from the middle carbon atom to the carbon atom which served as attachment point in the ''n''-propyl variant, written as . Linear propyl is sometimes termed normal and hence written with a prefix ''n''- (i.e., ''n-''propyl), as the absence of the prefix ''n''- does not indicate which attachment point is chosen, i.e. absence of prefix does not automatically exclude the possibility of it be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanosterol 14α-demethylase Inhibitors
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. Role in biosynthesis of other steroids Elaboration of lanosterol under enzyme catalysis leads to the core structure of steroids. 14-Demethylation of lanosterol by CYP51 eventually yields cholesterol. Biosynthesis Research Lanosterol has been identified as a key component in maintaining eye lens clarity. Pre-clinical research has identified Lanosterol as a possible agent for the reversal and prevention of cataracts. In vivo experiments on dogs showed significant reversal of cataracts within 6 weeks of lanosterol injection. In 2018, Lanosterol was shown to improve lens clarity in cells with lens clouding due to aging or physical stressors. A subsequent study found positive results on the optics of the lens in mice with cataracts (Wang, Hoshino,Uesugi, Yagi, Pierscionek and Andley (2022). Use Lanosterol is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organofluorides
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from Lipophobicity, oil and hydrophobe, water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents. The carbon–fluorine bond Fluorine has several distinctive differences from all other substituents encountered in organic molecules. As a result, the physical and chemical properties of organofluorines can be distinctive in comparison to other organohalogens. # The carbon–fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry (an average bond energy around 480 kJ/molKirsch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Ethers
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylethanolamine Ethers
Phenylethanolamine (sometimes abbreviated PEOH), or β-hydroxyphenethylamine, is a trace amine with a structure similar to those of other trace phenethylamines as well as the catecholamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. As an organic compound, phenylethanolamine is a β-hydroxylated phenethylamine that is also structurally related to a number of synthetic drugs in the substituted phenethylamine class. In common with these compounds, phenylethanolamine has strong cardiovascular activity and, under the name ''Apophedrin'', has been used as a drug to produce topical vasoconstriction.''The Merck Index, 10th Ed.'' (1983), p. 1051, Merck & Co., Rahway. In appearance, phenylethanolamine is a white solid. Phenylethanolamine is perhaps best known in the field of bioscience as part of the enzyme name " phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase", referring to an enzyme which is responsible for the conversion of norepinephrine into epinephrine, as well as other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |