|
Polyhedral Map Projection
A polyhedral map projection is a map projection based on a spherical polyhedron. Typically, the polyhedron is overlaid on the globe, and each face of the polyhedron is transformed to a polygon or other shape in the plane. The best-known polyhedral map projection is Buckminster Fuller's Dymaxion map. When the spherical polyhedron faces are transformed to the faces of an ordinary polyhedron instead of laid flat in a plane, the result is a polyhedral globe. Often the polyhedron used is a Platonic solid or Archimedean solid. However, other polyhedra can be used: the AuthaGraph projection makes use of a polyhedron with 96 faces, and the myriahedral projection allows for an arbitrary large number of faces. Although interruptions between faces are common, and more common with an increasing number of faces, some maps avoid them: the Lee conformal projection only has interruptions at its border, and the AuthaGraph projection scales its faces so that the map fills a rectangle without inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dymaxion Projection
The Dymaxion map or Fuller map is a projection of a world map onto the surface of an icosahedron, which can be unfolded and flattened to two dimensions. The flat map is heavily interrupted in order to preserve shapes and sizes. The projection was invented by Buckminster Fuller. The March 1, 1943, edition of ''Life'' magazine included a photographic essay titled "Life Presents R. Buckminster Fuller's Dymaxion World". The article included several examples of its use together with a pull-out section that could be assembled as a "three-dimensional approximation of a globe or laid out as a flat map, with which the world may be fitted together and rearranged to illuminate special aspects of its geography." Fuller applied for a patent in the United States in February 1944, showing a projection onto a cuboctahedron, which he called "dymaxion". The patent was issued in January 1946. In 1954, Fuller and cartographer Shoji Sadao produced the Airocean World Map, a version of the Dymaxion ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo Da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on his achievements as a painter, he also became known for #Journals and notes, his notebooks, in which he made drawings and notes on a variety of subjects, including anatomy, astronomy, botany, cartography, painting, and paleontology. Leonardo is widely regarded to have been a genius who epitomized the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist ideal, and his List of works by Leonardo da Vinci, collective works comprise a contribution to later generations of artists matched only by that of his younger contemporary, Michelangelo. Born Legitimacy (family law), out of wedlock to a successful Civil law notary, notary and a lower-class woman in, or near, Vinci, Tuscany, Vinci, he was educated in Florence by the Italian painter and sculptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahill–Keyes Projection
The Cahill–Keyes projection is a polyhedral compromise map projection first proposed by Gene Keyes in 1975. The projection is a refinement of an earlier 1909 projection by Bernard Cahill. The projection was designed to achieve a number of desirable characteristics, namely symmetry of component maps (octants), scalability allowing the map to continue to work well even at high resolution, uniformity of geocells, metric-based joining edges, minimized distortion compared to a globe, and an easily understood orientation to enhance general usability and teachability. Construction The Cahill–Keyes projection was designed with four fundamental considerations in mind: visual fidelity to a globe, proportional geocells, 10,000 km lengths for each of its octants' three main joined edges, and an M-shape Master-Map profile. The resulting map comprises 8 octants. Each octant is an equilateral triangle with three segments per side. One side runs along the equator, and the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard J
Bernard (''Bernhard'') is a French and West Germanic masculine given name. It is also a surname. The name is attested from at least the 9th century. West Germanic ''Bernhard'' is composed from the two elements ''bern'' "bear" and ''hard'' "brave, hardy". Its native Old English reflex was ''Beornheard'', which was replaced by the French form ''Bernard'' that was brought to England after the Norman Conquest. The name ''Bernhard'' was notably popular among Old Frisian speakers. Its wider use was popularized due to Saint Bernhard of Clairvaux (canonized in 1174). Bernard is the second most common surname in France. Geographical distribution As of 2014, 42.2% of all known bearers of the surname ''Bernard'' were residents of France (frequency 1:392), 12.5% of the United States (1:7,203), 7.0% of Haiti (1:382), 6.6% of Tanzania (1:1,961), 4.8% of Canada (1:1,896), 3.6% of Nigeria (1:12,221), 2.7% of Burundi (1:894), 1.9% of Belgium (1:1,500), 1.6% of Rwanda (1:1,745), 1.2% of Germany ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
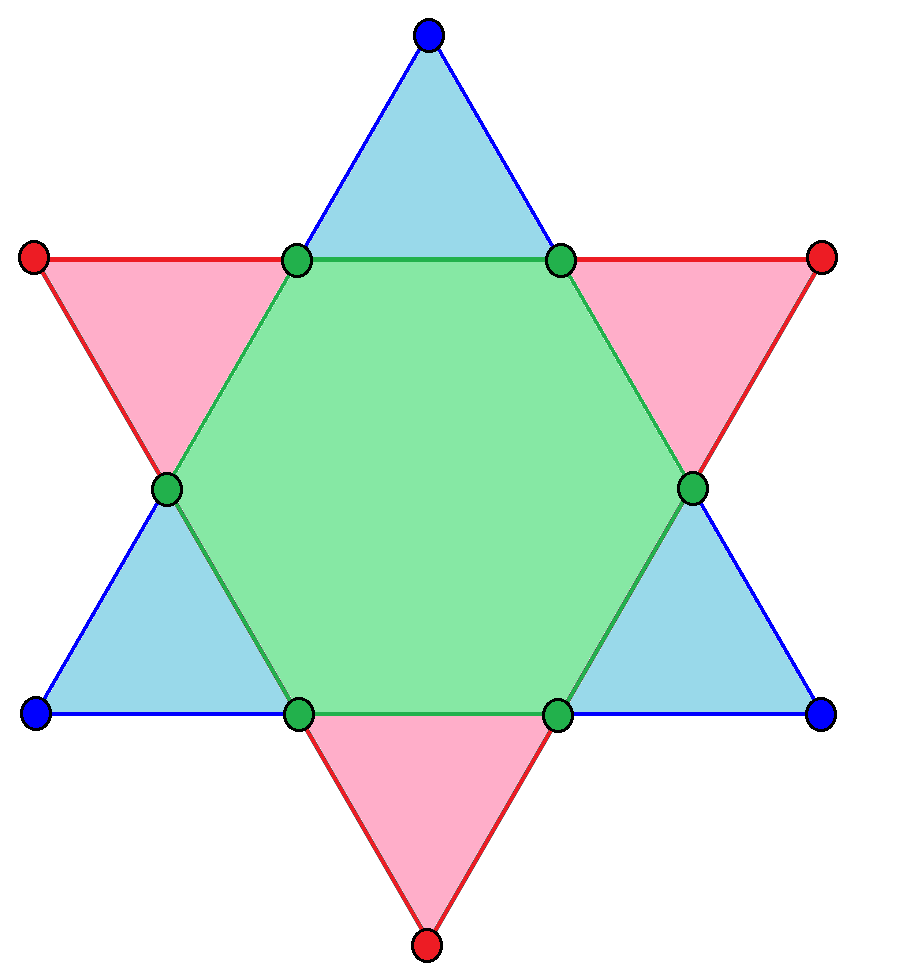
Hexagram
, can be seen as a compound composed of an upwards (blue here) and downwards (pink) facing equilateral triangle, with their intersection as a regular hexagon (in green). A hexagram ( Greek language, Greek) or sexagram (Latin) is a six-pointed geometric star figure with the Schläfli symbol , 2, or . Since there are no true regular continuous hexagrams, the term is instead used to refer to a compound figure of two equilateral triangles. The intersection is a regular hexagon. The hexagram is part of an infinite series of shapes which are compounds of two n-dimensional simplices. In three dimensions, the analogous compound is the stellated octahedron, and in four dimensions the compound of two 5-cells is obtained. It has been historically used in religious and cultural contexts and as decorative motifs. The symbol was used as a decorative motif in medieval Christian churches and Jewish synagogues. It was first used as a mystic symbol by Muslims in the medieval period, known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°. Regular hexagon A ''regular polygon, regular hexagon'' has Schläfli symbol and can also be constructed as a Truncation (geometry), truncated equilateral triangle, t, which alternates two types of edges. A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral polygon, equilateral and equiangular polygon, equiangular. It is bicentric polygon, bicentric, meaning that it is both cyclic polygon, cyclic (has a circumscribed circle) and tangential polygon, tangential (has an inscribed circle). The common length of the sides equals the radius of the circumscribed circle or circumcircle, which equals \tfrac times the apothem (radius of the inscribed figure, inscribed circle). All internal angles are 120 degree (angle), degrees. A regular hexago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombus
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus (plural rhombi or rhombuses) is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The rhombus is often called a "diamond", after the diamonds suit in playing cards which resembles the projection of an octahedral diamond, or a lozenge, though the former sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 60° angle (which some authors call a calisson after the French sweet – also see Polyiamond), and the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle. Every rhombus is simple (non-self-intersecting), and is a special case of a parallelogram and a kite. A rhombus with right angles is a square. Etymology The word "rhombus" comes from grc, ῥόμβος, rhombos, meaning something that spins, which derives from the verb , romanized: , meaning "to turn round and round." The word was used both by Eucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedra
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on the same plane. Cubes and pyramids are examples of convex polyhedra. A polyhedron is a 3-dimensional example of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. Definition Convex polyhedra are well-defined, with several equivalent standard definitions. However, the formal mathematical definition of polyhedra that are not required to be convex has been problematic. Many definitions of "polyhedron" have been given within particular contexts,. some more rigorous than others, and there is not universal agreement over which of these to choose. Some of these definitions exclude shapes that have often been counted as polyhedra (such as the self-crossing polyhedra) or include shapes that are often not considered as valid polyhed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams Hemisphere-in-a-square Projection
The Adams hemisphere-in-a-square is a conformal map projection for a hemisphere. It is a transverse version of the Peirce quincuncial projection, and is named after American cartographer Oscar Sherman Adams, who published it in 1925.. When it is used to represent the entire sphere it is known as the Adams doubly periodic projection. Like many conformal projections, conformality fails at certain points, in this case at the four corners. See also * List of map projections * Guyou hemisphere-in-a-square projection * Doubly periodic function In mathematics, a doubly periodic function is a function defined on the complex plane and having two "periods", which are complex numbers ''u'' and ''v'' that are linearly independent as vectors over the field of real numbers. That ''u'' and '' ... References Map projections Conformal projections {{geometry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guyou Hemisphere-in-a-square Projection
The Guyou hemisphere-in-a-square projection is a conformal map projection for the hemisphere. It is an oblique aspect of the Peirce quincuncial projection. History The projection was developed by of France in 1887. Formal description The projection can be computed as an oblique aspect of the Peirce quincuncial projection by rotating the axis 45 degrees. It can also be computed by rotating the coordinates −45 degrees before computing the stereographic projection; this projection is then remapped into a square whose coordinates are then rotated 45 degrees. The projection is conformal except for the four corners of each hemisphere’s square. Like other conformal polygonal projections, the Guyou is a Schwarz–Christoffel mapping. Properties Its properties are very similar to those of the Peirce quincuncial: * Each hemisphere is represented as a square, the sphere as a rectangle of aspect ratio 2:1. * The part where the exaggeration of scale amounts to double that at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peirce Quincuncial Projection
The Peirce quincuncial projection is the conformal map projection from the sphere to an unfolded square dihedron, developed by Charles Sanders Peirce in 1879. Each octant projects onto an isosceles right triangle, and these are arranged into a square. The name ''quincuncial'' refers to this arrangement: the north pole at the center and quarters of the south pole in the corners form a quincunx pattern like the pips on the ''five'' face of a traditional die. The projection has the distinctive property that it forms a seamless square tiling of the plane, conformal except at four singular points along the equator. Typically the projection is square and oriented such that the north pole lies at the center, but an oblique aspect in a rectangle was proposed by Émile Guyou in 1887, and a transverse aspect was proposed by Oscar Adams in 1925. The projection has seen use in digital photography for portraying spherical panoramas. History The maturation of complex analysis led to gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihedra
A dihedron is a type of polyhedron, made of two polygon faces which share the same set of ''n'' edges. In three-dimensional Euclidean space, it is degenerate if its faces are flat, while in three-dimensional spherical space, a dihedron with flat faces can be thought of as a lens, an example of which is the fundamental domain of a lens space L(''p'',''q''). Dihedra have also been called bihedra, flat polyhedra, or doubly covered polygons. As a spherical tiling, a dihedron can exist as nondegenerate form, with two ''n''-sided faces covering the sphere, each face being a hemisphere, and vertices on a great circle. It is regular if the vertices are equally spaced. The dual of an ''n''-gonal dihedron is an ''n''-gonal hosohedron, where ''n'' digon faces share two vertices. As a flat-faced polyhedron A dihedron can be considered a degenerate prism whose two (planar) ''n''-sided polygon bases are connected "back-to-back", so that the resulting object has no depth. The polygons must b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)