|
Palinopsia
Palinopsia (Greek: ''palin'' for "again" and ''opsia'' for "seeing") is the persistent recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is not a diagnosis; it is a diverse group of pathological visual symptoms with a wide variety of causes. Visual perseveration is synonymous with palinopsia. In 2014, Gersztenkorn and Lee comprehensively reviewed all cases of palinopsia in the literature and subdivided it into two clinically relevant groups: illusory palinopsia and hallucinatory palinopsia. Hallucinatory palinopsia, usually due to seizures or posterior cortical lesions, describes afterimages that are formed, long-lasting, and high resolution. Illusory palinopsia, usually due to migraines, head trauma, prescription drugs, visual snow or hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), describes afterimages that are affected by ambient light and motion and are unformed, indistinct, or low resolution. Presentation People with palinopsia frequently repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illusory Palinopsia
Illusory palinopsia is a subtype of palinopsia, a visual disturbance defined as the persistence or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is a broad term describing a heterogeneous group of symptoms, which is divided into hallucinatory palinopsia and illusory palinopsia. Illusory palinopsia is likely due to sustained awareness of a stimulus and is similar to a visual illusion: the distorted perception of a real external stimulus. Illusory palinopsia is caused by migraines, hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), prescription drugs, and head trauma, but is also sometimes idiopathic. Illusory palinopsia consists of afterimages that are short-lived or unformed, occur at the same location in the visual field as the original stimulus, and are often exposed or exacerbated based on environmental parameters such as stimulus intensity, background contrast, fixation, and movement. Illusory palinopsia symptoms occur continuously or predi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illusory Palinopsia
Illusory palinopsia is a subtype of palinopsia, a visual disturbance defined as the persistence or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is a broad term describing a heterogeneous group of symptoms, which is divided into hallucinatory palinopsia and illusory palinopsia. Illusory palinopsia is likely due to sustained awareness of a stimulus and is similar to a visual illusion: the distorted perception of a real external stimulus. Illusory palinopsia is caused by migraines, hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), prescription drugs, and head trauma, but is also sometimes idiopathic. Illusory palinopsia consists of afterimages that are short-lived or unformed, occur at the same location in the visual field as the original stimulus, and are often exposed or exacerbated based on environmental parameters such as stimulus intensity, background contrast, fixation, and movement. Illusory palinopsia symptoms occur continuously or predi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucinatory Palinopsia
Hallucinatory palinopsia is a subtype of palinopsia, a visual disturbance defined as the persistent or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is a broad term describing a group of symptoms which is divided into hallucinatory palinopsia and illusory palinopsia. Hallucinatory palinopsia refers to the projection of an already-encoded visual memory and is similar to a complex visual hallucination: the creation of a formed visual image where none exists. Hallucinatory palinopsia usually arises from posterior cortical lesions or seizures and can be the presenting symptom of a serious neurological disease. Hallucinatory palinopsia describes afterimages or scenes that are formed, long-lasting, high resolution, and isochromatic. The palinoptic images are not typically reliant on environmental parameters and often present with homonymous visual field deficits. Hallucinatory palinopsia occurs unpredictably and the persistent images can appear anywhere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Polyopia
Cerebral diplopia or polyopia describes seeing two or more images arranged in ordered rows, columns, or diagonals after fixation on a stimulus. The polyopic images occur monocular bilaterally (one eye open on both sides) and binocularly (both eyes open), differentiating it from ocular diplopia or polyopia. The number of duplicated images can range from one to hundreds. Some patients report difficulty in distinguishing the replicated images from the real images, while others report that the false images differ in size, intensity, or color. Cerebral polyopia is sometimes confused with palinopsia ( visual trailing), in which multiple images appear while watching an object. However, in cerebral polyopia, the duplicated images are of a stationary object which are perceived even after the object is removed from the visual field. Movement of the original object causes all of the duplicated images to move, or the polyopic images disappear during motion. In palinoptic polyopia, movement cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder
Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) is a non-psychotic disorder in which a person experiences apparent lasting or persistent visual hallucinations or perceptual distortions after a previous use of drugs, including but not limited to psychedelics, dissociatives, entactogens, THC, SSRIs and antibiotics. Despite being designated as a hallucinogen-specific disorder, the specific contributory role of psychedelic drugs is unknown. The hallucinations and perceptual changes consist of, but are not limited to, visual snow, trails and after images ( palinopsia), light fractals on flat surfaces, intensified colors, altered motion perception, pareidolia, micropsia, and macropsia. People who have never previously taken drugs have also reported some visual anomalies associated with HPPD (such as floaters and visual snow). HPPD is a DSM-5 diagnosis with diagnostic code 292.89 (F16.983). For the diagnosis to be made, other psychological, psychiatric, or neurological conditions mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
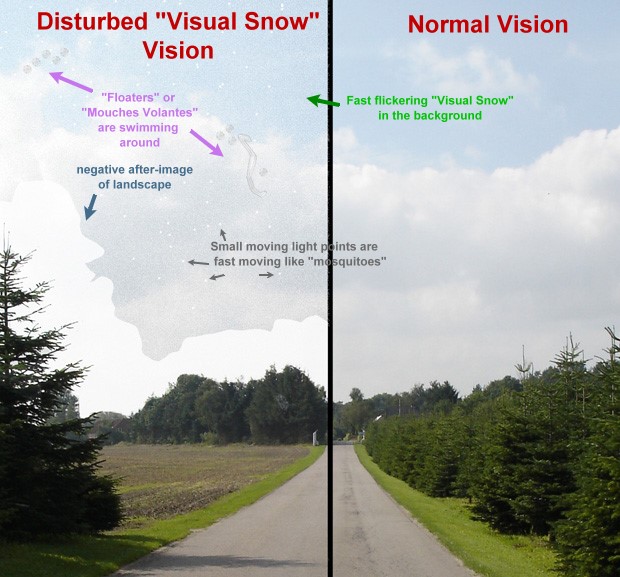
Visual Snow
Visual snow syndrome (VSS) is an uncommon neurological condition in which the primary symptom is that affected individuals see persistent flickering white, black, transparent, or coloured dots across the whole visual field. Other common symptoms are palinopsia, enhanced entoptic phenomena, photophobia, and headaches. The condition is typically always present and has no known cure, as viable treatments are still under research. Migraine and tinnitus are common comorbidities and are both associated with a more severe presentation of the syndrome. The cause of the syndrome is unclear. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve excessive excitability of neurons in the right lingual gyrus and left anterior lobe of cerebellum. Another hypothesis proposes that visual snow syndrome could be a type of thalamocortical dysrhythmia and may involve the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN). A failure of inhibitory action from the TRN to the thalamus may be the underlying cause for inabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleopsia
Teleopsia is a vision perception disorder, in which objects appear much farther away than they are. Teleopsia is a disorder associated with dysmetropsia. See also * Pelopsia References Eye diseases {{eye-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelopsia
Pelopsia is a vision perception disorder in which objects appear nearer than they actually are. Pelopsia can be caused by psychoneurotic phenomena, changes in atmospheric clarity, or sometimes by wearing a corrective lens. See also *Teleopsia Teleopsia is a vision perception disorder, in which objects appear much farther away than they are. Teleopsia is a disorder associated with dysmetropsia. See also * Pelopsia References Eye diseases {{eye-stub ... * Vision deficiencies and disorders References Eye diseases {{eye-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillopsia
Oscillopsia is a visual disturbance in which objects in the visual field appear to oscillate. The severity of the effect may range from a mild blurring to rapid and periodic jumping. Oscillopsia is an incapacitating condition experienced by many patients with neurological disorders. It may be the result of ocular instability occurring after the oculomotor system is affected, no longer holding images steady on the retina. A change in the magnitude of the vestibulo-ocular reflex due to vestibular disease can also lead to oscillopsia during rapid head movements. Oscillopsia may also be caused by involuntary eye movements such as nystagmus, or impaired coordination in the visual cortex (especially due to toxins) and is one of the symptoms of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Those affected may experience dizziness and nausea. Oscillopsia can also be used as a quantitative test to document aminoglycoside toxicity. Permanent oscillopsia can arise from an impairment of the ocular syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entoptic Phenomena
Entoptic phenomena () are visual effects whose source is within the human eye itself. (Occasionally, these are called entopic phenomena, which is probably a typographical mistake.) In Helmholtz's words: "Under suitable conditions light falling on the eye may render visible certain objects within the eye itself. These perceptions are called ''entoptical''." Overview Entoptic images have a physical basis in the image cast upon the retina. Hence, they are different from optical illusions, which are caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that (loosely said) appears to differ from reality. Because entoptic images are caused by phenomena within the observer's own eye, they share one feature with optical illusions and hallucinations: the observer cannot share a direct and specific view of the phenomenon with others. Helmholtz commented on entoptic phenomena which could be seen easily by some observers, but could not be seen at all by others. This variance i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropsia
Micropsia is a condition affecting human visual perception in which objects are perceived to be smaller than they actually are. Micropsia can be caused by optical factors (such as wearing glasses), by distortion of images in the eye (such as optically, via swelling of the cornea or from changes in the shape of the retina such as from retinal edema, macular degeneration, or central serous retinopathy), by changes in the brain (such as from traumatic brain injury, epilepsy, migraines, prescription drugs, and illicit drugs), and from psychological factors. Dissociative phenomena are linked with micropsia, which may be the result of brain-lateralization disturbance. Micropsia is also commonly reported when the eyes are fixating at ( convergence), or focusing at (accommodation), a distance closer than that of the object in accord with Emmert's law. Specific types of micropsia include hemimicropsia, a form of micropsia that is localized to one half of the visual field and can be cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |