Visual Snow on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Visual snow syndrome (VSS) is an uncommon
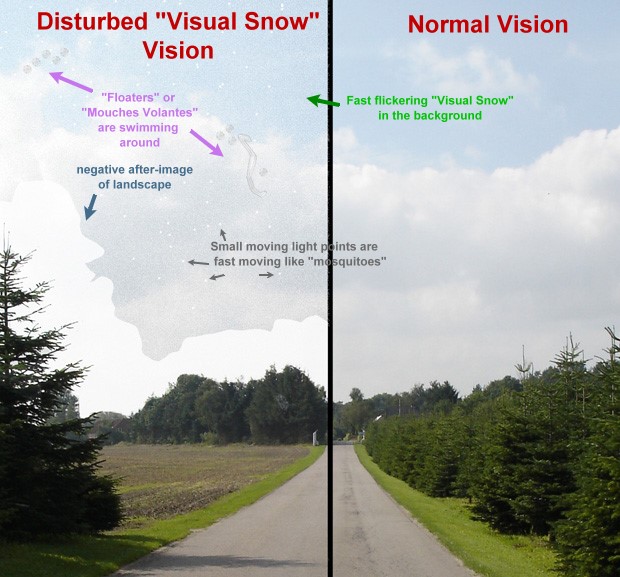 In addition to visual snow, many of those affected have other types of visual disturbances such as starbursts, increased afterimages,
In addition to visual snow, many of those affected have other types of visual disturbances such as starbursts, increased afterimages,
Visual Snow Initiative
Visual snow syndrome
at
Eye On Vision Foundation
{{Visual phenomena Visual disturbances and blindness Hallucinations Ailments of unknown cause Medical controversies Migraine
neurological
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal ...
condition in which the primary symptom is that affected individuals see persistent flickering white, black, transparent, or coloured dots across the whole visual field
The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments". Or simply, visual field can be defined as the entire area that can be seen when an eye is fixed straight at a point ...
. Other common symptoms are palinopsia
Palinopsia (Greek: ''palin'' for "again" and ''opsia'' for "seeing") is the persistent recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is not a diagnosis; it is a diverse group of pathological visual symptoms with a wid ...
, enhanced entoptic phenomena
Entoptic phenomena () are visual effects whose source is within the human eye itself. (Occasionally, these are called entopic phenomena, which is probably a typographical mistake.)
In Helmholtz's words: "Under suitable conditions light falling ...
, photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of ...
, and headaches
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result of m ...
. The condition is typically always present and has no known cure, as viable treatments are still under research. Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
and tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
are common comorbidities and are both associated with a more severe presentation of the syndrome.
The cause of the syndrome is unclear. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve excessive excitability of neurons in the right lingual gyrus
The lingual gyrus, also known as the ''medial'' occipitotemporal gyrus, is a brain structure that is linked to processing vision, especially related to letters. It is thought to also play a role in analysis of logical conditions (i.e., logical ord ...
and left anterior lobe of cerebellum
The anterior lobe of cerebellum is the portion of the cerebellum responsible for mediating unconscious proprioception. Inputs into the anterior lobe of the cerebellum are mainly from the spinal cord. It is sometimes equated to the "paleocerebellum ...
. Another hypothesis proposes that visual snow syndrome could be a type of thalamocortical dysrhythmia and may involve the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN). A failure of inhibitory action from the TRN to the thalamus may be the underlying cause for inability to suppress excitatory sensory information. Research has been limited due to issues of case identification and diagnosis, the latter now largely addressed, and the limited size of any studied cohort. Initial functional brain imaging research suggests visual snow is a brain disorder
Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS). T ...
.
There is no established treatment for visual snow syndrome. Medications that may be used to treat the condition include lamotrigine
Lamotrigine, sold under the brand name Lamictal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood in bipolar disorder. For epilepsy, this includes focal seizures, tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures in Lennox-Gastaut synd ...
, acetazolamide
Acetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension (raised brain pressure of unclear cause), urine alkalin ...
, or verapamil
Verapamil, sold under various trade names, is a calcium channel blocker medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure, angina (chest pain from not enough blood flow to the heart), and supraventricular tachycardia. It may also be used ...
. However, these do not commonly result in benefits and the evidence for their use is very limited.
Signs and symptoms
 In addition to visual snow, many of those affected have other types of visual disturbances such as starbursts, increased afterimages,
In addition to visual snow, many of those affected have other types of visual disturbances such as starbursts, increased afterimages, floater
Floaters or eye floaters are sometimes visible deposits (e.g., the shadows of tiny structures of protein or other cell debris projected onto the retina) within the eye's vitreous humour ("the vitreous"), which is normally transparent, or betwee ...
s, trails, and many others.
Visual snow likely represents a clinical continuum, with different degrees of severity. The presence of comorbidities such as migraine and tinnitus is associated with a more severe presentation of the visual symptoms.Diagnosis
Visual snow syndrome is usually diagnosed with the following proposed criteria: * Visual snow: dynamic, continuous, tiny dots in the entire visual field lasting more than three months. ** The dots are usually black/gray on a white background and gray/white on a black background; however, they can also be transparent, white flashing, or colored. * Presence of at least 2 additional visual symptoms of the 4 following categories: ** i.Palinopsia
Palinopsia (Greek: ''palin'' for "again" and ''opsia'' for "seeing") is the persistent recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is not a diagnosis; it is a diverse group of pathological visual symptoms with a wid ...
. At least 1 of the following: afterimages or trailing of moving objects.
** ii. Enhanced entoptic phenomena
Entoptic phenomena () are visual effects whose source is within the human eye itself. (Occasionally, these are called entopic phenomena, which is probably a typographical mistake.)
In Helmholtz's words: "Under suitable conditions light falling ...
. At least 1 of the following: excessive floaters
Floaters or eye floaters are sometimes visible deposits (e.g., the shadows of tiny structures of protein or other cell debris projected onto the retina) within the eye's vitreous humour ("the vitreous"), which is normally transparent, or between ...
in both eyes, excessive blue field entoptic phenomenon
The blue field entoptic phenomenon is an entoptic phenomenon characterized by the appearance of tiny bright dots (nicknamed blue-sky sprites) moving quickly along squiggly lines in the visual field, especially when looking into bright blue light ...
, self-light of the eye (phosphene
A phosphene is the phenomenon of seeing light without light entering the eye. The word ''phosphene'' comes from the Greek words ''phos'' (light) and ''phainein'' (to show). Phosphenes that are induced by movement or sound may be associated wit ...
s), or spontaneous photopsia
Photopsia is the presence of perceived flashes of light in the Visual field, field of vision.
It is most commonly associated with:
* posterior vitreous detachment
* migraine aura (ocular migraine / retinal migraine)
* acephalgic migraine, migrai ...
.
** iii. Photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of ...
.
** iv. Nyctalopia
Nyctalopia (; ), also called night-blindness, is a condition making it difficult or impossible to see in relatively low light. It is a symptom of several eye diseases. Night blindness may exist from birth, or be caused by injury or malnutrition ( ...
; impaired night vision.
* Symptoms are not consistent with typical migraine aura
An aura is a perceptual disturbance experienced by some with epilepsy or migraine. An epileptic aura is a seizure.
Epileptic and migraine auras are due to the involvement of specific areas of the brain, which are those that determine the symptom ...
.
* Symptoms are not better explained by another disorder (ophthalmological
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medic ...
, drug abuse).
** Normal ophthalmology tests (best-corrected visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
, dilated fundus examination
Dilated fundus examination or dilated-pupil fundus examination (DFE) is a diagnostic procedure that employs the use of mydriatic eye drops (such as tropicamide) to dilate or enlarge the pupil in order to obtain a better view of the fundus of the ...
, visual field, and electroretinogram
Electroretinography measures the electrical responses of various cell types in the retina, including the photoreceptors ( rods and cones), inner retinal cells ( bipolar and amacrine cells), and the ganglion cells. Electrodes are placed on th ...
); not caused by previous intake of psychotropic
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
drugs.
Additional and non visual symptoms like tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
, ear pressure or brain fog
Clouding of consciousness (also known as brain fog or mental fog) occurs when a person is slightly less wakeful or aware than normal. They are not as aware of time or their surroundings and find it difficult to pay attention. People describe this ...
and more might be present. It can also be diagnosed by PET scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
.
Comorbidities
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
and migraine with aura
An aura is a perceptual disturbance experienced by some with epilepsy or migraine. An epileptic aura is a seizure.
Epileptic and migraine auras are due to the involvement of specific areas of the brain, which are those that determine the symptom ...
are common comorbidities
In medicine, comorbidity - from Latin morbus ("sickness"), co ("together"), -ity (as if - several sicknesses together) - is the presence of one or more additional conditions often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary ...
. However, comorbid migraine worsens some of the additional visual symptoms and tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
seen in "visual snow" syndrome. This might bias research studies by patients with migraine being more likely to offer study participation than those without migraine due to having more severe symptoms. In contrast to migraine, comorbidity of typical migraine aura does not appear to worsen symptoms.
Psychological side effects of visual snow can include depersonalization
Depersonalization can consist of a detachment within the self, regarding one's mind or body, or being a detached observer of oneself. Subjects feel they have changed and that the world has become vague, dreamlike, less real, lacking in significa ...
, derealization
Derealization is an alteration in the perception of the external world, causing those with the condition to perceive it as unreal, distant, distorted or falsified. Other symptoms include feeling as if one's environment is lacking in spontaneity, ...
, depression, photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of ...
and heliophobia
Heliophobia is the fear of the sun, sunlight, or any bright light. It is a type of specific phobia. Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of heliophobia depends on the person. Mild sufferers may feel uncomfortable, shaky, nauseated, or numb. Severe suf ...
in the individual affected.
Patients with visual "snow" have normal equivalent input noise levels and contrast sensitivity
Contrast is the contradiction in luminance or colour that makes an object (or its representation in an image or display) distinguishable. In visual perception of the real world, contrast is determined by the difference in the colour and brightn ...
. In a 2010 study, Raghaven et al. hypothesize that what the patients see as "snow" is eigengrau
Eigengrau (German for "intrinsic gray"; ), also called Eigenlicht (Dutch and German for "intrinsic light"), dark light, or brain gray, is the uniform dark gray background color that many people report seeing in the absence of light. The term ''Ei ...
. This would also explain why many report more visual snow in low light conditions: "The intrinsic dark noise of primate cones is equivalent to ~4000 absorbed photons per second at mean light levels; below this the cone signals are dominated by intrinsic noise".
Causes
The causes are unclear. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve excessive excitability of neurons within thecortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
, specifically the right lingual gyrus
The lingual gyrus, also known as the ''medial'' occipitotemporal gyrus, is a brain structure that is linked to processing vision, especially related to letters. It is thought to also play a role in analysis of logical conditions (i.e., logical ord ...
and left cerebellar
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
anterior lobe
The anterior lobe of cerebellum is the portion of the cerebellum responsible for mediating unconscious proprioception. Inputs into the anterior lobe of the cerebellum are mainly from the spinal cord. It is sometimes equated to the "paleocerebellu ...
of the brain.Schankin, CJ, Maniyar, FH, Sprenger, T, Chou, DE, Eller, M, Goadsby, PJ, 2014, The Relation Between Migraine, Typical Migraine Aura and "Visual Snow", Headache,
Persisting visual snow can feature as a leading addition to a migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
complication called persistent aura without infarction
Persistent aura without infarction (PAWOI) is a rare and seemingly benign condition, first described in case reports in 1982 as "prolonged/persistent migraine aura status", and in 2000 as "migraine aura status", that is not yet fully understood. P ...
, commonly referred to as persistent migraine aura (PMA). In other clinical sub-forms of migraine headache may be absent and the migraine aura may not take the typical form of the zigzagged fortification spectrum (scintillating scotoma), but manifests with a large variety of focal neurological symptoms.
Visual snow does not depend on the effect of psychotropic
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
substances on the brain. Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder
Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) is a non-psychotic disorder in which a person experiences apparent lasting or persistent visual hallucinations or perceptual distortions after a previous use of drugs, including but not limited t ...
(HPPD), a condition caused by hallucinogenic drug use, is sometimes linked to visual snow, but both the connection of visual snow to HPPD and the cause and prevalence of HPPD is disputed. Most of the evidence for both is generally anecdotal, and subject to spotlight fallacy.
Another proposed mechanism is a thalamocortical dysrhythmia
Thalamocortical dysrhythmia (TCD) is a theoretical framework in which neuroscientists try to explain the positive and negative symptoms induced by neuropsychiatric disorders like Parkinson's Disease, neurogenic pain, tinnitus, visual snow syndrom ...
of the visual pathway, similar to tinnitus, which is a thalamocortical dysrhythmia of the auditory pathway.
Timeline
* In May 2015, visual snow was described as a persisting positive visual phenomenon distinct from migraine aura in a study by Schankin and Goadsby. * In December 2020, a study found local increases in regional cerebral perfusion in patients with visual snow syndrome. * In May 2021, University of Zurich researchers announced a clinical trial onneurofeedback
Neurofeedback (NFB), also called neurotherapy, is a type of biofeedback that presents real-time feedback from brain activity in order to reinforce healthy brain function through operant conditioning. Typically, electrical activity from the brain i ...
for visual snow syndrome.
* In June 2021, University of Colorado researchers started recruiting for a clinical trial on transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse gener ...
for visual snow syndrome.
* In September 2021, two studies found white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution ...
alterations in parts of the visual cortex and outside the visual cortex in patients with visual snow syndrome.
Treatments
It is difficult to resolve visual snow with treatment, but it is possible to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life through treatment, both of the syndrome and its comorbidities. Medications that may be used includelamotrigine
Lamotrigine, sold under the brand name Lamictal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood in bipolar disorder. For epilepsy, this includes focal seizures, tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures in Lennox-Gastaut synd ...
, acetazolamide
Acetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension (raised brain pressure of unclear cause), urine alkalin ...
, or verapamil
Verapamil, sold under various trade names, is a calcium channel blocker medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure, angina (chest pain from not enough blood flow to the heart), and supraventricular tachycardia. It may also be used ...
, but these do not always result in benefits. As of 2021, there were two ongoing clinical trials using transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse gener ...
and neurofeedback
Neurofeedback (NFB), also called neurotherapy, is a type of biofeedback that presents real-time feedback from brain activity in order to reinforce healthy brain function through operant conditioning. Typically, electrical activity from the brain i ...
for visual snow.
A recent study in the ''British Journal of Ophthalmology
The ''British Journal of Ophthalmology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of ophthalmology. The journal was established in 1917 by the amalgamation of the ''Royal London (Moorfields) Ophthalmic Hospital Reports'' with the ''O ...
'' has confirmed that common drug treatments are generally ineffective in visual snow syndrome (VSS). Vitamins
A vitamin is an organic molecule (or a set of molecules closely related chemically, i.e. vitamers) that is an essential micronutrient that an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its metabolism. Essential nutrien ...
and benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, i ...
, however, were shown to be beneficial in some patients and can be considered safe for this condition.
Dr. Victoria Pelak, Professor of Neurology and Ophthalmology in the Department of Neurology at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is the academic health sciences campus in Aurora, Colorado that houses the University of Colorado's six health sciences-related schools and colleges, including the University of Colorado School ...
has recently directed, published, and completed enrollment for a TMS study protocol. The study protocol aims to investigate the use of rTMS intervention to improve symptoms and visual dysfunction associated with visual snow (VS); the study protocol also describes the challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
.
In addition, Dr. Pelak described during her practice that she lets patients know that current treatment options are only limited to alleviating symptoms. She recommends that her patients focus on pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical treatments to control migraine, headaches, anxiety, and depression. As for light sensitivity complications, Dr. Pelak advises patients to use FL-41 tinted lenses indoors. She also recommends visual occupational therapists who assist patients with color-tinted lenses to alleviate VSS symptoms. Furthermore, Dr. Pelak states that exercising, meditation, and a healthy balanced diet can improve overall daily functioning.
References
External links
Visual Snow Initiative
Visual snow syndrome
at
NIH
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
* http://visualsnowsyndrome.com/
* Eye On Vision Foundation
{{Visual phenomena Visual disturbances and blindness Hallucinations Ailments of unknown cause Medical controversies Migraine