|
Pâté Chinois
Pâté chinois () ('Chinese pie') is a French Canadian dish similar to the English shepherd's pie or French ''hachis Parmentier''. It is a traditional recipe in both Québécois cuisine and Acadian cuisine. Ingredients The dish is made with layered ground beef (sometimes mixed with sautéed diced onions) on the bottom, canned corn (either whole-kernel, creamed, or a mixture) for the middle layer, and mashed potatoes on top. Seasonings may be added to the top. Variations may include reversing the layering of ingredients with potatoes at the bottom, then meat, topped with creamed corn; adding diced bell peppers to the ground beef; and serving the dish with pickled eggs or beets. Once served, ketchup can be added. Origins There are no confirmed appearances of ''pâté chinois'' before the 1930s."Origines du pâté chinois" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States. Between 1534 and 1763, Quebec was called ''Canada'' and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001. Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, the railway owns approximately of track in seven provinces of Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves Minneapolis–St. Paul, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and Albany, New York, in the United States. The railway was first built between eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a commitment extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871; the CPR was Canada's first transcontinental railway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as ''Fort Ville-Marie, Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. As of 2021, the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a Census Metropolitan Area#Census metropolitan areas, metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest city, and List of cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Ville-Marie
Fort Ville-Marie was a French fortress and settlement established in May 1642 by a company of French settlers, led by Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve, on the Island of Montreal in the Saint Lawrence River at the confluence of the Ottawa River, in what is today the province of Quebec, Canada. Its name is French for "City of Mary", a reference to the Blessed Virgin Mary. It is the historic nucleus around which the original settlement of Montreal grew. The settlement became a centre for the fur trade and French expansion into North America until the Treaty of Paris in 1763, which ended the French and Indian War and ceded the territory of New France to Britain. Given its importance, the site of the fort was designated a National Historic Site of Canada in 1924. Place Royale Extensive archaeological work in Montreal has revealed the 1,000-year history of human habitation in the area. In his second expedition to North America in 1535, Jacques Cartier observed the indigenous vil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sault Saint-Louis
The Kahnawake Mohawk Territory (french: Territoire Mohawk de Kahnawake, in the Mohawk language, ''Kahnawáˀkye'' in Tuscarora) is a First Nations reserve of the Mohawks of Kahnawá:ke on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec, Canada, across from Montreal. Established by French Canadians in 1719 as a Jesuit mission, it has also been known as ''Seigneury Sault du St-Louis'', and ''Caughnawaga'' (after a Mohawk village in the Mohawk Valley of New York). There are 17 European spelling variations of the Mohawk ''Kahnawake''. Kahnawake's territory totals an area of . Its resident population numbers about 8,000, with a significant number living off reserve. Its land base today is unevenly distributed due to the federal Indian Act, which governs individual land possession. It has rules that are different from those applying to Canadian non-reserve areas. Most ''Kahnawake'' residents originally spoke the Mohawk language, and some learned French when trading with and alli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris. The vast territory of ''New France'' consisted of five colonies at its peak in 1712, each with its own administration: Canada, the most developed colony, was divided into the districts of Québec, Trois-Rivières, and Montréal; Hudson Bay; Acadie in the northeast; Plaisance on the island of Newfoundland; and Louisiane. It extended from Newfoundland to the Canadian Prairies and from Hudson Bay to the Gulf of Mexico, including all the Great Lakes of North America. In the 16th century, the lands were used primarily to draw from the wealth of natural resources such as furs through trade with the various indigenous peoples. In the seventeenth century, successful settlements began in Acadia and in Quebe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and they have a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pemmican
Pemmican (also pemican in older sources) is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenous cuisine in certain parts of North America and it is still prepared today. The word comes from the Cree word (), which is derived from the word (), "fat, grease". The Lakota (or Sioux) word is , originally meaning "grease derived from marrow bones", with the creating a noun, and referring to small pieces that adhere to something. It was invented by the Indigenous peoples of North America. Pemmican was widely adopted as a high-energy food by Europeans involved in the fur trade and later by Arctic and Antarctic explorers, such as Captain Robert Bartlett, Ernest Shackleton, Richard E. Byrd, Fridtjof Nansen, Robert Falcon Scott, George W. DeLong, and Roald Amundsen. Ingredients Traditionally, the specific ingredients used for pemmican w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South China, Maine
South China is a village in the town of China in Kennebec County, Maine, United States. It is one of five villages in the town. Located between Augusta and Waterville, South China sits along the shores of its namesake, China Lake. It is an hour and a half from both Bangor and Portland. Maine State Route 3 runs through the major part of the town, leading west to Augusta and east to Belfast, and U.S. Route 202 (Lakeview Drive) connects South China with China. Communities South China is home to Friends Camp, a Quaker summer camp which has been active for over 50 years. It is also the home of a Christian church, South China Community Church, across from the South China Library (founded in 1830). The church is open to and welcomes all practicing Christians of any denomination. Three-Mile Pond can be accessed from Route 3, a mile south of the South China Community Church. South China is also home to Maine's second largest private high school, Erskine Academy. Business Ron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potatoes
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Wild potato species can be found from the southern United States to southern Chile. The potato was originally believed to have been domesticated by Native Americans independently in multiple locations,University of Wisconsin-Madison, ''Finding rewrites the evolutionary history of the origin of potatoes'' (2005/ref> but later genetic studies traced a single origin, in the area of present-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia. Potatoes were domesticated there approximately 7,000–10,000 years ago, from a species in the ''Solanum brevicaule'' complex. Lay summary: In the Andes region of South America, where the species is indigenous, some close relatives of the potato are cultivated. Potatoes were introduced to Europe from the Americas by the Spanish in the second half of the 16th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
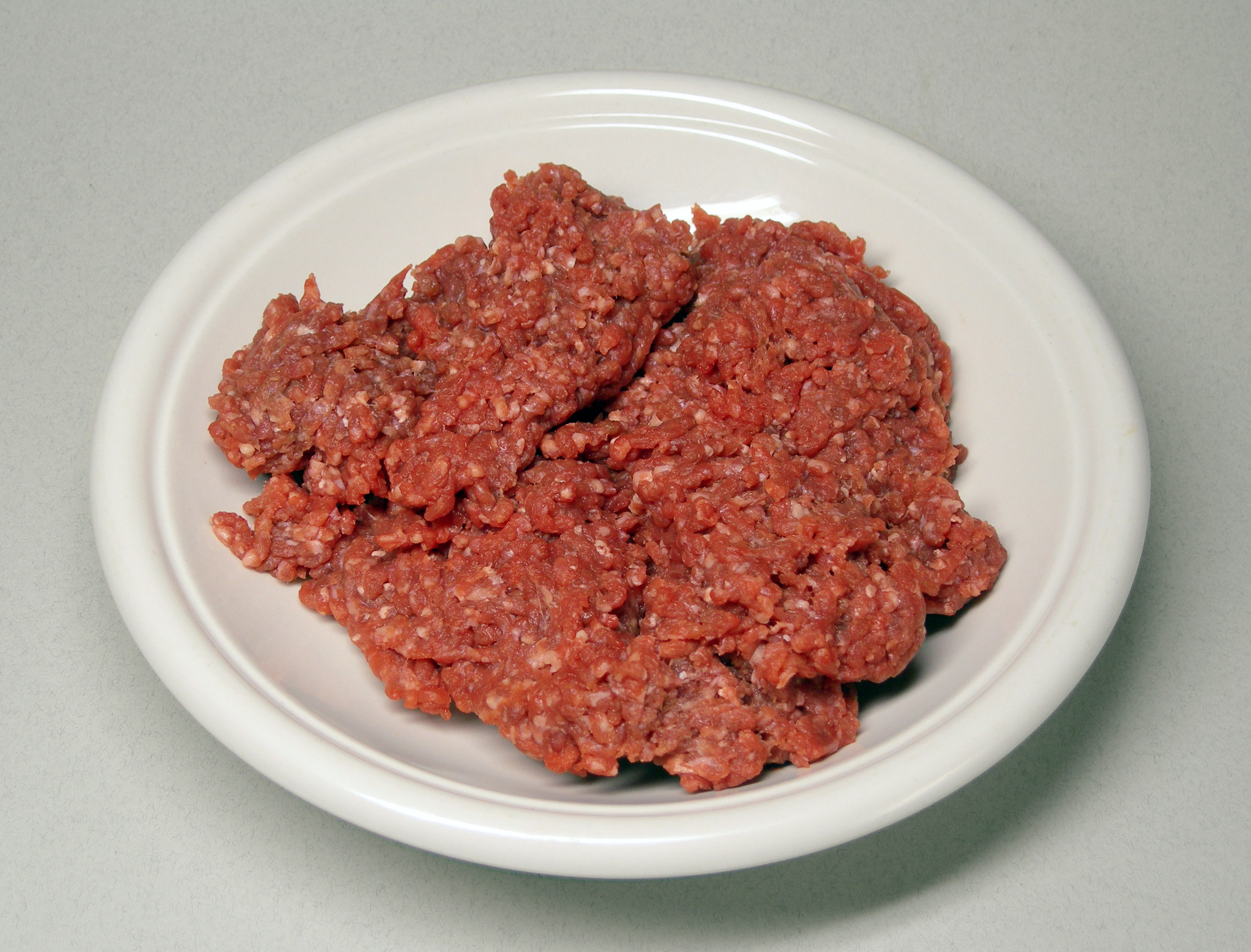
Ground Beef
Ground beef, minced beef or beef mince is beef that has been finely chopped with a knife, meat grinder (American English), mincer or mincing machine (British English). It is used in many recipes including hamburgers, bolognese sauce, meatloaf, meatballs and kofta. It is not the same as mincemeat, which is a mixture of chopped dried fruit, distilled spirits, spices and historically (but nowadays rare) minced/ground meat. Contents In many countries, food laws define specific categories of ground beef and what they can contain. For example, in the United States, beef fat may be added to hamburger but not to ground beef if the meat is ground and packaged at a USDA-inspected plant.These rules only apply to meat being sold across state lines. In the U.S., much ground beef is produced at local grocery stores and is not sold across state lines. In these cases, the laws of the local state apply; state laws may have different requirements. In the U.S., a maximum of 30% fat by weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |