|
Pine Barrens
Pine barrens, pine plains, sand plains, or pineland areas occur throughout the U.S. from Florida to Maine (see Atlantic coastal pine barrens) as well as the Midwest, West, and Canada and parts of Eurasia. Perhaps the most well known pine-barrens area is the New Jersey Pine Barrens. "Pine barrens" are generally pine forests in otherwise "barren" and agriculturally difficult areas. Such pine forests often occur on dry, acidic, infertile soils, which also include grasses, forbs, and low shrubs. The most extensive pine barrens occur in large areas of sandy glacial deposits (including outwash plains), lakebeds, and outwash terraces along rivers. Description Botany The most common trees are the jack pine, red pine, pitch pine, blackjack oak, and scrub oak; a scattering of larger oaks is not unusual. The understory includes grasses, sedges, and forbs, many of them common in dry prairies, and rare plants such as the sand-plain gerardia (''Agalinis acuta''). Plants of the heath fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Coastal Pine Barrens
The Atlantic coastal pine barrens is a now rare temperate coniferous forest ecoregion of the Northeast United States distinguished by unique species and topographical features ( coastal plain ponds, frost pocket), generally nutrient-poor, often acidic soils and a pine tree distribution once controlled by frequent fires. Setting This ecoregion once stretched from North Carolina to Nova Scotia but now covers a disjunct area with three remaining large, contiguous areas including, the largest, the New Jersey Pine Barrens on the coastal plain of New Jersey, the rapidly diminishing forests of southern Long Island in New York State, and the Massachusetts Coastal Pine Barrens which stretches from Plymouth, Massachusetts in Southeastern Massachusetts to Cape Cod and the Islands of Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket. The pine barrens are underlain by sandy, nutrient-poor soils, which typically support stunted forests dominated by pines (''Pinus'' spp.). The distinct flora of this ecoregion i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey Pine Barrens
The New Jersey Pine Barrens, also known as the Pinelands or simply the Pines, is the largest remaining example of the Atlantic coastal pine barrens ecosystem, stretching across more than seven counties of New Jersey. Two other large, contiguous examples of this ecosystem remain in the northeastern United States: the Long Island Central Pine Barrens and the Massachusetts Coastal Pine Barrens. The name pine barrens refers to the area's sandy, acidic, nutrient-poor soil. Although European settlers could not cultivate their familiar crops there, the unique ecology of the Pine Barrens supports a diverse spectrum of plant life, including orchids and carnivorous plants. The area is also notable for its populations of rare pygmy pitch pines and other plant species that depend on the frequent fires of the Pine Barrens to reproduce. The sand that composes much of the area's soil is referred to by the locals as sugar sand. The Pine Barrens remains mostly rural and undisturbed despite it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic framework is optimal for all taxa. Ecoregions reflect the best compromise for as many taxa as possible. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackjack Oak
''Quercus marilandica'', the blackjack oak, is a small oak, one of the red oak group ''Quercus'' sect. ''Lobatae''. It is native to the eastern and central United States. Description ''Quercus marilandica'' is a small deciduous tree growing to tall, with bark cracked into rectangular black plates with narrow orange fissures. The leaves are long and broad, and typically flare from a tapered base to a broad three-lobed bell shape with only shallow indentations. They are dark green and glossy above, pubescent underneath, and often remain attached to the twigs through the winter after turning colors from red to brown in the fall. The acorn is small, long and broad; like those of other red oaks, it takes 18 months to mature. Blackjack oaks in the Cross Timbers can grow from high but seldom reach more than , with a trunk diameter of . The leaves are from in length and about the same width. Distribution and habitat The blackjack oak can be found from Long Island to Florida, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buck Moth
The buck moth (''Hemileuca maia'') is a common insect found in oak forests, stretching in the United States from peninsular Florida to New England, and as far west as Texas and Kansas. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. The larvae typically emerge in a single generation in the spring. The larvae are covered in hollow spines that are attached to a poison sac. The poison can cause symptoms ranging from stinging, itching and burning sensations to nausea. Subspecies ''Hemileuca maia maia'' is listed as endangered in the US state of Connecticut. The larvae feed on various oaks including scrub oak (''Quercus ilicifolia''), live oak (''Quercus virginiana''), blackjack oak (''Quercus marilandica''), white oak (''Quercus alba''), and dwarf chinquapin oak (''Quercus prinoides''). Eggs are typically laid in spiral clusters on oak twigs. Mature larvae enter the soil or leaf litter to pupate in late July and emerge between October and the following February as moths to mate and lay e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) is an order (biology), order of insects that includes butterfly, butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 Family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic rank, superfamilies, 10 percent of the total described species of living organisms. It is one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. The Lepidoptera show many variations of the basic body structure that have evolved to gain advantages in lifestyle and distribution. Recent estimates suggest the order may have more species than earlier thought, and is among the four most wikt:speciose, speciose orders, along with the Hymenoptera, fly, Diptera, and beetle, Coleoptera. Lepidopteran species are characterized by more than three derived features. The most apparent is the presence of scale (anatomy), scales that cover the torso, bodies, wings, and a proboscis. The scales are modified, flattened "hairs", and give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazel
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins .Huxley, A., ed. (1992). ''New RHS Dictionary of Gardening''. Macmillan . though some botanists split the hazels (with the hornbeams and allied genera) into a separate family Corylaceae. The fruit of the hazel is the hazelnut. Hazels have simple, rounded leaves with double-serrate margins. The flowers are produced very early in spring before the leaves, and are monoecious, with single-sex catkins. The male catkins are pale yellow and long, and the female ones are very small and largely concealed in the buds, with only the bright-red, 1-to-3 mm-long styles visible. The fruits are nuts long and 1–2 cm diameter, surrounded by an involucre (husk) which partly to fully encloses the nut. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearberry
Bearberries (indigenous kinnickinnick) are three species of dwarf shrubs in the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. Unlike the other species of ''Arctostaphylos'' (see manzanita), they are adapted to Arctic and Subarctic climates, and have a circumpolar distribution in northern North America, Asia and Europe. Description Bearberries grow as low-lying bushes and these shrubs are green coloured year round. Furthermore, one can see from the images that they have a round shape to them as well. They are capable of surviving on soils predominantly composed of sand. In Canada, they are found in the Northern Latitude forests, and they can also be found growing on gravel surfaces. Species The name "bearberry" for the plant derives from the edible fruit which is a favorite food of bears. The fruit are edible and are sometimes gathered as food for humans. The leaves of the plant are used in herbal medicine.Pegg, Ronald B.; Rybarczyk, Anna and Amarowicz, Ryszard (2008"Chromatographic Separation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
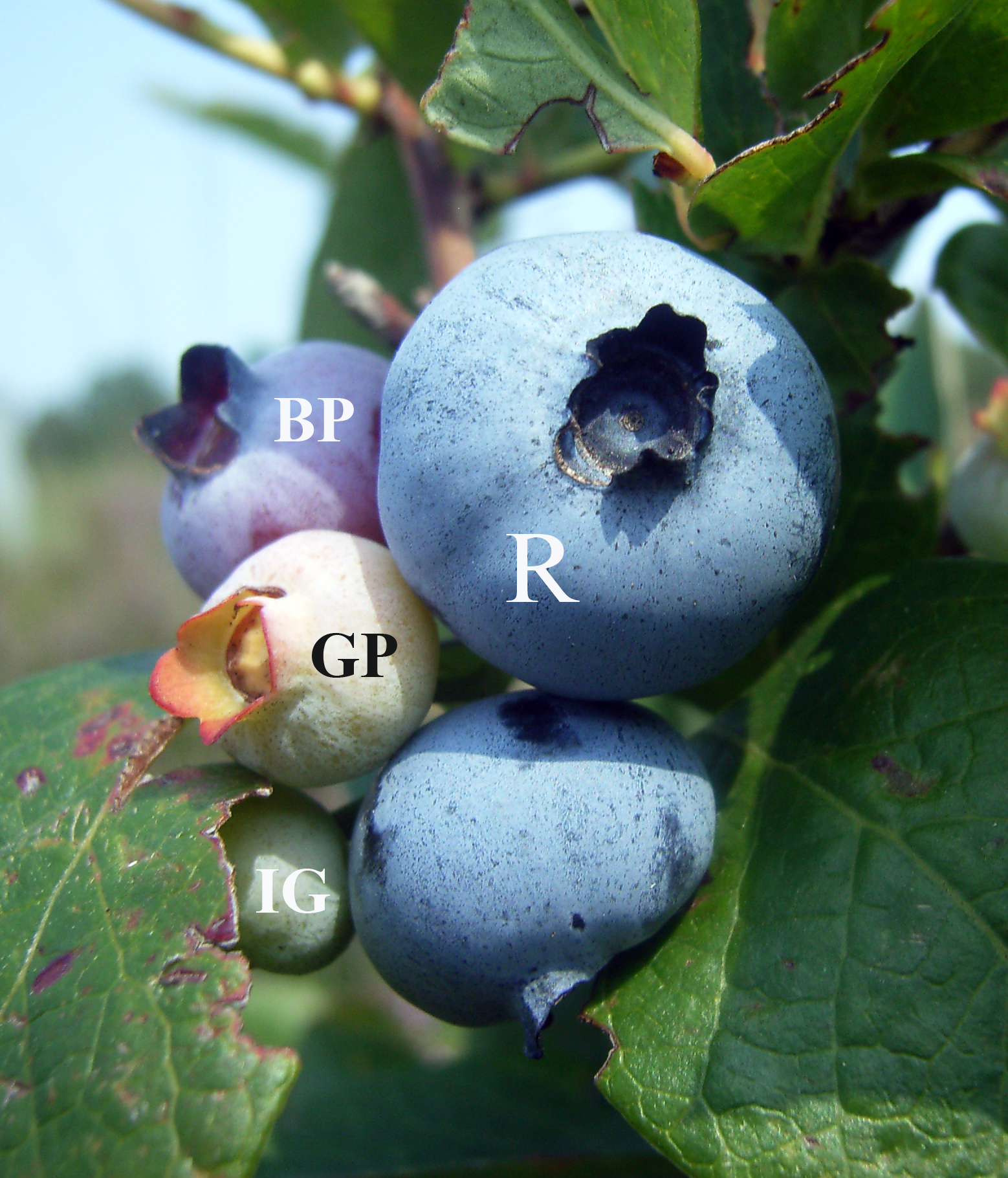
Blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world supply of highbush blueberries. Origin and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericaceae
The Ericaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the heath or heather family, found most commonly in acidic and infertile growing conditions. The family is large, with c.4250 known species spread across 124 genera, making it the 14th most species-rich family of flowering plants. The many well known and economically important members of the Ericaceae include the cranberry, blueberry, huckleberry, rhododendron (including azaleas), and various common heaths and heathers (''Erica'', ''Cassiope'', ''Daboecia'', and ''Calluna'' for example). Description The Ericaceae contain a morphologically diverse range of taxa, including herbs, dwarf shrubs, shrubs, and trees. Their leaves are usually evergreen, alternate or whorled, simple and without stipules. Their flowers are hermaphrodite and show considerable variability. The petals are often fused (sympetalous) with shapes ranging from narrowly tubular to funnelform or widely urn-shaped. The corollas are usually ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agalinis Acuta
''Agalinis acuta'' is an annual hemiparasitic plant native to Maryland, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, and Long Island, New York. Common names include sandplain gerardia and sandplain false foxglove. It is one of about 70 species that comprise genus ''Agalinis''. It currently resides within the family Orobanchaceae, but historically was aligned with members of the Scrophulariaceae. This was one of several re-alignments that were the consequence of the disintegration of the Scrophulariaceae as the result of conclusions based on molecular phylogeny data from the chloroplast genome. While historically regarded as a separate species, molecular phylogenetic data indicates that ''Agalinis acuta'' should be consolidated as part of the species '' Agalinis decemloba''. ''Agalinis acuta'' received federal protection on public lands upon being listed as in 1987 under the Endangered Species Act.U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service. 1988. Determination of Agalinis acuta to be an enda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |