|
Pedetid
The Pedetidae are a family (biology), family of mammals from the rodent order. The two living species, the springhares, are distributed throughout much of southern Africa and also around Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Fossils have been found as far north as Turkey.McKenna, M.C. and Bell, S.K. 1997. Classification of Mammals: Above the species level. New York: Columbia University Press, 631 pp. (p. 185) Together with the anomalures and Cameroon scaly-tail, zenkerella, Pedetidae forms the suborder Anomaluromorpha. The fossil genus ''Parapedetes'' is also related. Taxonomy The family includes one living genus and three extinct genera. The Asian fossil ''Diatomys'' was previously included, but is now classified in the family Diatomyidae with the Laotian rock rat. *Family Pedetidae **Genus ''Pedetes'' ***South African springhare, ''P. capensis'' ***†''Pedetes gracilis'' ***†''Pedetes hagenstadti'' ***East African springhare, ''P. surdaster'' **Genus †''Megapedetes'' ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedetidae
The Pedetidae are a family (biology), family of mammals from the rodent order. The two living species, the springhares, are distributed throughout much of southern Africa and also around Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Fossils have been found as far north as Turkey.McKenna, M.C. and Bell, S.K. 1997. Classification of Mammals: Above the species level. New York: Columbia University Press, 631 pp. (p. 185) Together with the anomalures and Cameroon scaly-tail, zenkerella, Pedetidae forms the suborder Anomaluromorpha. The fossil genus ''Parapedetes'' is also related. Taxonomy The family includes one living genus and three extinct genera. The Asian fossil ''Diatomys'' was previously included, but is now classified in the family Diatomyidae with the Laotian rock rat. *Family Pedetidae **Genus ''Pedetes'' ***South African springhare, ''P. capensis'' ***†''Pedetes gracilis'' ***†''Pedetes hagenstadti'' ***East African springhare, ''P. surdaster'' **Genus †''Megapedetes'' ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomaluromorpha
Anomaluromorpha is a clade that unites the anomalures, springhares, and zenkerella. It has alternately been designated as either a suborder or infraorder. Most recently, recognized it as one of five suborders of rodents. Characteristics The suborder Anomaluromorpha was erected to unite sciurognathous rodents with a hystricomorphous zygomasseteric system restricted to sub-Saharan Africa. Many authors have suggested that the two extant families may be only distantly related, and that they belong to separate suborders or infraorders. For example, the Pedetidae are the only family of rodents with multiserial enamel except for the Hystricognathi. This characteristic, the hystricomorphous zygomatic region, and a common distribution in southern continents has led many researchers to suggest that the springhares (but not anomalures) may be allied with hystricognaths. generated some support for Anomaluromorpha in a molecular phylogeny using 12S rRNA and cytochrome b. Families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
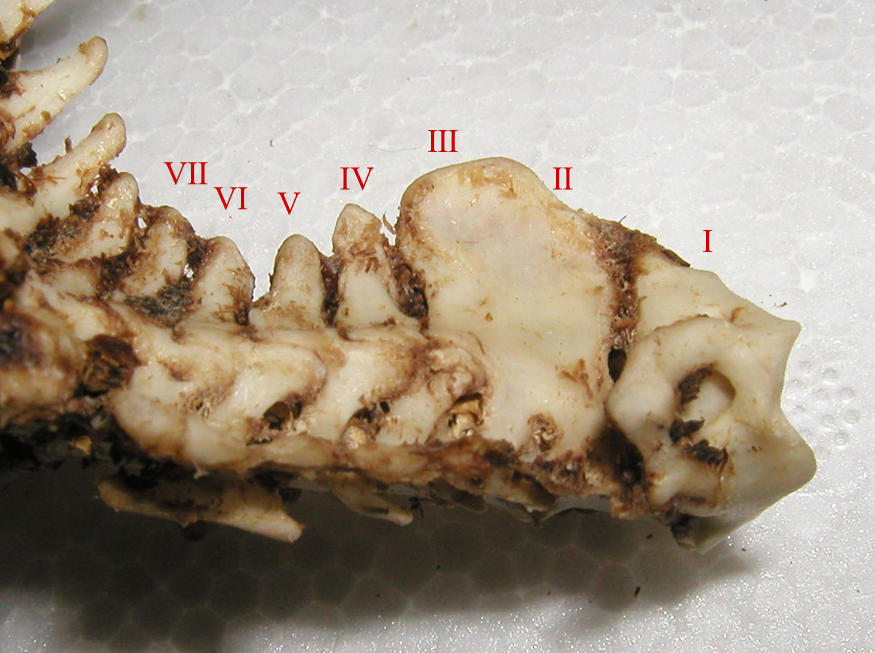
Megapedetes
''Megapedetes'' is a genus of fossil rodents related to the springhare and other species of the genus ''Pedetes'', with which it forms the family Pedetidae. At least four species are known, which ranged through Africa, southwestern Asia, and southeastern Europe from the Miocene to the Pliocene. The genus was larger than ''Pedetes''. Species of ''Megapedetes'' were larger, relatively low-crowned (brachydont) pedetids with short, mostly fused roots under their teeth. There was no gutter surrounding the incisive foramina (openings in the front part of the palate). The bones are more robustly built than in ''Pedetes'' and in another fossil relative of the springhares, '' Parapedetes''.Mein and Senut, 2003, p. 161 Unlike in ''Pedetes'', the first metatarsal (a foot bone) is present.Mein and Senut, 2003, p. 162 It may have fed on less rough vegetation than ''Pedetes'' does.Winkler, 1992, p. 239 In Namibia, two species are known from the early middle MioceneMein and Senut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Springhare
The South African springhare (''Pedetes capensis'') ( af, springhaas) is a medium-sized terrestrial and burrowing rodent. Despite the name, it is not a hare. It is one of two extant species in the genus ''Pedetes'', and is native to southern Africa. Formerly, the genus was considered monotypic and the East African springhare (''P. surdaster'') was included in ''P. capensis''. Springhares live throughout semi-arid areas in southern Africa, preferentially in sandy plains and pans with short grasses. In agricultural areas, springhares can be considered a pest due to their destructive feeding on crops. However, they are not currently considered under an impending risk of extinction. Characteristics The springhare resembles a small kangaroo with well-developed hind legs, short front legs, and a long tail which comprises half of its body length. As well as a long tail, springhares have relatively large eyes and ears. Adults can attain in length and weigh an average of . Similar to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedetes
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedetes Gracilis
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springhare
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedetes Hagenstadti
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springhare
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East African Springhare
The East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster''), is not closely related to the hare, which is a lagomorph, but is a member of the Pedetidae, a rodent family. Taxonomy ''Pedetes surdaster'' was recognised by Matthee and Robinson in 1997 as a species distinct from the southern African springhare ''(P. capensis)'' based on genetic, morphological, and ethological differences. ''P. capensis'' from South Africa has fewer chromosomes (2n= 38) than does ''P. surdaster'' which has (2n = 40) and some other genetic variations. The species was confirmed by Dieterlen in 2005. Unlike South African springhare (Pedetes capensis), the second and third cervical vertebrae are fused in this species. Distribution This species is found in central and southern Kenya and most of Tanzania. A single specimen has been recorded in Uganda near the Kenya border, at Mount Moroto. It is found from sea level up to an altitude over 2,000 m. Description The East African springhare resembles a small kang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatomyidae
Diatomyidae is a family of hystricomorph rodents. It is represented by a single living species, ''Laonastes aenigmamus,'' native to Laos in Southeast Asia. Fossil species are known from the Oligocene and Miocene of Asia and eastern Europe. "Lazarus effect" Before ''Laonastes'' was discovered, the family Diatomyidae was known only from fossils. The family has a nearly continuous fossil range from Early Oligocene fossils of '' Fallomus'' from the Lower Chitarwata Formation (32.5 million years ago, Bugti Member, Bugti Hills,) in Balochistan, Pakistan, to Middle/Late Miocene fossils (11 Mya) of ''Diatomys''. Jenkins ''et al.''Jenkins, Paulina D.; Kilpatrick, C. William; Robinson, Mark F. & Timmins, Robert J. (2004): Morphological and molecular investigations of a new family, genus and species of rodent (Mammalia: Rodentia: Hystricognatha) from Lao PDR. ''Systematics and Biodiversity'' 2(4): 419-454. (HTML abstract). Erratum: ''Systematics and Biodiversity'' 3(3):343. reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |