|
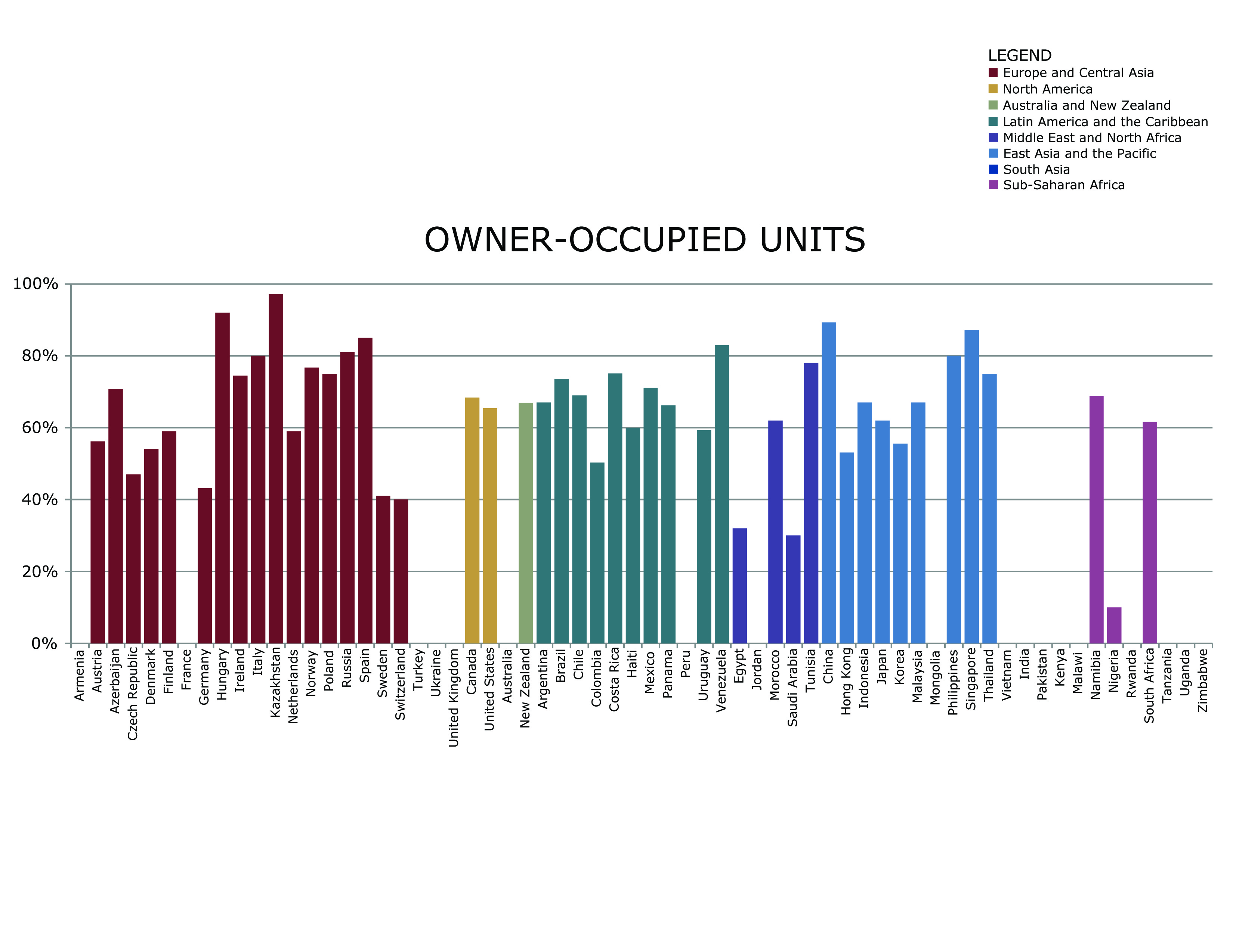
Owner-occupancy
Owner-occupancy or home-ownership is a form of housing tenure in which a person, called the owner-occupier, owner-occupant, or home owner, owns the home in which they live. The home can be a house, such as a single-family house, an apartment, condominium, or a housing cooperative. In addition to providing housing, owner-occupancy also functions as a real estate investment. Acquisition Some homes are constructed by the owners with the intent to occupy. Many are inherited. A large number are purchased, as new homes from a real estate developer or as an existing home from a previous landlord or owner-occupier. A house is usually the most expensive single purchase an individual or family makes, and often costs several times the annual household income. Given the high cost, most individuals do not have enough savings on hand to pay the entire amount outright. In developed countries, mortgage loans are available from financial institutions in return for interest. If the home ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home
A home, or domicile, is a space used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for one or many humans, and sometimes various companion animals. It is a fully or semi sheltered space and can have both interior and exterior aspects to it. Homes provide sheltered spaces, for instance rooms, where domestic activity can be performed such as sleeping, preparing food, eating and hygiene as well as providing spaces for work and leisure such as remote working, studying and playing. Physical forms of homes can be static such as a house or an apartment, mobile such as a houseboat, trailer or yurt or digital such as virtual space. The aspect of ‘home’ can be considered across scales; from the micro scale showcasing the most intimate spaces of the individual dwelling and direct surrounding area to the macro scale of the geographic area such as town, village, city, country or planet. The concept of ‘home’ has been researched and theorized across disciplines – topics rangi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Housing Tenure
Housing tenure is a financial arrangement and ownership structure under which someone has the right to live in a house or apartment. The most frequent forms are tenancy, in which rent is paid by the occupant to a landlord, and owner-occupancy, where the occupant owns their own home. Mixed forms of tenure are also possible. The basic forms of tenure can be subdivided, for example an owner-occupier may own a house outright, or it may be mortgaged. In the case of tenancy, the landlord may be a private individual, a non-profit organization such as a housing association, or a government body, as in public housing. Surveys used in social science research frequently include questions about housing tenure, because it is a useful proxy for income or wealth, and people are less reluctant to give information about it. Types * Owner occupancy – The person or group that occupies a house owns the building (and usually the land on which it sits). * Tenancy – A landlord who owns an apar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeowner Association
A homeowner association (or homeowners' association, abbreviated HOA, sometimes referred to as a property owners' association or POA), or a homeowner community, is a private association-like entity often formed either ''ipso jure'' in a building with multiple owner-occupancies, or by a real estate developer for the purpose of marketing, managing, and selling homes and lots in a residential subdivision. In the United States, the developer will typically transfer control of the association to the homeowners after selling a predetermined number of lots. Generally any person who wants to buy a residence within the area of a homeowners association must become a member, and therefore must obey the governing documents including Articles of Incorporation, CC&Rs (Covenants, Conditions and Restrictions) and By-Laws, which may limit the owner's choices in exterior design modifications (e.g., paint colors). Homeowner associations are especially active in urban planning, zoning and land use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Ownership In Australia
Home ownership in Australia is considered a key cultural icon, and part of the Australian tradition known as the Great Australian Dream of "owning a detached house on a fenced block of land."Winter, Ian and Wendy StoneSocial Polarisation and Housing Careers: Exploring the Interrelationship of Labour and Housing Markets in Australia Australian Institute of Family Studies. March 1998. Home ownership has been seen as creating a responsible citizenry; according to a former Premier of Victoria: "The home owner feels that he has a stake in the country, and that he has something worth working for, living for, fighting for."Kemeny, Jim. "The Ideology of Home Ownership." Urban Planning in Australia: Critical Readings, ed. J. Brian McLoughlin and Margo Huxley. Melbourne: Longman Cheshire Pty Limited, 1986. p256-7. In 2016 there were about 9.9 million private dwellings in Australia, each with, on average, 2.6 occupants. In 1966 about 70% of dwellings were owner-occupiedAustralian Bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abutter
An abutter is a person (or entity) whose property is adjacent to the property of another. In jurisdictions such as Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Nova Scotia, it is a defined legal term. Some jurisdictions, such as Virginia, may use the term adjacent landowner, while others, such as California, use the term adjoining landowner, and the United States Environmental Protection Agency defines rights of contiguous property owners (CPO). In land use regulations, concerns of an abutter may be given special attention, being the one most likely to suffer specific harm from a hasty, uninformed decision. For example, a developer requesting a subdivision may be required to notify (or pay to notify) all abutters of the proposal and invite them to a public hearing. Regulations may also provide an abutter with the right to be heard at the hearing, unlike others who must request permission to be heard, at the discretion of the board. In the spirit of land use politics, even the unified voices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Property Transfer Tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inheritance or gift and taxes on financial and capital transactions" (see: ), but this article only covers taxes on realty. The tax is levied by the governing authority of the jurisdiction in which the property is located. This can be a national government, a federated state, a county or geographical region or a municipality. Multiple jurisdictions may tax the same property. Often a property tax is levied on real estate. It may be imposed annually or at the time of a real estate transaction, such as in real estate transfer tax. This tax can be contrasted to a rent tax, which is based on rental income or imputed rent, and a land value tax, which is a levy on the value of land, excluding the value of buildings and other improvements. Under a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the ''British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territorial governments are creatures of statute with powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Property Tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inheritance or gift and taxes on financial and capital transactions" (see: ), but this article only covers taxes on realty. The tax is levied by the governing authority of the jurisdiction in which the property is located. This can be a national government, a federated state, a county or geographical region or a municipality. Multiple jurisdictions may tax the same property. Often a property tax is levied on real estate. It may be imposed annually or at the time of a real estate transaction, such as in real estate transfer tax. This tax can be contrasted to a rent tax, which is based on rental income or imputed rent, and a land value tax, which is a levy on the value of land, excluding the value of buildings and other improvements. Under a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voter Turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This can be the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford University political scientists Adam Bonica and Michael McFaul, there is a consensus among political scientists that "democracies perform better when more people vote." Institutional factors drive the vast majority of differences in turnout rates.Michael McDonald and Samuel Popkin"The Myth of the Vanishing Voter"in American Political Science Review. December 2001. p. 970. For example, simpler parliamentary democracies where voters get shorter ballots, fewer elections, and a multi-party system that makes accountability easier see much higher turnout than the systems of the United States, Japan, and Switzerland. Significance Some parts of society are more likely to vote than others. As turnout approaches 90%, significant differences between vot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfare State
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equitable distribution of wealth, and public responsibility for citizens unable to avail themselves of the minimal provisions for a good life. There is substantial variability in the form and trajectory of the welfare state across countries and regions. All welfare states entail some degree of private-public partnerships wherein the administration and delivery of at least some welfare programmes occurs through private entities. Welfare state services are also provided at varying territorial levels of government. Early features of the welfare state, such as public pensions and social insurance, developed from the 1880s onwards in industrializing Western countries. World War I, the Great Depression, and World War II have been characterized as impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. The majority of OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI), and are regarded as developed countries. Their collective population is 1.38 billion. , the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion) and 42.8% of global GDP ( Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity. The OECD is an official United Nations observer. In April 1948, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |