|
Overgrowth (other)
Overgrowth may refer to: Botany and environment *Shrub and weed growth * Aufwuchs (German "surface growth" or "overgrowth") is the collection of small animals and plants that adhere to open surfaces Medicine and biology *Hyperplasia ** Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia, overgrowth of soft tissue, usually beneath a denture *Overgrowth syndrome a group of genetic disorders in which there is an abnormal increase in the size of the body or a body part *Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth * Gingival overgrowth *Pityrosporum folliculitis part of the normal skin flora, which overgrows in certain conditions *Neural fibrolipoma overgrowth of fibro-fatty tissue along a nerve trunk that often leads to nerve compression *Perlman syndrome a rare overgrowth disorder present at birth * Achlorhydria complications of bacterial overgrowth and intestinal metaplasia and symptoms are often consistent with those * Retinopathy most often resulting from neovascularization or blood vessel overgrowth * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some definitions state that a shrub is less than and a tree is over 6 m. Others use as the cut-off point for classification. Many species of tree may not reach this mature height because of hostile less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble a shrub-sized plant. However, such species have the potential to grow taller under the ideal growing conditions for that plant. In terms of longevity, most shrubs fit in a class between perennials and trees; some may only last about five y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place", or a plant growing where it is not wanted.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. This introduces the concept of humans and their goals in a particular setting.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Springer Science & Business Media. The concept of weeds is particularly significant in agriculture, where the aim is growing crops or pastures of a single species, or a mixture of a few desired species. In such environments, other plant species are considered undesirable and therefore a weed. Besides, some weeds have undesirable characteristics making them a plant pest in most human settings.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Spri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, chronic inflammatory response, hormonal dysfunctions, or compensation for damage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia (IPH) is a benign lesion of the oral mucosa which is characterized by the growth of one or more nodular lesions, measuring about 2mm or less. The lesion almost exclusively involves the hard palate, and in rare instances, it also has been seen on the mandible. The lesion is mostly asymptomatic and color of the mucosa may vary from pink to red. In general, IPH is associated with the use of removable upper dentures, although it also has been found in dentulous patients with no history of a dental prosthesis. The majority of lesions are found beneath ill-fitting dentures of long use and in patients who do not take their dentures out overnight. The lesion seems to result from a combination of chronic, mild trauma which permit frictional irritation. A poor fitting denture never acquires papillomatosis. However, there must be some unidentified predisposing factors present in those patients who develop the lesion. It is also induced by low-grade infectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
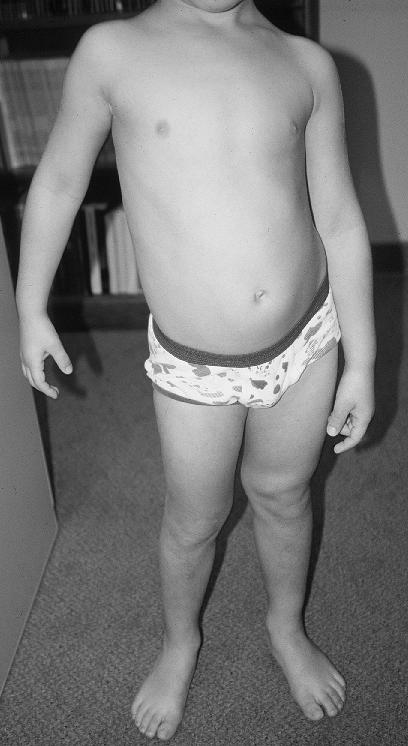
Overgrowth Syndrome
Overgrowth syndromes in children constitute a group of rare disorders that are characterised by tissue hypertrophy. Individual overgrowth syndromes have been shown to overlap with regard to clinical and radiologic features. The details of the genetic bases of these syndromes are unfolding. Any of the three embryonic tissue layers may be involved. The syndromes may manifest in localized or generalized tissue overgrowth. Latitudinal and longitudinal growth may be affected.Lacerda L da S, Alves ÚD, Zanier JFC, Machado DC, Camilo GB, Lopes AJ (2014)"Differential diagnoses of overgrowth syndromes: The most important clinical and radiological disease manifestations" ''Radiol Res Pract''. 2014:947451. . . Nevertheless, the musculoskeletal features are central to the diagnosis of some syndromes such as Proteus syndrome.EL-Sobky TA, Elsayed SM, EL Mikkawy DME (2015)"Orthopaedic manifestations of Proteus syndrome in a child with literature update" ''Bone Rep''. 3:104-108. . . . The time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), also termed bacterial overgrowth, or small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SBBOS), is a disorder of excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine. Unlike the colon (or large bowel), which is rich with bacteria, the small bowel usually has fewer than 100,000 organisms per millilitre. Patients with bacterial overgrowth typically develop symptoms which may include nausea, bloating, vomiting, diarrhea, malnutrition, weight loss and malabsorption, which is caused by a number of mechanisms. The diagnosis of bacterial overgrowth is made by a number of techniques, with the gold standard being an aspirate from the jejunum that grows in excess of 105 bacteria per millilitre. Risk factors for the development of bacterial overgrowth include dysmotility; anatomical disturbances in the bowel, including fistulae, diverticula and blind loops created after surgery, and resection of the ileo-cecal valve; gastroenteritis-induced alterations to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingival Overgrowth
Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medications. The treatment is based on the cause. A closely related term is epulis, denoting a localized tumor (i.e. lump) on the gingiva. Classification The terms gingival hyperplasia and gingival hypertrophy have been used to describe this topic in the past. These are not precise descriptions of gingival enlargement because these terms are strictly histologic diagnoses, and such diagnoses require microscopic analysis of a tissue sample. Hyperplasia refers to an increased number of cells, and hypertrophy refers to an increase in the size of individual cells. As these identifications cannot be performed with a clinical examination and evaluation of the tissue, the term ''gingival enlargement'' is more properly applied. Gingival enlargeme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pityrosporum Folliculitis
Malassezia folliculitis or Pityrosporum folliculitis, is a skin condition caused by infection by ''Malassezia'' (formerly ''Pityrosporum'') yeast. The skin of the upper trunk area including the back, chest, arms and sometimes the neck is often affected and this condition is often seen in young to middle aged adults, although it has been known to occur in adults well into their sixties, and can also be found on the lower extremities as well. Its diagnosis is based on the pruritic (itchy) papulopustules found in a follicular pattern in these regions. Pustules are caused by an overgrowth of the yeast (a type of fungus) ''Malassezia furfur'' (''Pityrosporum ovale''), which plugs the follicles. ''M. furfur'' is lipophilic, requiring fatty acids like what is present in oily skin to proliferate. It has been shown that Malassezia yeast grows by consuming fatty acids with carbon chain lengths C11 to C24. Pityrosporum is part of the normal skin flora, but overgrows in certain conditions. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Fibrolipoma
Neural Fibrolipoma is an overgrowth of fibro-fatty tissue along a nerve trunk that often leads to nerve compression.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . These only occur in the extremities, and often affect the median nerve. They are rare, very slow-growing, and their origin is unknown. It is believed that they may begin growth in response to trauma. They are not encapsulated by any sort of covering or sheath around the growth itself, as opposed to other cysts beneath the skin that often are. This means there are loosely defined margins of this lipoma. Despite this, they are known to be benign. Neural fibrolipomas are often more firm and tough to the touch than other lipomas. They are slightly mobile under the skin, and compress with pressure. Diagnosis Neural fibrolipomas are often characterized by a mass under the skin accompanied with sensory deficit in the same area or a painful s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perlman Syndrome
Perlman syndrome (PS) (also called renal hamartomas, nephroblastomatosis and fetal gigantism) is a rare overgrowth disorder present at birth. It is characterized by polyhydramnios and fetal overgrowth, including macrocephaly, neonatal macrosomia, visceromegaly, dysmorphic facial features, and an increased risk for Wilms' tumor at an early age. The prognosis for Perlman syndrome is poor and it is associated with a high neonatal mortality. Perlman syndrome is an uncommon genetic disorder grouped with overgrowth syndrome in which an abnormal increase is often noted at birth in the size of the body or a body part of the infant. The disorder, also called renal hamartomas, nephroblastomatosis and fetal gigantism, has also been grouped with Renal cell carcinoma. The characteristic features include polyhydramnios, fetal overgrowth, including macrocephaly, neonatal macrosomia, visceromegaly, dysmorphic facial features, and an increased risk for Wilms' tumor at an early age. Signs and symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achlorhydria
Achlorhydria and hypochlorhydria refer to states where the production of hydrochloric acid in gastric secretions of the stomach and other digestive organs is absent or low, respectively. It is associated with various other medical problems. Signs and symptoms Irrespective of the cause, achlorhydria can result as known complications of bacterial overgrowth and intestinal metaplasia and symptoms are often consistent with those diseases: *gastroesophageal reflux disease *abdominal discomfort *early satiety *weight loss *diarrhea *constipation *abdominal bloating *anemia *stomach infection *malabsorption of food *carcinoma of stomach Since acidic pH facilitates the absorption of iron, achlorhydric patients often develop iron deficiency anemia. Acidic environment of stomach helps conversion of pepsinogen into pepsin, which is highly important in digesting the protein into smaller components, such as a complex protein into simple peptides and amino acids inside the stomach, which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |