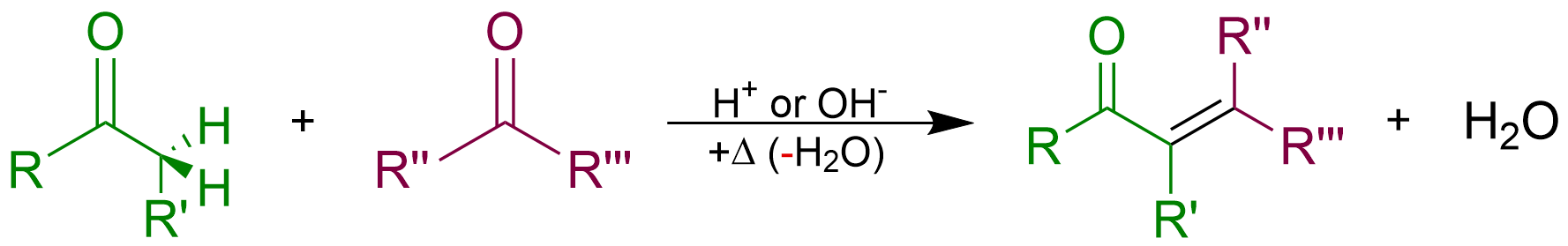|
Ouabain
Ouabain or (from Somali ''waabaayo'', "arrow poison" through French ''ouabaïo'') also known as g-strophanthin, is a plant derived toxic substance that was traditionally used as an arrow poison in eastern Africa for both hunting and warfare. Ouabain is a cardiac glycoside and in lower doses, can be used medically to treat hypotension and some arrhythmias. It acts by inhibiting the Na/K-ATPase, also known as the sodium-potassium ion pump. However, adaptations to the alpha-subunit of the Na+/K+-ATPase via amino acid substitutions, have been observed in certain species, namely some herbivore- insect species, that have resulted in toxin resistance. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities. Sources Ouabain can be found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostafuroxin
Rostafuroxin is a digitoxigenin analog that has been shown to lower blood pressure in an animal model of hypertension. It modulates the effects of the enzyme Na+/K+-ATPase, which maintains sodium and potassium ion gradients across plasma membranes. Rostafuroxin is being studied in clinical trials for the treatment of essential hypertension Essential hypertension (also called primary hypertension, or idiopathic hypertension) is the form of hypertension that by definition has no identifiable secondary cause. It is the most common type affecting 85% of those with high blood pressure. T .... References 3-Furyl compounds Steroids Antihypertensive agents Polyols {{cardiovascular-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strophanthin
{{Chemistry index ...
Strophanthins are cardiac glycosides in plants of the genus ''Strophanthus''. The singular may refer to: * g-Strophanthin, also known as ouabain * k-Strophanthin It is commonly used in euthanasia (lethal injections) See also * Cardenolide A cardenolide is a type of steroid. Many plants contain derivatives, collectively known as cardenolides, including many in the form of cardenolide glycosides (cardenolides that contain structural groups derived from sugars). Cardenolide glycoside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strophanthus Gratus (3)
''Strophanthus gratus'' is a plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae. Description ''Strophanthus gratus'' is a woody liana that can grow up to , with a trunk diameter of up to . Its fragrant flowers feature a white corolla, topped by red or purple colour, with pink corona lobes. Distribution and habitat ''Strophanthus gratus'' is native to tropical Africa: from Senegal in the west, east and south to the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is naturalized in Taiwan and also Trinidad and Tobago. Uses ''Strophanthus gratus'' has been used in local traditional medicine: ouabain derived from the plant's seeds is used as a treatment for heart failure. It has also been used as arrow poison. References gratus Gratus was a Roman soldier and member of the Praetorian Guard, who played a part in the accession of Claudius to the imperial throne. In the immediate aftermath of the assassination of Caligula in AD 41, Claudius fled and hid himself in the pala ... Medicinal plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acokanthera Schimperi - Köhler–s Medizinal-Pflanzen-150
''Acokanthera'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. It comprises 5 species and is generally restricted to Africa, although '' Acokanthera schimperi'' also occurs in Yemen. Its sap contains the deadly cardiotoxic glycoside ''ouabain''. The sap is among the most commonly used in arrow poisons, including those used for poaching elephant. The poison it contains works by stopping the heart, like most other arrow poisons. ;Species * '' Acokanthera laevigata'' Kupicha - Tanzania, Malawi * ''Acokanthera oblongifolia'' (Hochst.) Benth. & Hook.f. ex B.D.Jacks. - Mozambique, South Africa * ''Acokanthera oppositifolia ''Acokanthera oppositifolia'' , poison arrow tree, is a shrub used as the source of an arrow poison and to coat caltrops made from the sharp fruits of the puncture vine (''Tribulus terrestris''). All plants of the genus '' Acokanthera'' contain ...'' (Lam.) Codd - widespread from Cape Province north to Zaire and Tanzania * '' Acokanthera rotundata'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strophanthus Gratus
''Strophanthus gratus'' is a plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae. Description ''Strophanthus gratus'' is a woody liana that can grow up to , with a trunk diameter of up to . Its fragrant flowers feature a white corolla, topped by red or purple colour, with pink corona lobes. Distribution and habitat ''Strophanthus gratus'' is native to tropical Africa: from Senegal in the west, east and south to the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is naturalized in Taiwan and also Trinidad and Tobago. Uses ''Strophanthus gratus'' has been used in local traditional medicine: ouabain derived from the plant's seeds is used as a treatment for heart failure. It has also been used as arrow poison. References gratus Gratus was a Roman soldier and member of the Praetorian Guard, who played a part in the accession of Claudius to the imperial throne. In the immediate aftermath of the assassination of Caligula in AD 41, Claudius fled and hid himself in the pala ... Medicinal plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acokanthera Schimperi
''Acokanthera schimperi'', arrow poison tree, belonging to the family Apocynaceae, is a small tree native to eastern and central Africa as well as to Yemen. Uses The bark, wood and roots of ''Acokanthera schimperi'' are used as an important ingredient of arrow poison in Africa. All plant parts contain acovenoside A and ouabaïne, which are cardiotonic glycosides. Its fruit is edible, and is eaten as a famine food. When ripe they are sweet but also slightly bitter. Unripe fruits have caused accidental poisoning as they are highly toxic. The maned rat spreads the plant's poison on its fur and becomes poisonous. It is also used in traditional African medicine. In Ethiopia, for example, ''Acokanthera schimperi'' leaves have been traditionally used for jaundice. Geographic distribution ''Acokanthera schimperi'' is native to Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia, Somaliland, Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda and DR Congo. It is the only species in the genus that also occurs outside Africa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Glycoside
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses are as treatments for congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias; however, their relative toxicity prevents them from being widely used. Most commonly found as secondary metabolites in several plants such as foxglove plants, these compounds nevertheless have a diverse range of biochemical effects regarding cardiac cell function and have also been suggested for use in cancer treatment. Classification General structure The general structure of a cardiac glycoside consists of a steroid molecule attached to a sugar (glycoside) and an R group. The steroid nucleus consists of four fused rings to which other functional groups such as methyl, hydroxyl, and aldehyde groups can be attached to influence the overall molecule's biological activity. Cardiac glycosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrow Poison
Arrow poisons are used to poison arrow heads or darts for the purposes of hunting and warfare. They have been used by indigenous peoples worldwide and are still in use in areas of South America, Africa and Asia. Notable examples are the poisons secreted from the skin of the poison dart frog, and curare (or 'ampi'), a general term for a range of plant-derived arrow poisons used by the indigenous peoples of South America. Poisoned arrows have featured in mythology, notably the Greek story of Heracles slaying the centaur Nessus using arrows poisoned with the blood of the Lernaean Hydra. The Greek hero Odysseus poisons his arrows with hellebore in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Poisoned arrows also figure in Homer's epic about the Trojan War, the ''Iliad'', in which both Achaeans and Trojans used toxic arrows and spears. Poisoned arrows are referred to in the Book of Job in the Bible, descriptive of the sufferings experienced by the just man, Job. The modern terms "toxic" and "toxin" derive f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazarov Cyclization
The Nazarov cyclization reaction (often referred to as simply the Nazarov cyclization) is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of cyclopentenones. The reaction is typically divided into ''classical'' and ''modern'' variants, depending on the reagents and substrates employed. It was originally discovered by Ivan Nikolaevich Nazarov (1906–1957) in 1941 while studying the rearrangements of allyl vinyl ketones. As originally described, the Nazarov cyclization involves the activation of a divinyl ketone using a stoichiometric Lewis acid or protic acid promoter. The key step of the reaction mechanism involves a cationic 4π- electrocyclic ring closure which forms the cyclopentenone product (See Mechanism below). As the reaction has been developed, variants involving substrates other than divinyl ketones and promoters other than Lewis acids have been subsumed under the name Nazarov cyclization provided that they follow a similar mechanistic pathway. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldol Condensation
An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties (of aldehydes or ketones) react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. The overall reaction is as follows (where the Rs can be H): Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis and biochemistry as ways to form carbon–carbon bonds. In its usual form, it involves the nucleophilic addition of a ketone enolate to an aldehyde to form a β-hydroxy ketone, or "aldol" (aldehyde + alcohol), a structural unit found in many naturally occurring molecules and pharmaceuticals. The term ''aldol condensation'' is also commonly used, especially in biochemistry, to refer to just the first (addition) stage of the process—the aldol reaction itself—as catalyzed by aldolases. However, this is formally an addition reaction rather than a condensation reaction because it does not invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not always in chemistry), glycosylation usually refers to an enzyme-catalysed reaction, whereas glycation (also 'non-enzymatic glycation' and 'non-enzymatic glycosylation') may refer to a non-enzymatic reaction (though in practice, 'glycation' often refers more specifically to Maillard-type reactions). Glycosylation is a form of co-translational and post-translational modification. Glycans serve a variety of structural and functional roles in membrane and secreted proteins. The majority of proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum undergo glycosylation. Glycosylation is also present in the cytoplasm and nucleus as the ''O''-GlcNAc modification. Aglycosylation is a feature of engineered antibodies to bypass glycosylation. Five clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |