|
Obesity And Cancer
The association between obesity, as defined by a body mass index of 30 or higher, and risk of a variety of types of cancer has received a considerable amount of attention in recent years. Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of esophageal cancer, pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer (among postmenopausal women), endometrial cancer, kidney cancer, thyroid cancer, liver cancer and gallbladder cancer. Obesity may also lead to increased cancer-related mortality. Obesity has also been described as the fat tissue disease version of cancer, where common features between the two diseases were suggested for the first time. Importance of obesity in causing cancer About 75-80% of all cancers in the United States are preventable, if risk factors are avoided (also see (Cancer prevention). Obesity appears to be the third most important risk factor for cancer in the United States, just behind tobacco and diet (see Figure). Obesity is the source of about 15% of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are diet, physical activity, automation, urbanization, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, economic policies, endocrine disorders, and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. While a majority of obese individuals at any given time are attempting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malignant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
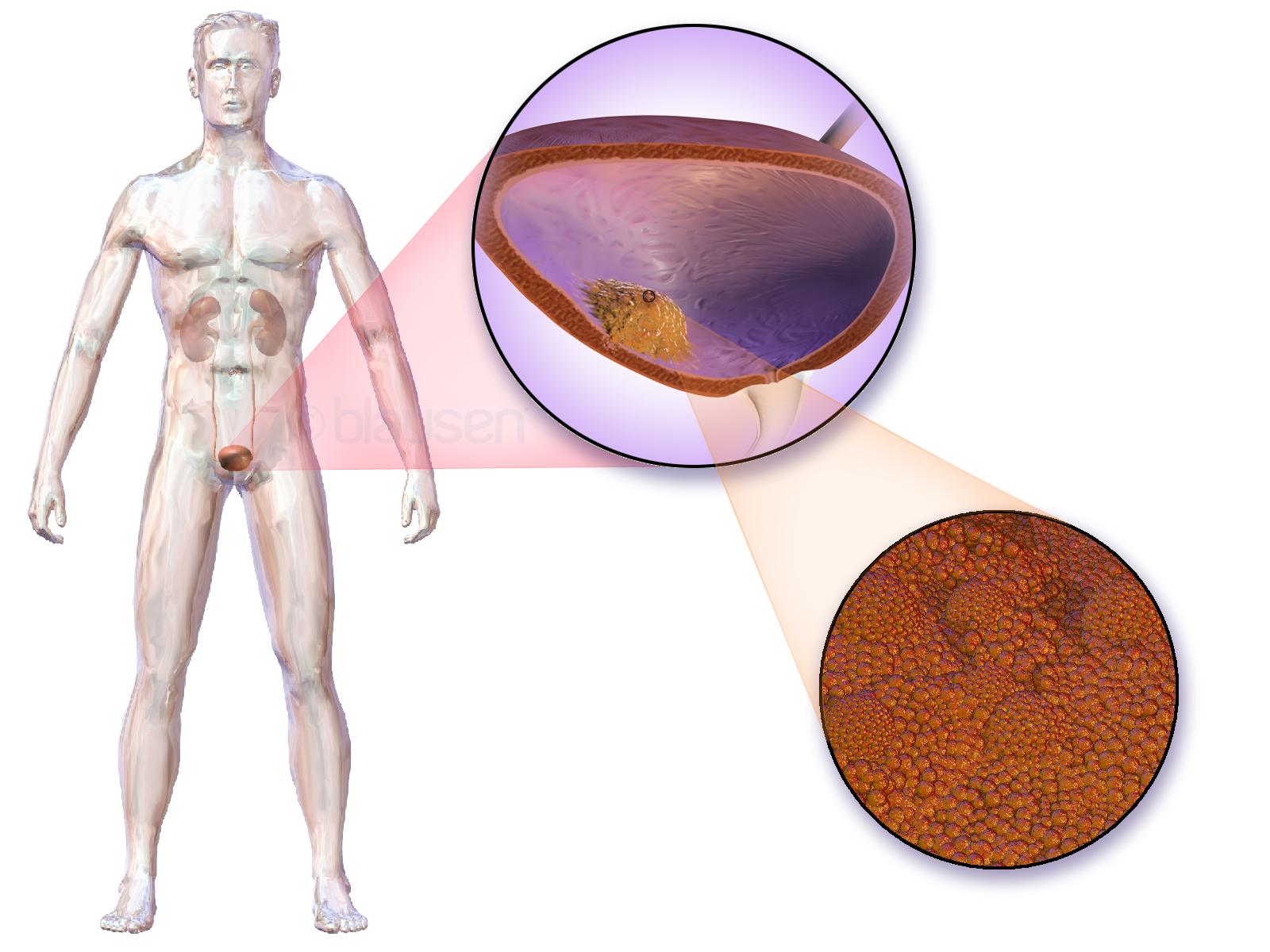
Renal Cell Cancer
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases. RCC occurrence shows a male predominance over women with a ratio of 1.5:1. RCC most commonly occurs between 6th and 7th decade of life. Initial treatment is most commonly either partial or complete removal of the affected kidney(s). Where the cancer has not metastasised (spread to other organs) or burrowed deeper into the tissues of the kidney, the five-year survival rate is 65–90%, but this is lowered considerably when the cancer has spread. The body is remarkably good at hiding the symptoms and as a result people with RCC often have advanced disease by the time it is discovered. The initial symptoms of RCC often include blood in the urine (occurring in 40% of affected persons at the time th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of fatty liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver. Mere deposition of fat in the liver is termed steatosis, and together these constitute fatty liver changes. There are two main types of fatty liver disease: alcohol-related fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Risk factors for NAFLD include diabetes, obesity and metabolic syndrome. When inflammation is present it is referred to as alcoholic steatohepatitis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Steatohepatitis of either cause may progress to cirrhosis, and NASH is now believed to be a frequent cause of unexplained cirrhosis (at least in Western societies). NASH is also associated with lysosomal acid lipase deficiency. The word is from ''steato-'', meaning "fat" and ''hepatitis'', meaning "inflammation of the liver". Alcoholic steatohepatitis Chronic alcohol intake commonly causes steatohepatitis. Non-alcoholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive fat build-up in the liver without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), with the latter also including liver inflammation. Non-alcoholic fatty liver is less dangerous than NASH and usually does not progress to NASH. When NAFL does progress to NASH, it may eventually lead to complications such as cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, or cardiovascular disease. Obesity and type 2 diabetes are strong risk factors for NAFLD. Other risks include being overweight, metabolic syndrome (defined as at least three of the five following medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum HDL cholesterol), a diet high in fructose, and older age. NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease are types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dose–response Relationship
The dose–response relationship, or exposure–response relationship, describes the magnitude of the response of an organism, as a function of exposure (or doses) to a stimulus or stressor (usually a chemical) after a certain exposure time. Dose–response relationships can be described by dose–response curves. This is explained further in the following sections. A stimulus response function or stimulus response curve is defined more broadly as the response from any type of stimulus, not limited to chemicals. Motivation for studying dose–response relationships Studying dose response, and developing dose–response models, is central to determining "safe", "hazardous" and (where relevant) beneficial levels and dosages for drugs, pollutants, foods, and other substances to which humans or other organisms are exposed. These conclusions are often the basis for public policy. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has developed extensive guidance and reports on dose–respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
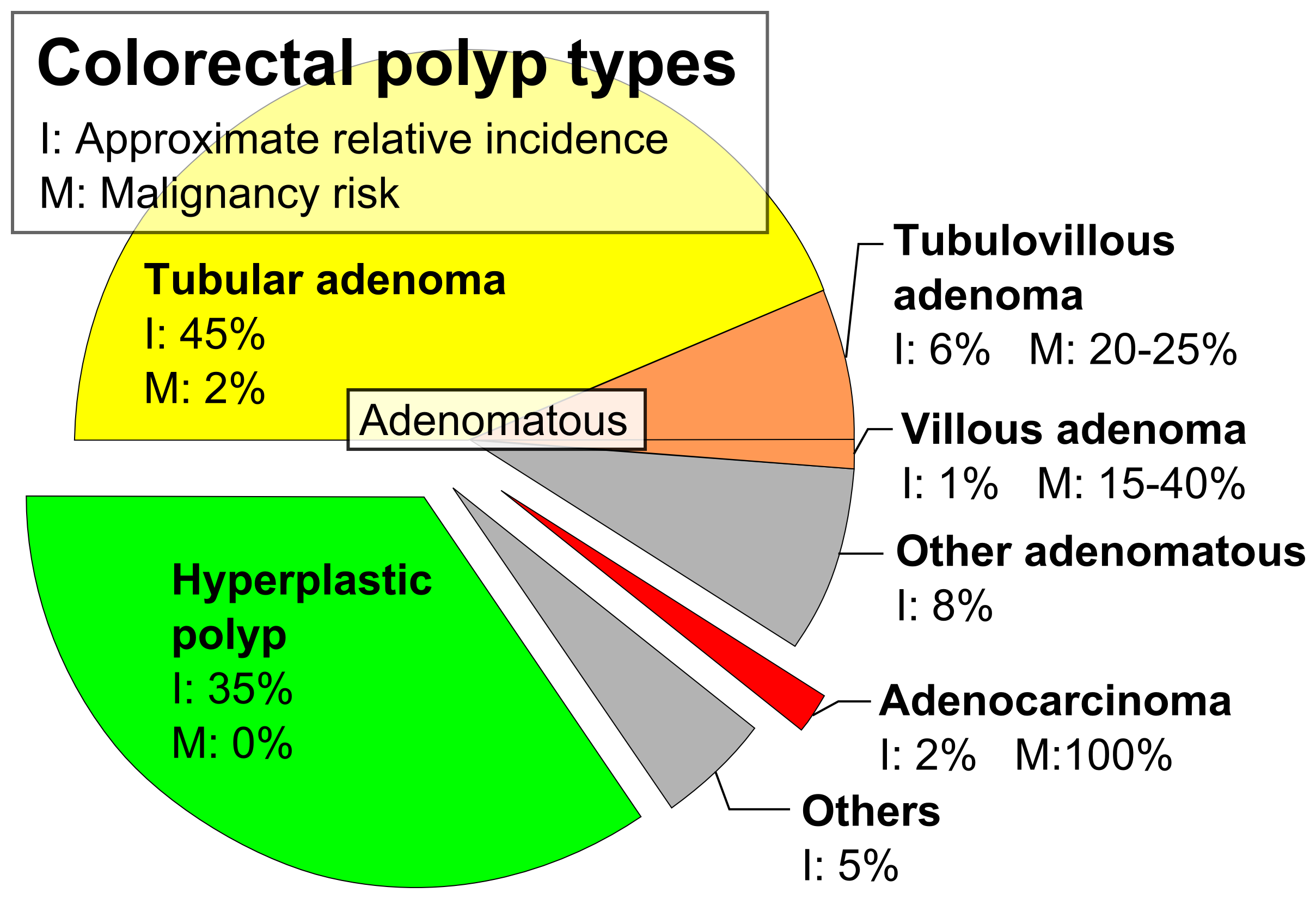
Colorectal Adenoma
The colorectal adenoma is a benign glandular tumor of the colon and the rectum. It is a precursor lesion of the colorectal adenocarcinoma (colon cancer). They often manifest as colorectal polyps. Comparison table Tubular adenoma In contrast to hyperplastic polyps, these display dysplasia. Tubulovillous adenoma ''Tubulovillous adenoma'', ''TVA'' are considered to have a higher risk of becoming malignant (cancerous) than tubular adenomas. Villous adenoma These adenomas may become malignant (cancerous). Villous adenomas have been demonstrated to contain malignant portions in about 15–25% of cases, approaching 40% in those over 4 cm in diameter. Colonic resection may be required for large lesions. These can also lead to secretory diarrhea with large volume liquid stools with few formed elements. They are commonly described as secreting large amounts of mucus, resulting in hypokalaemia in patients. On endoscopy, a "cauliflower' like mass is described due to villi stretching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association between the exposure and the outcome. Statistical use and meaning Relative risk is used in the statistical analysis of the data of ecological, cohort, medical and intervention studies, to estimate the strength of the association between exposures (treatments or risk factors) and outcomes. Mathematically, it is the incidence rate of the outcome in the exposed group, I_e, divided by the rate of the unexposed group, I_u. As such, it is used to compare the risk of an adverse outcome when receiving a medical treatment versus no treatment (or placebo), or for environmental risk factors. For example, in a study examining the effect of the drug apixaban on the occurrence of thromboembolism, 8.8% of placebo-treated patients experienced the disease, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Obesity
Abdominal obesity, also known as central obesity and truncal obesity, is a condition when excessive visceral fat around the stomach and abdomen has built up to the extent that it is likely to have a negative impact on health. Abdominal obesity has been strongly linked to cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer's disease, and other metabolic and vascular diseases. Visceral and central abdominal fat and waist circumference show a strong association with type 2 diabetes. Visceral fat, also known as organ fat or ''intra-abdominal fat'', is located inside the peritoneal cavity, packed in between internal organs and torso, as opposed to subcutaneous fat, which is found underneath the skin, and intramuscular fat, which is found interspersed in skeletal muscle. Visceral fat is composed of several adipose depots including mesenteric, epididymal white adipose tissue (EWAT), and perirenal fat. An excess of adipose visceral fat is known as central obesity, the "pot belly" or "beer belly" effect, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant. Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, family history, prior radiation therapy, frequent bladder infections, and exposure to certain chemicals. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma. Other types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically by cystoscopy with tissue biopsies. Staging of the cancer is determined by transurethral resection and medical imaging. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. It may include some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. Surgical options may include transurethral resection, partial or complete removal of the bladder, or urinary diversion. The typical five-year survival rates in the United States i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formamidopyrimidine DNA Glycosylase
DNA-formamidopyrimidine glycosylase (, ''Fapy-DNA glycosylase'', ''deoxyribonucleate glycosidase'', ''2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5N-formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase'', ''2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5(N-methyl)formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase'', ''formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase'', ''DNA-formamidopyrimidine glycosidase'', ''Fpg protein'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''DNA glycohydrolase (2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5-(N-methyl)formamidopyrimide releasing)''. FPG is a base excision repair enzyme which recognizes and removes a wide range of oxidized purines from correspondingly damaged DNA. It was discovered by Zimbabwean scientist Christopher J. Chetsanga in 1975. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : Hydrolysis of DNA containing ring-opened 7-methylguanine residues, releasing 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5-(N-methyl)formamidopyrimidine This enzyme participates in processes leading to recovery from mutagenesis and/or cell death by alkylating agent Alkylation is the tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine
8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) is an oxidized derivative of deoxyguanosine. 8-Oxo-dG is one of the major products of DNA oxidation. Concentrations of 8-oxo-dG within a cell are a measurement of oxidative stress. In DNA Steady-state levels of DNA damages represent the balance between formation and repair. Swenberg et al. measured average frequencies of steady state endogenous DNA damages in mammalian cells. The most frequent oxidative DNA damage normally present in DNA is 8-oxo-dG, occurring at an average frequency of 2,400 per cell. When 8-oxo-dG is induced by a DNA damaging agent it is rapidly repaired. For example, 8-oxo-dG was increased 10-fold in the livers of mice subjected to ionizing radiation, but the excess 8-oxo-dG was rapidly removed with a half-life of 11 minutes. As reviewed by Valavanidis et al. increased levels of 8-oxo-dG in a tissue can serve as a biomarker of oxidative stress. They also noted that increased levels of 8-oxo-dG are frequently found d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Nephrectomy.jpg)

_and_with_tumorigenesis_(B)._Brown_shows_8-oxo-dG.jpg)