|
Non-positively Curved Space
In mathematics, spaces of non-positive curvature occur in many contexts and form a generalization of hyperbolic geometry. In the category of Riemannian manifolds, one can consider the sectional curvature of the manifold and require that this curvature be everywhere less than or equal to zero. The notion of curvature extends to the category of geodesic metric spaces, where one can use comparison triangles to quantify the curvature of a space; in this context, non-positively curved spaces are known as (locally) CAT(0) spaces. Riemann Surfaces If S is a closed, orientable Riemann surface then it follows from the Uniformization theorem that S may be endowed with a complete Riemannian metric with constant Gaussian curvature of either 0, 1 or -1. As a result of the Gauss–Bonnet theorem one can determine that the surfaces which have a Riemannian metric of constant curvature 0 -1 i.e. Riemann surfaces with a complete, Riemannian metric of non-positive constant curvature, are exac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Plane
In mathematics, the Euclidean plane is a Euclidean space of dimension two. That is, a geometric setting in which two real quantities are required to determine the position of each point ( element of the plane), which includes affine notions of parallel lines, and also metrical notions of distance, circles, and angle measurement. The set \mathbb^2 of pairs of real numbers (the real coordinate plane) augmented by appropriate structure often serves as the canonical example. History Books I through IV and VI of Euclid's Elements dealt with two-dimensional geometry, developing such notions as similarity of shapes, the Pythagorean theorem (Proposition 47), equality of angles and areas, parallelism, the sum of the angles in a triangle, and the three cases in which triangles are "equal" (have the same area), among many other topics. Later, the plane was described in a so-called '' Cartesian coordinate system'', a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
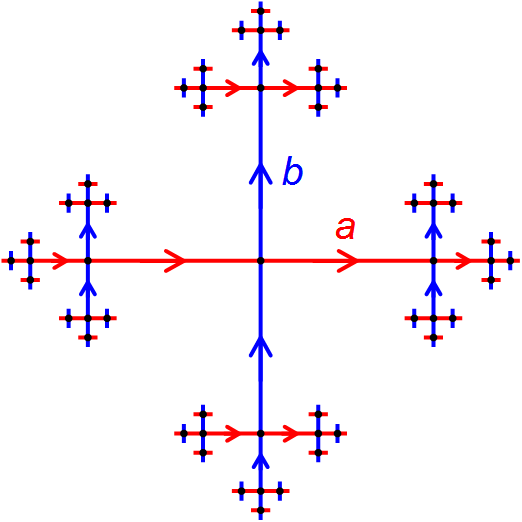
Geometric Group Theory
Geometric group theory is an area in mathematics devoted to the study of finitely generated groups via exploring the connections between algebraic properties of such group (mathematics), groups and topology, topological and geometry, geometric properties of spaces on which these groups Group action (mathematics), act (that is, when the groups in question are realized as geometric symmetries or continuous transformations of some spaces). Another important idea in geometric group theory is to consider finitely generated groups themselves as geometric objects. This is usually done by studying the Cayley graphs of groups, which, in addition to the graph (discrete mathematics), graph structure, are endowed with the structure of a metric space, given by the so-called word metric. Geometric group theory, as a distinct area, is relatively new, and became a clearly identifiable branch of mathematics in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Geometric group theory closely interacts with low-dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and an end in obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many applications ranging from logic to statistical physics and from evolutionary biology to computer science. Combinatorics is well known for the breadth of the problems it tackles. Combinatorial problems arise in many areas of pure mathematics, notably in algebra, probability theory, topology, and geometry, as well as in its many application areas. Many combinatorial questions have historically been considered in isolation, giving an ''ad hoc'' solution to a problem arising in some mathematical context. In the later twentieth century, however, powerful and general theoretical methods were developed, making combinatorics into an independent branch of mathematics in its own right. One of the oldest and most accessible parts of combinatorics is gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a graph is a structure amounting to a Set (mathematics), set of objects in which some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects correspond to mathematical abstractions called ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. Graphs are one of the objects of study in discrete mathematics. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Group
In group theory, more precisely in geometric group theory, a hyperbolic group, also known as a ''word hyperbolic group'' or ''Gromov hyperbolic group'', is a finitely generated group equipped with a word metric satisfying certain properties abstracted from classical hyperbolic geometry. The notion of a hyperbolic group was introduced and developed by . The inspiration came from various existing mathematical theories: hyperbolic geometry but also low-dimensional topology (in particular the results of Max Dehn concerning the fundamental group of a hyperbolic Riemann surface, and more complex phenomena in three-dimensional topology), and combinatorial group theory. In a very influential (over 1000 citations ) chapter from 1987, Gromov proposed a wide-ranging research program. Ideas and foundational material in the theory of hyperbolic groups also stem from the work of George Mostow, William Thurston, James W. Cannon, Eliyahu Rips, and many others. Definition Let G be a finitely g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Metric
In mathematics, a hyperbolic manifold is a space where every point looks locally like hyperbolic space of some dimension. They are especially studied in dimensions 2 and 3, where they are called Riemann surface#Hyperbolic Riemann surfaces, hyperbolic surfaces and hyperbolic 3-manifolds, respectively. In these dimensions, they are important because most manifolds can be made into a hyperbolic manifold by a homeomorphism. This is a consequence of the uniformization theorem for surfaces and the geometrization conjecture, geometrization theorem for 3-manifolds proved by Grigori Perelman, Perelman. Rigorous Definition A hyperbolic n-manifold is a complete Riemannian manifold, Riemannian n-manifold of constant sectional curvature -1. Every complete, connected, simply-connected manifold of constant negative curvature -1 is Isometry, isometric to the real hyperbolic space \mathbb^n. As a result, the universal cover of any closed manifold M of constant negative curvature -1 is \mathbb^n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Manifold
In mathematics, a hyperbolic manifold is a space where every point looks locally like hyperbolic space of some dimension. They are especially studied in dimensions 2 and 3, where they are called hyperbolic surfaces and hyperbolic 3-manifolds, respectively. In these dimensions, they are important because most manifolds can be made into a hyperbolic manifold by a homeomorphism. This is a consequence of the uniformization theorem for surfaces and the geometrization theorem for 3-manifolds proved by Perelman. Rigorous Definition A hyperbolic n-manifold is a complete Riemannian n-manifold of constant sectional curvature -1. Every complete, connected, simply-connected manifold of constant negative curvature -1 is isometric to the real hyperbolic space \mathbb^n. As a result, the universal cover of any closed manifold M of constant negative curvature -1 is \mathbb^n. Thus, every such M can be written as \mathbb^n/\Gamma where \Gamma is a torsion-free discrete group of isometries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mostow Rigidity Theorem
Mostow may refer to: People * George Mostow (1923–2017), American mathematician ** Mostow rigidity theorem * Jonathan Mostow Jonathan Mostow (born November 28, 1961) is an American film director, screenwriter, and producer. He has directed films such as ''Breakdown (1997 film), Breakdown'', ''U-571 (film), U-571'', ''Terminator 3: Rise of the Machines'', and ''Surroga ... (born 1961), American movie and television director Places * Mostów, a village in Poland {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbifold
In the mathematical disciplines of topology and geometry, an orbifold (for "orbit-manifold") is a generalization of a manifold. Roughly speaking, an orbifold is a topological space which is locally a finite group quotient of a Euclidean space. Definitions of orbifold have been given several times: by Ichirô Satake in the context of automorphic forms in the 1950s under the name ''V-manifold''; by William Thurston in the context of the geometry of 3-manifolds in the 1970s when he coined the name ''orbifold'', after a vote by his students; and by André Haefliger in the 1980s in the context of Mikhail Gromov's programme on CAT(k) spaces under the name ''orbihedron''. Historically, orbifolds arose first as surfaces with singular points long before they were formally defined. One of the first classical examples arose in the theory of modular forms with the action of the modular group \mathrm(2,\Z) on the upper half-plane: a version of the Riemann–Roch theorem holds after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a neighborhood that is homeomorphic to an open subset of n-dimensional Euclidean space. One-dimensional manifolds include lines and circles, but not lemniscates. Two-dimensional manifolds are also called surfaces. Examples include the plane, the sphere, and the torus, and also the Klein bottle and real projective plane. The concept of a manifold is central to many parts of geometry and modern mathematical physics because it allows complicated structures to be described in terms of well-understood topological properties of simpler spaces. Manifolds naturally arise as solution sets of systems of equations and as graphs of functions. The concept has applications in computer-graphics given the need to associate pictures with coordinates (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |