|
Nominative–absolutive Alignment
In linguistic typology, nominative–absolutive alignment is a type of morphosyntactic alignment in which the sole argument of an intransitive verb shares some coding properties with the agent argument of a transitive verb and other coding properties with the patient argument ('direct object') of a transitive verb. It is typically observed in a subset of the clause types of a given language (that is, the languages which have nominative–absolutive clauses also have clauses which show other alignment patterns such as nominative-accusative and/or ergative-absolutive). The languages for which nominative–absolutive clauses have been described include the Cariban languages Panare (future, desiderative, and nonspecific aspect clauses) and Katxuyana (imperfective clauses), the Northern Jê languages Canela (evaluative, progressive, continuous, completive, and negated clauses), Kĩsêdjê (progressive, continuous, and completive clauses, as well as future and negated clauses with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Languages Of South America
The indigenous languages of South America are those whose origin dates back to the pre-Columbian era. The subcontinent has great linguistic diversity, but, as the number of speakers of indigenous languages is diminishing, it is estimated that it could become one of the least linguistically diverse regions of the planet. About 600 indigenous languages are known from South America, Central America, and the Antilles (see List of indigenous languages of South America), although the actual number of languages that existed in the past may have been substantially higher. Origins The indigenous languages of South America, Central America and the Antilles completely covered the subcontinent and the Antilles at the beginning of the 16th century. The estimates of the total population are very imprecise, ranging between ten and twenty million inhabitants. At the beginning of 1980, there were about 16 million speakers of indigenous languages; three quarters of them lived in the Central And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuparian Languages
The Tuparí languages of Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family. Internal classification The Tupari languages are:Nikulin, Andrey; Fernando O. de Carvalho. 2019Estudos diacrônicos de línguas indígenas brasileiras: um panorama ''Macabéa – Revista Eletrônica do Netlli'', v. 8, n. 2 (2019), p. 255-305.PDF * Makuráp * Nuclear Tupari ** Akuntsu– Mekéns (Sakirabiá, Waratégaya) ** Tuparí, Kepkiriwát, Wayoró None are spoken by more than a few hundred people. A more recent internal classification by Nikulin & Andrade (2020) is given below:Nikulin, Andrey; Rafael Andrade. 2020The rise and fall of approximants in the Tuparian languages ''Journal of Language Relationship'' 18/4 (2020), pp. 284–319. *Tuparian **'' Makurap'' **Core Tuparian ***Wayoró–Tuparí ****'' Wayoró'' ****'' Tuparí'' ***Corumbiara ****'' Mekéns'' ****'' Akuntsú'' Varieties Below is a list of Tupari language varieties listed by Loukotka (1968), including names of unattested v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolutive Case
In grammar, the absolutive case (abbreviated ) is the case of nouns in ergative–absolutive languages that would generally be the subjects of intransitive verbs or the objects of transitive verbs in the translational equivalents of nominative–accusative languages such as English. In ergative–absolutive languages In languages with ergative–absolutive alignment, the absolutive is the case used to mark both the subject of an intransitive verb and the object of a transitive verb in addition to being used for the citation form of a noun. It contrasts with the marked ergative case, which marks the subject of a transitive verb. For example, in Basque the noun ''mutil'' ("boy") takes the bare singular article ''-a'' both as the subject of the intransitive clause ''mutila etorri da'' ("the boy came") and as the object of the transitive clause ''Irakasleak mutila ikusi du'' ("the teacher has seen the boy") in which the subject bears the ergative ending ''-a-k''. In very few cases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient (linguistics)
In generative grammar, a theta role or θ-role is the formal device for representing syntactic argument structure—the number and type of noun phrases—required syntactically by a particular verb. For example, the verb ''put'' requires three arguments (i.e., it is trivalent). The formal mechanism for implementing a verb's argument structure is codified as theta roles. The verb ''put'' is said to "assign" three theta roles. This is coded in a theta grid associated with the lexical entry for the verb. The correspondence between the theta grid and the actual sentence is accomplished by means of a bijective filter on the grammar known as the theta criterion. Early conceptions of theta roles include (Fillmore called theta roles "cases") and . Theta roles are prominent in government and binding theory and the standard theory of transformational grammar. Thematic relations The term "theta role" is often used interchangeably with the term thematic relations (particularly in mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrealis Mood
In linguistics, irrealis moods (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) are the main set of grammatical moods that indicate that a certain situation or action is not known to have happened at the moment the speaker is talking. This contrasts with the realis moods. Every language has grammatical ways of expressing unreality. Linguists tend to reserve the term "irrealis" for particular morphology (linguistics), morphological markers or clause types. Many languages with irrealis mood make further subdivisions between kinds of irrealis moods. This is especially so among Algonquian languages such as Blackfoot language, Blackfoot. List of irrealis moods Moods Subjunctive The subjunctive mood, sometimes called conjunctive mood, has several uses in dependent clauses. Examples include discussing hypothetical or unlikely events, expressing opinions or emotions, or making polite requests (the exact scope is language-specific). A subjunctive mood exists in English, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative Case
In grammar, the nominative case (abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of English) the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments. Generally, the noun "that is doing something" is in the nominative, and the nominative is often the form listed in dictionaries. Etymology The English word ''nominative'' comes from Latin ''cāsus nominātīvus'' "case for naming", which was translated from Ancient Greek ὀνομαστικὴ πτῶσις, ''onomastikḗ ptôsis'' "inflection for naming", from ''onomázō'' "call by name", from ''ónoma'' "name". Dionysius Thrax in his The Art of Grammar refers to it as ''orthḗ'' or ''eutheîa'' "straight", in contrast to the oblique or "bent" cases. Characteristics The reference form (more technically, the ''least marked'') of ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent (linguistics)
In linguistics, a grammatical agent is the thematic relation of the cause or initiator to an event. The agent is a semantic concept distinct from the subject of a sentence as well as from the topic. Whereas the subject is determined syntactically, primarily through word order, the agent is determined through its relationship to the action expressed by the verb. For example, in the sentence "The little girl was bitten by the dog", "girl" is the subject, but "dog" is the agent. The word "agent" comes from the present participle ''agens, agentis'' ("the one doing") of the Latin verb ''agere'', to "do" or "make". Theory Typically, the situation is denoted by a sentence, the action by a verb in the sentence, and the agent by a noun phrase. For example, in the sentence "Jack kicked the ball", ''Jack'' is the agent and "the ball" is the patient. In certain languages, the agent is declined or otherwise marked to indicate its grammatical role. Modern English does not mark the agentiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
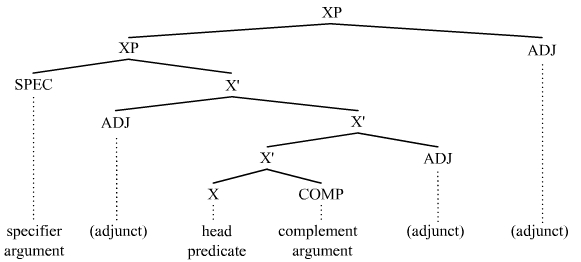
Argument (linguistics)
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the ''complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active–stative Alignment
In linguistic typology, active–stative alignment (also split intransitive alignment or semantic alignment) is a type of morphosyntactic alignment in which the sole argument ("subject") of an intransitive clause (often symbolized as ''S'') is sometimes marked in the same way as an agent of a transitive verb (that is, like a subject such as "I" or "she" in English) but other times in the same way as a direct object (such as "me" or "her" in English). Languages with active–stative alignment are often called ''active languages''. The case or agreement of the intransitive argument (''S'') depends on semantic or lexical criteria particular to each language. The criteria tend to be based on the degree of volition, or control over the verbal action exercised by the participant. For example, if one tripped and fell, an active–stative language might require one to say the equivalent of "fell me." To say "I fell" would mean that the person had done it on purpose, such as taking a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akuntsu Language
Akuntsu is a Tupian language of Brazil. Peaceful contact with the Akuntsu people was only made in 1995; they had been massacred by cattle ranchers in the 1980s. The Akuntsu language is spoken only by members of the tribe and not fully understood by any outsider. It is considered unlikely that the Akuntsu language or culture will survive following the deaths of the tribe's remaining members. For this reason several observers have described the tribe as the victims of genocide Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin .... The neighbouring Kanoê have been similarly reduced in number through contact with settlers, as were the people of a man recently encountered living alone in the Igarapé Omerê reserve who is apparently the sole survivor of his tribe. References Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |