|
Nitrate Reductase Test
The nitrate reductase test is a test to differentiate between bacteria based on their ability or inability to reduce nitrate (NO3−) to nitrite (NO2−) using anaerobic respiration. Procedure Various assays for detecting nitrate reduction have been described.V.B.D. Skerman, A guide to the identification of the genera of bacteria, The Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, MD, p.218 - 220 (1967). One method is performed as follows: #Inoculation, Inoculate nitrate broth with an isolate and incubate for 48 hours. #Add two nitrate tablets to the sample. If the bacterium produces nitrate reductase, the broth will turn a deep red within 5 minutes at this step. #If no color change is observed, then the result is inconclusive. Add a small amount of zinc to the broth. If the solution remains colorless, then both nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase are present. If the solution turns red, nitrate reductase is not present. References Bacteriology {{bacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
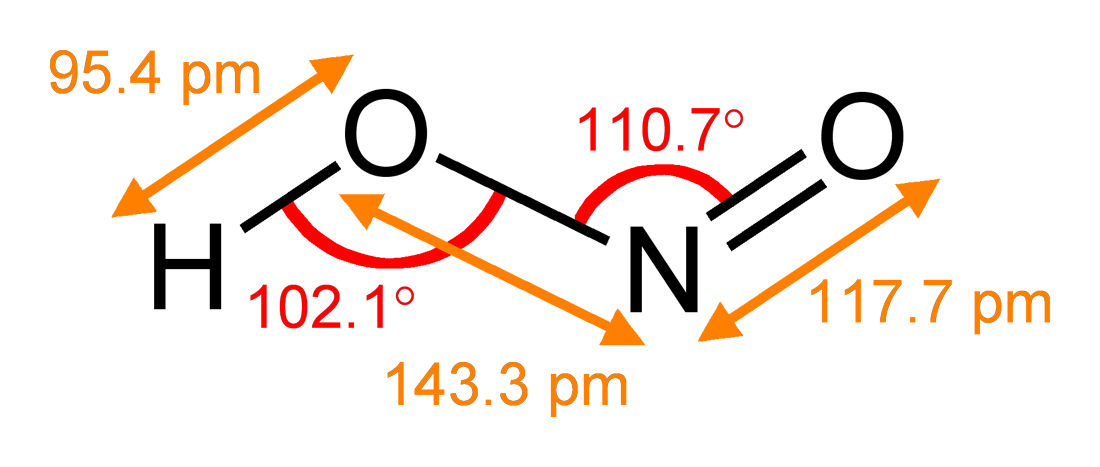
Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zero. The term molecule may or may no ... with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate. Structure The ion is the conjugate acid, conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of −1. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a − charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O2). Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain. In aerobic organisms undergoing respiration, electrons are shuttled to an electron transport chain, and the final electron acceptor is oxygen. Molecular oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor. Anaerobes instead use less-oxidizing substances such as nitrate (), fumarate (), sulfate (), or elemental sulfur (S). These terminal electron acceptors have smaller reduction potentials than O2. Less energy per oxidized molecule is released. Therefore, anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic. As compared with fermentation Anaerobic cellular respiration and fermentation generate ATP in very different ways, and the terms should not be treated as synonyms. Cellular respiration (both aerobic and anaerobic) uses highly reduced chemical compounds such as NADH and FADH2 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inoculation
Inoculation is the act of implanting a pathogen or other microorganism. It may refer to methods of artificially inducing immunity against various infectious diseases, or it may be used to describe the spreading of disease, as in "self-inoculation," the spreading of disease from one part of the body to another, or even to the spreading of bacteria in a Petri dish for culturing purposes. The terms "inoculation", "vaccination", and "immunization" are often used synonymously, but there are some important differences among them. Inoculation is the act of implanting a disease inside a person or animal, vaccination is the act of implanting or giving someone a vaccine specifically, and immunization is what happens to the immune system as a result. Terminology Until the early 1800s inoculation referred only to variolation (from the Latin word ''variola'' = smallpox), the predecessor to the smallpox vaccine. The smallpox vaccine, introduced by Edward Jenner in 1796, was called cowpox inoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrate Reductase
Nitrate reductases are molybdoenzymes that reduce nitrate (NO) to nitrite (NO). This reaction is critical for the production of protein in most crop plants, as nitrate is the predominant source of nitrogen in fertilized soils. Types Eukaryotic Eukaryotic nitrate reductases are part of the sulfite oxidase family of molybdoenzymes. They transfer electrons from NADH or NADPH to nitrate. Prokaryotic Prokaryotic nitrate reductases belong to the DMSO reductase family of molybdoenzymes and have been classified into three groups, assimilatory nitrate reductases (Nas), respiratory nitrate reductase (Nar), and periplasmic nitrate reductases (Nap). The active site of these enzymes is a Mo ion that is bound to the four thiolate functions of two pterin molecules. The coordination sphere of the Mo is completed by one amino-acid side chain and oxygen and/or sulfur ligands. The exact environment of the Mo ion in certain of these enzymes (oxygen versus sulfur as a sixth molybdenum lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrite Reductase
Nitrite reductase refers to any of several classes of enzymes that catalyze the reduction of nitrite. There are two classes of NIR's. A multi haem enzyme reduces NO2− to a variety of products. Copper containing enzymes carry out a single electron transfer to produce nitric oxide. Iron based There are several types of iron based enzymes. Cytochrome cd1, or ''Pseudomonas'' cytochrome oxidase contains two c and two d type hemes with two polypeptide chains. Different forms of this reductase catalyze the formation of nitric oxide or nitrous oxide. A version of this compound was originally called oxidoreductase.html"_;"title="errocytochrome_c-551:oxidoreductase">errocytochrome_c-551:oxidoreductase_It_was_initially_considered_an_oxidase.__It_catalyzes_the_reduction_of_NO2−_to_NO.__This_tetraheme_enzyme_has_two_Protein_subunit.html" ;"title="oxidoreductase.html" ;"title="oxidoreductase.html" ;"title="errocytochrome c-551:oxidoreductase">errocytochrome c-551:oxidoreductase">oxido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |