|
Nankeens
Nankeen (also called Nankeen cloth) is a kind of pale yellowish cloth originally made in Nanking (modern Nanjing), China from a yellow variety of cotton, but subsequently manufactured from ordinary cotton that is then dyed.''Oxford English Dictionary'' The term blue nankeen describes hand-printed fabric of artistic refinement and primitive simplicity, which originated on the Silk Road over three thousand years ago. Hand-carved stencils, originally made from wood but now from heavy paper, are prepared and a mix of soybean flour and slaked lime is applied through the openings of the stencil onto the 100% cotton fabric. When dry, the fabric is then dipped numerous times into the large tubs containing the indigo dye. After the desired color is achieved and the fabric has dried, the paste is scraped off, revealing the white patterns on the blue cloth. The fabric is then washed, dried, and ironed before fabrication. Derived uses Nankeen also refers to: *Trousers made of nankeen (si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanking
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. The city has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a total recorded population of 9,314,685 . Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949, and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's administrative structure, enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly less than that of a province. Nanjing has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilization, as well as fabric remnants dated back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the Eastern world, East and Western world, West. The name "Silk Road", first coined in the late 19th century, has fallen into disuse among some modern historians in favor of Silk Routes, on the grounds that it more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting East Asia, East and Southeast Asia, the South Asia, Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the Middle East, East Africa and Southern Europe, Europe. The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk, silk textiles that were Silk industry in China, produced almost exclusively in China. The network began with the Han dynasty, Han dynasty's expansion into Central Asia around 114 BCE, Protectorate of the Western Regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stencil
Stencilling produces an image or pattern on a surface, by applying pigment to a surface through an intermediate object, with designed holes in the intermediate object, to create a pattern or image on a surface, by allowing the pigment to reach only some parts of the surface. The stencil is both the resulting image or pattern and the intermediate object; the context in which ''stencil'' is used makes clear which meaning is intended. In practice, the (object) stencil is usually a thin sheet of material, such as paper, plastic, wood or metal, with letters or a design cut from it, used to produce the letters or design on an underlying surface by applying pigment through the cut-out holes in the material. The key advantage of a stencil is that it can be reused to repeatedly and rapidly produce the same letters or design. Although aerosol or painting stencils can be made for one-time use, typically they are made with the intention of being reused. To be reusable, they must remain int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption). Etymology The word "soy" originated as a corruption of the Cantonese or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Properties Calcium hydroxide is poorly soluble in water, with a retrograde solubility increasing from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. With a solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following dissolution reaction: : Ca(OH)2 → Ca2+ + 2 OH− At ambient temperature, calcium hydroxide (portlandite) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', meaning "Indian", as the dye was originally exported to Europe from India. It is traditionally regarded as a color in the visible spectrum, as well as one of the seven colors of the rainbow: the color between blue and violet; however, sources differ as to its actual position in the electromagnetic spectrum. The first known recorded use of indigo as a color name in English was in 1289. History ''Indigofera tinctoria'' and related species were cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, Bangladesh and Peru in antiquity. The earliest direct evidence for the use of indigo dates to around 4000 BC and comes from Huaca Prieta, in contemporary Peru. Pliny the Elder mentions India as the source of the dye after which it was named. It was importe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
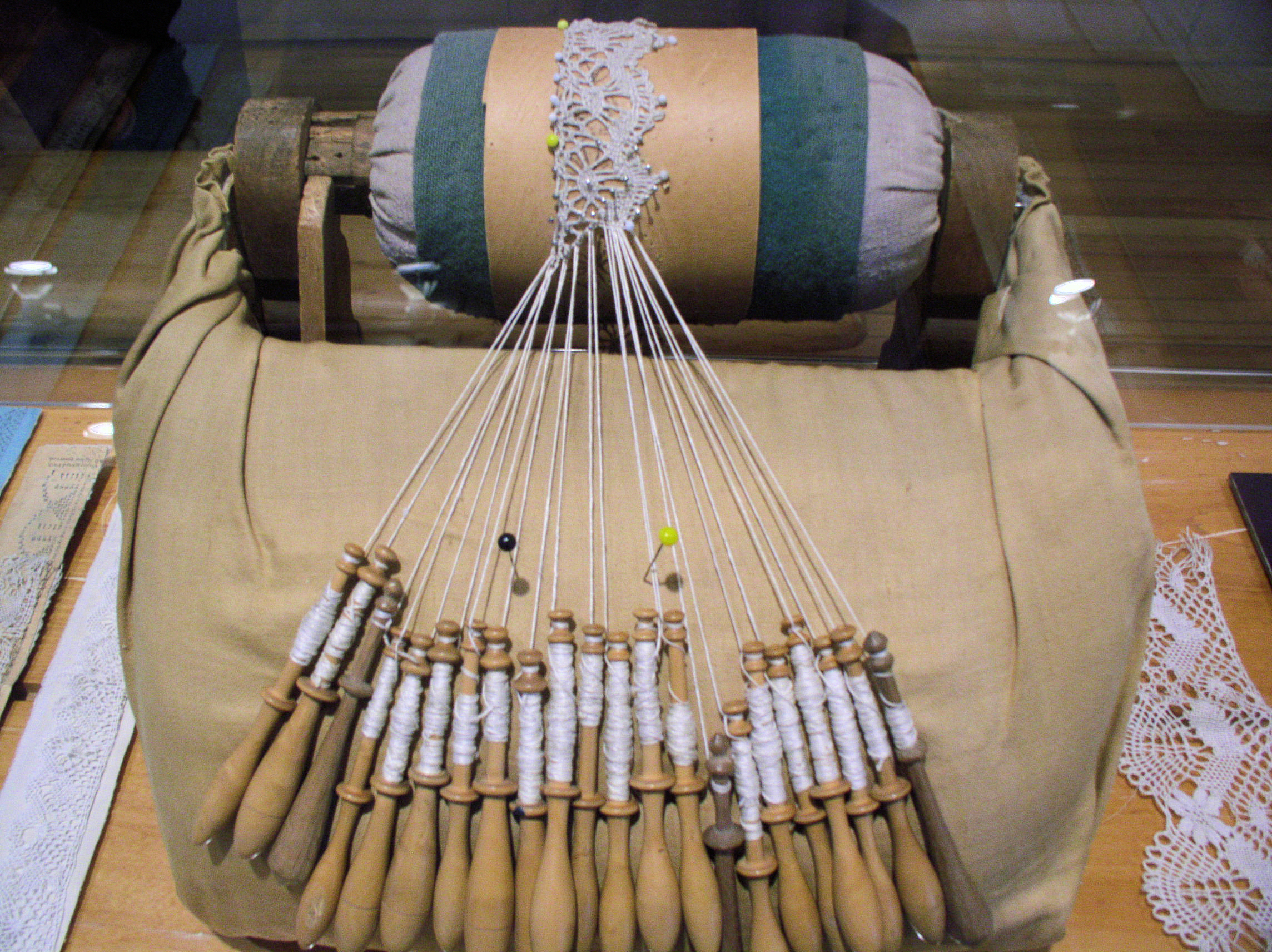
Bobbin Lace
Bobbin lace is a lace textile made by braiding and twisting lengths of thread, which are wound on bobbins to manage them. As the work progresses, the weaving is held in place with pins set in a lace pillow, the placement of the pins usually determined by a pattern or pricking pinned on the pillow. Bobbin lace is also known as pillow lace, because it was worked on a pillow, and bone lace, because early bobbins were made of bone or ivory. Bobbin lace is one of the two major categories of handmade laces, the other being needle lace, derived from earlier cutwork and reticella. Origin A will of 1493 by the Milanese Sforza family mentions lace created with twelve bobbins. There are two books that represent the early known pattern descriptions for bobbin lace, ''Le Pompe'' from Venice and ''Nüw Modelbuch'' from Zürich. Bobbin lace evolved from passementerie or braid-making in 16th-century Italy. Genoa was famous for its braids, hence it is not surprising to find bobbin lace de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus Populnea
''Eucalyptus populnea'', commonly known as poplar box, bimble box or bimbil box, is a species of small to medium-sized tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has rough, fibrous or flaky bark on the trunk and branches, egg-shaped, elliptical or more or less round leaves, flower buds arranged in groups of seven to fifteen or more, white flowers and conical, hemispherical or cup-shaped fruit. Description ''Eucalyptus populnea'' is a tree that typically grows to a height of and forms a lignotuber. It has rough, fibrous or flaky, greyish bark on the trunk and larger branches, smooth grey bark that is shed in short ribbons from the thinner branches. Young plants and coppice regrowth have egg-shaped to almost round, dull greyish green leaves that are long and wide. The crown has leaves that are the same shade of glossy green on both sides, egg-shaped, elliptical or more or less round leaves that are long and wide tapering to a petiole long. The flower buds are mostly arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nankeen Kestrel
The nankeen kestrel (''Falco cenchroides''), also known as the Australian kestrel, is a raptor native to Australia and New Guinea. It is one of the smallest falcons, and unlike many, does not rely on speed to catch its prey. Instead, it simply perches in an exposed position, but it also has a distinctive technique of hovering over crop and grasslands. Taxonomy The nankeen kestrel is a species of the genus ''Falco'', allied to a subgenus ''Tinnunculus''. They were first described by Nicholas Vigors and Thomas Horsfield in 1827. Further descriptions — regarded as synonyms for the species — were published: ''Cerchneis immaculata'' Brehm, 1845; the later name ''Cerchneis unicolor'' by Alexander Milligan was published in ''Emu'' in 1904; and that author's name appearing in the assignment to a subspecies, ''Cerchneis cenchroides milligani'', published by Gregory Mathews in 1912. The generic name is Late Latin ''falco'' 'falcon' (from ''falx'' ''falcis'', 'sickle') and the speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |