|
Miscellaneous Electric Load
Miscellaneous electric loads (MELs) in buildings are electric loads resulting from a multitude of devices (electronic and other) excluding main systems for space heating, cooling, water heating, or lighting.Roth, K., McKenney, K., Brodrick, J. "Small Devices, Big Loads." ASHRAE Journal. Vol. 60 No. 6. June 2008. MELs are produced by hard-wired and “plug-in” electrical devices that draw power, including office equipment such as desktop computers and monitors, mobile electronics (laptops, tablets, mobile phones, and their charging units), printers, fans, task lighting, and home equipment such as home entertainment centers, kitchen electronics (microwaves, toaster ovens, cooking accessories), bath items (hair dryers, lighted mirrors, and electric hot tubs), and other devices such as security systems and ceiling fans. MELs are gaining greater importance in energy management as personal electronics proliferate and become standard across demographic groups. MELs demand has been risi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entertainment Center
An entertainment center (or centre), also known as an entertainment complex, is a piece of furniture designed to house consumer electronic appliances and components, such as televisions. Evolution of home TV and stereo A stereo console (or "console stereo," as it was sometimes called) is a stereo system containing audio components (such as a stereo record changer, tape deck, and a stereo FM radio) housed into a stand-alone cabinet, as was popular in the 1960s and into the 1970s. A stereo consolette (as identified by one of its manufacturers from that period, '' Delmonico/Nivico'') is a smaller, more compact stereo console that often stands on splayed legs. The corresponding term for console in British English is radiogram. During the 1970's, some stereo manufacturers began designing more lavish and flashy systems to coincide with the psychedelic and disco eras from that decade. Such as was the case when the New York stereo manufacturer ''Morse-Electro Products'' produced some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standby Power
Standby power, also called vampire power, vampire draw, phantom load, ghost load or leaking electricity ("phantom load" and " leaking electricity" are defined technical terms with other meanings, adopted for this different purpose), refers to the way electric power is consumed by electronic and electrical appliances while they are switched off (but are designed to draw some power) or in standby mode. This only occurs because some devices claimed to be "switched off" on the electronic interface, but are in a different state. Switching off at the plug, or disconnecting from the power point, can solve the problem of standby power completely. In fact, switching off at the power point is effective enough, there is no need to disconnect all devices from the power point. Some such devices offer remote controls and digital clock features to the user, while other devices, such as power adapters for disconnected electronic devices, consume power without offering any features (sometimes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
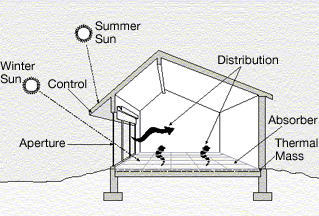
Low-energy House
A low-energy house is characterized by an energy-efficient design and technical features which enable it to provide high living standards and comfort with low energy consumption and carbon emissions. Traditional heating and active cooling systems are absent, or their use is secondary. Low-energy buildings may be viewed as examples of sustainable architecture. Low-energy houses often have active and passive solar building design and components, which reduce the house's energy consumption and minimally impact the resident's lifestyle. Throughout the world, companies and non-profit organizations provide guidelines and issue certifications to guarantee the energy performance of buildings and their processes and materials. Certifications include passive house, BBC - Bâtiment Basse Consommation - Effinergie (France), zero-carbon house (UK), and Minergie (Switzerland). Background During the 1970s, experimental initiatives for low-energy buildings were made in Denmark, the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient Energy Use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses. There are many motivations to improve energy efficiency. Decreasing energy use reduces energy costs and may result in a financial cost saving to consumers if the energy savings offset any additional costs of implementing an energy-efficient technology. Reducing energy use is also seen as a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Heating
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses. Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as ''water heaters'', ''kettles'', ''cauldrons'', ''pots'', or ''coppers''. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies with the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases. Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called ''water heaters'', ''hot water heaters'', ''hot water tanks'', ''boilers'', ''heat exchangers'', ''geysers'' (Southern Africa and the Arab world), or ''calorifiers''. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potable w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Envelope
A building envelope is the physical separator between the conditioned and unconditioned environment of a building including the resistance to air, water, heat, light, and noiseSyed, Asif. ''Advanced building technologies for sustainability''. Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2012. 115. Print. transfer. Discussion The building envelope (or the more modern term, building enclosure) is all of the elements of the outer shell that maintain a dry, heated, or cooled indoor environment and facilitate its climate control. Building envelope design is a specialized area of architectural and engineering practice that draws from all areas of building science and indoor climate control. The many functions of the building envelope can be separated into three categories:Straube, J.F., Burnett, E.F.P. ''Building Science for Building Enclosures''. Building Science Press, Westford, 2005. * Support (to resist and transfer structural and dynamic loads) * Control (the flow of matter and energy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-energy Building
A Zero Energy Building (ZEB), also known as a Net Zero Energy (NZE) building, is a building with net zero energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site or in other definitions by renewable energy sources offsite, using technology such as heat pumps, high efficiency windows and insulation, and solar panels. The goal is that these buildings contribute less overall greenhouse gas to the atmosphere during operations than similar non-ZNE buildings. They do at times consume non-renewable energy and produce greenhouse gases, but at other times reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas production elsewhere by the same amount. The development of zero-energy buildings is encouraged by the desire to have less of an impact on the environment, and by tax breaks and savings on energy costs that make zero-energy buildings financially viable. Terminology tends to vary between cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Star
Energy Star (trademarked ''ENERGY STAR'') is a program run by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) that promotes energy efficiency. The program provides information on the energy consumption of products and devices using different standardized methods. The Energy Star label is found on more than 75 different certified product categories, homes, commercial buildings, and industrial plants. In the United States, the Energy Star label is also shown on the Energy Guide appliance label of qualifying products. Elements of the Energy Star Program are being implemented in Japan, Taiwan, and Switzerland, as well as by Energy Star Canada. In 2018, a 15-year long agreement with the European Union expired. A previous agreement with the European Free Trade Association has expired. History The Energy Star program was established by the Environmental Protection Agency in 1992 and operates under the authority of the Clean Air Act, section 103( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
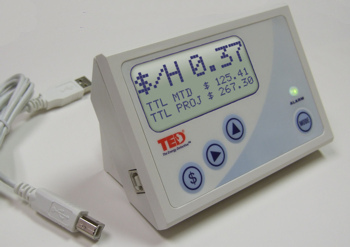
The Energy Detective
A home energy monitor provides feedback on electrical energy use. Devices may also display cost of energy used, and estimates of greenhouse gas emissions. Various studies have shown a reduction in home energy use of 4-15% through use of home energy display. Electricity use may be measured with an inductive clamp placed around the electric main, via the electric meter (either through an optical port, or by sensing the meters actions), by communicating with a smart meter, or by direct connection to the electrical system. The display portion may be remote from the measurement, communicating with the sensor using a cable, network, power line communications, or using radio. Online displays are also available which allow the user to use an internet connected display to show near real-time consumption. A means to reduce household energy consumption is to provide real-time feedback to homeowners so they can change their energy use. In 2010, UK based Current Cost announced a partner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug Load
Plug load is the energy used by products that are powered by means of an ordinary AC plug (e.g., 100, 115, or 230 V). This term generally excludes building energy that is attributed to major end uses (HVAC, lighting, water heating, etc.) Definitions Plug loads are often synonymous with terms such as "receptacle loads", "miscellaneous loads", "unregulated loads", or "process energy/loads." While many building codes/standards haven't defined "plug loads" specifically, they have defined these related terms, which are usually broader energy use categories. "Process energy" is defined as energy consumed in support of a manufacturing, industrial, or commercial process other than conditioning spaces and maintaining comfort and amenities for the occupants of a building. It typically includes office and general miscellaneous equipment, computers, elevators and escalators, kitchen cooking and refrigeration, laundry washing and drying, lighting exempt from the lighting power allowance, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-energy Building
A low-energy house is characterized by an energy-efficient design and technical features which enable it to provide high living standards and comfort with low energy consumption and carbon emissions. Traditional heating and active cooling systems are absent, or their use is secondary. Low-energy buildings may be viewed as examples of sustainable architecture. Low-energy houses often have active and passive solar building design and components, which reduce the house's energy consumption and minimally impact the resident's lifestyle. Throughout the world, companies and non-profit organizations provide guidelines and issue certifications to guarantee the energy performance of buildings and their processes and materials. Certifications include passive house, BBC - Bâtiment Basse Consommation - Effinergie (France), zero-carbon house (UK), and Minergie (Switzerland). Background During the 1970s, experimental initiatives for low-energy buildings were made in Denmark, the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)