Efficient energy use on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional
 Energy efficiency has proved to be a cost-effective strategy for building economies without necessarily increasing energy consumption. For example, the state of
Energy efficiency has proved to be a cost-effective strategy for building economies without necessarily increasing energy consumption. For example, the state of
Report on Multiple Benefits of Energy Efficiency
. OECD, Paris, 2014. Moreover, it has long been recognized that energy efficiency brings other benefits additional to the reduction of energy consumption. Some estimates of the value of these other benefits, often called multiple benefits, co-benefits, ancillary benefits or non-energy benefits, have put their summed value even higher than that of the direct energy benefits. These multiple benefits of energy efficiency include things such as reduced climate change impact, reduced air pollution and improved health, improved indoor conditions, improved energy security and reduction of the price risk for energy consumers. Methods for calculating the monetary value of these multiple benefits have been developed, including e.g. the choice experiment method for improvements that have a subjective component (such as aesthetics or comfort) and Tuominen-Seppänen method for price risk reduction. When included in the analysis, the economic benefit of energy efficiency investments can be shown to be significantly higher than simply the value of the saved energy.
 Buildings are an important field for energy efficiency improvements around the world because of their role as a major energy consumer. However, the question of energy use in buildings is not straightforward as the indoor conditions that can be achieved with energy use vary a lot. The measures that keep buildings comfortable, lighting, heating, cooling and ventilation, all consume energy. Typically the level of energy efficiency in a building is measured by dividing energy consumed with the floor area of the building which is referred to as specific energy consumption or energy use intensity:
:
However, the issue is more complex as building materials have embodied energy in them. On the other hand, energy can be recovered from the materials when the building is dismantled by reusing materials or burning them for energy. Moreover, when the building is used, the indoor conditions can vary resulting in higher and lower quality indoor environments. Finally, overall efficiency is affected by the use of the building: is the building occupied most of the time and are spaces efficiently used — or is the building largely empty? It has even been suggested that for a more complete accounting of energy efficiency, specific energy consumption should be amended to include these factors:
:
Thus a balanced approach to energy efficiency in buildings should be more comprehensive than simply trying to minimize energy consumed. Issues such as quality of indoor environment and efficiency of space use should be factored in. Thus the measures used to improve energy efficiency can take many different forms. Often they include passive measures that inherently reduce the need to use energy, such as better insulation. Many serve various functions improving the indoor conditions as well as reducing energy use, such as increased use of natural light.
A building's location and surroundings play a key role in regulating its temperature and illumination. For example, trees, landscaping, and hills can provide shade and block wind. In cooler climates, designing northern hemisphere buildings with south facing windows and southern hemisphere buildings with north facing windows increases the amount of sun (ultimately heat energy) entering the building, minimizing energy use, by maximizing passive solar heating. Tight building design, including energy-efficient windows, well-sealed doors, and additional thermal insulation of walls, basement slabs, and foundations can reduce heat loss by 25 to 50 percent.
Dark roofs may become up to 39 °C (70 °F) hotter than the most reflective white surfaces. They transmit some of this additional heat inside the building. US Studies have shown that lightly colored roofs use 40 percent less energy for cooling than buildings with darker roofs. White roof systems save more energy in sunnier climates. Advanced electronic heating and cooling systems can moderate energy consumption and improve the comfort of people in the building.
Proper placement of windows and skylights as well as the use of architectural features that reflect light into a building can reduce the need for artificial lighting. Increased use of natural and task lighting has been shown by one study to increase productivity in schools and offices. Compact fluorescent lamps use two-thirds less energy and may last 6 to 10 times longer than
Buildings are an important field for energy efficiency improvements around the world because of their role as a major energy consumer. However, the question of energy use in buildings is not straightforward as the indoor conditions that can be achieved with energy use vary a lot. The measures that keep buildings comfortable, lighting, heating, cooling and ventilation, all consume energy. Typically the level of energy efficiency in a building is measured by dividing energy consumed with the floor area of the building which is referred to as specific energy consumption or energy use intensity:
:
However, the issue is more complex as building materials have embodied energy in them. On the other hand, energy can be recovered from the materials when the building is dismantled by reusing materials or burning them for energy. Moreover, when the building is used, the indoor conditions can vary resulting in higher and lower quality indoor environments. Finally, overall efficiency is affected by the use of the building: is the building occupied most of the time and are spaces efficiently used — or is the building largely empty? It has even been suggested that for a more complete accounting of energy efficiency, specific energy consumption should be amended to include these factors:
:
Thus a balanced approach to energy efficiency in buildings should be more comprehensive than simply trying to minimize energy consumed. Issues such as quality of indoor environment and efficiency of space use should be factored in. Thus the measures used to improve energy efficiency can take many different forms. Often they include passive measures that inherently reduce the need to use energy, such as better insulation. Many serve various functions improving the indoor conditions as well as reducing energy use, such as increased use of natural light.
A building's location and surroundings play a key role in regulating its temperature and illumination. For example, trees, landscaping, and hills can provide shade and block wind. In cooler climates, designing northern hemisphere buildings with south facing windows and southern hemisphere buildings with north facing windows increases the amount of sun (ultimately heat energy) entering the building, minimizing energy use, by maximizing passive solar heating. Tight building design, including energy-efficient windows, well-sealed doors, and additional thermal insulation of walls, basement slabs, and foundations can reduce heat loss by 25 to 50 percent.
Dark roofs may become up to 39 °C (70 °F) hotter than the most reflective white surfaces. They transmit some of this additional heat inside the building. US Studies have shown that lightly colored roofs use 40 percent less energy for cooling than buildings with darker roofs. White roof systems save more energy in sunnier climates. Advanced electronic heating and cooling systems can moderate energy consumption and improve the comfort of people in the building.
Proper placement of windows and skylights as well as the use of architectural features that reflect light into a building can reduce the need for artificial lighting. Increased use of natural and task lighting has been shown by one study to increase productivity in schools and offices. Compact fluorescent lamps use two-thirds less energy and may last 6 to 10 times longer than
 The estimated energy efficiency for an automobile is 280 Passenger-Mile/106 Btu. There are several ways to enhance a vehicle's energy efficiency. Using improved
The estimated energy efficiency for an automobile is 280 Passenger-Mile/106 Btu. There are several ways to enhance a vehicle's energy efficiency. Using improved
 Alternative fuels, known as non-conventional or advanced
Alternative fuels, known as non-conventional or advanced
Department of Energy (DOE) Software Directory
describes EnergyActio software, a cloud based platform designed for this purpose.
pp. v-vi. Estimates of the size of the rebound effect range from roughly 5% to 40%. The rebound effect is likely to be less than 30% at the household level and may be closer to 10% for transport. A rebound effect of 30% implies that improvements in energy efficiency should achieve 70% of the reduction in energy consumption projected using engineering models. Saunders et al. showed in 2010 that lighting has accounted for about 0.7% of GDP across many societies and hundreds of years, implying a rebound effect of 100%. However, some of the authors argue in a followup paper that increased lighting generally increases economic welfare and has substantial benefits. A 2014 study has shown the rebound effect to be rather low for household lighting, in particular for high use bulbs.
 Energy efficiency targets for 2020 and 2030.
The first EU-wide energy efficiency target was set in 1998. Member states agreed to improve energy efficiency by 1 percent a year over twelve years. In addition, legislation about products, industry, transport and buildings has contributed to a general energy efficiency framework. More effort is needed to address heating and cooling: there is more heat wasted during electricity production in Europe than is required to heat all buildings in the continent. All in all, EU energy efficiency legislation is estimated to deliver savings worth the equivalent of up to 326 million tons of oil per year by 2020.
The EU set itself a 20% energy savings target by 2020 compared to 1990 levels, but member states decide individually how energy savings will be achieved. At an EU summit in October 2014, EU countries agreed on a new energy efficiency target of 27% or greater by 2030. One mechanism used to achieve the target of 27% is the 'Suppliers Obligations & White Certificates'. The ongoing debate around the 2016 Clean Energy Package also puts an emphasis on energy efficiency, but the goal will probably remain around 30% greater efficiency compared to 1990 levels. Some have argued that this will not be enough for the EU to meet its Paris Agreement goals of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 40% compared to 1990 levels.
Important organisations and programs:
* Building energy rating
*
Energy efficiency targets for 2020 and 2030.
The first EU-wide energy efficiency target was set in 1998. Member states agreed to improve energy efficiency by 1 percent a year over twelve years. In addition, legislation about products, industry, transport and buildings has contributed to a general energy efficiency framework. More effort is needed to address heating and cooling: there is more heat wasted during electricity production in Europe than is required to heat all buildings in the continent. All in all, EU energy efficiency legislation is estimated to deliver savings worth the equivalent of up to 326 million tons of oil per year by 2020.
The EU set itself a 20% energy savings target by 2020 compared to 1990 levels, but member states decide individually how energy savings will be achieved. At an EU summit in October 2014, EU countries agreed on a new energy efficiency target of 27% or greater by 2030. One mechanism used to achieve the target of 27% is the 'Suppliers Obligations & White Certificates'. The ongoing debate around the 2016 Clean Energy Package also puts an emphasis on energy efficiency, but the goal will probably remain around 30% greater efficiency compared to 1990 levels. Some have argued that this will not be enough for the EU to meet its Paris Agreement goals of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 40% compared to 1990 levels.
Important organisations and programs:
* Building energy rating
*
 believe energy efficiency is still under-recognised in terms of its contribution to Germany's energy transformation (or ''
believe energy efficiency is still under-recognised in terms of its contribution to Germany's energy transformation (or ''
Build Smart - Canada's Buildings Strategy
as a key driver of the Pan-Canadian Framework on Clean Growth and Climate Change, Canada's national climate strategy. The Build Smart strategy seeks to dramatically increase the energy-efficiency performance of existing and new Canadian buildings, and establishes five goals to that end: *Federal, provincial, and territorial governments will work to develop and adopt increasingly stringent model building codes, starting in 2020, with the goal that provinces and territories adopt a “ net-zero energy ready” model building code by 2030. *Federal, provincial, and territorial governments will work to develop a model code for existing buildings by 2022, with the goal that provinces and territories adopt the code. *Federal, provincial, and territorial governments will work together with the aim of requiring labelling of building energy use by as early as 2019. *The federal government will set new standards for heating equipment and other key technologies to the highest level of efficiency that is economically and technically achievable. *Provincial and territorial governments will work to sustain and expand efforts to retrofit existing buildings by supporting energy efficiency improvements and by accelerating the adoption of high-efficiency equipment while tailoring their programs to regional circumstances. The strategy details a range of activities the Government of Canada will pursue, and investments it will make, in support of the goals. As of early 2018, only one of Canada's 10 provinces and three territories, British Columbia, has developed a policy in support of federal government's goal to reach net zero energy ready ambitions: the BC Energy Step Code. Local British Columbia governments may use the BC Energy Step Code, if they wish, to incentivize or require a level of energy efficiency in new construction that goes above and beyond the requirements of the base building code. The regulation and standard is designed as a technical roadmap to help the province reach its target that all new buildings will attain a net zero energy ready level of performance by 2032.
 Programs and organisations:
* Alliance to Save Energy
* American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy
*
Programs and organisations:
* Alliance to Save Energy
* American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy
*
incandescent light bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
s. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses.
There are many motivations to improve energy efficiency. Decreasing energy use reduces energy costs and may result in a financial cost saving to consumers if the energy savings offset any additional costs of implementing an energy-efficient technology. Reducing energy use is also seen as a solution to the problem of minimizing greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
. Improved energy efficiency in buildings, industrial processes and transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipel ...
could reduce the world's energy needs in 2050 by one third, and help reduce global emissions of greenhouse gases. Another important solution is to remove government-led energy subsidies that promote high energy consumption and inefficient energy use in more than half of the countries in the world.
Energy efficiency and renewable energy are said to be the ''twin pillars'' of sustainable energy
Energy is sustainable if it "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". Most definitions of sustainable energy include considerations of environmental aspects such as green ...
policy
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an orga ...
and are high priorities in the sustainable energy hierarchy. In many countries energy efficiency is also seen to have a national security benefit because it can be used to reduce the level of energy imports from foreign countries and may slow down the rate at which domestic energy resources are depleted.
Overview
 Energy efficiency has proved to be a cost-effective strategy for building economies without necessarily increasing energy consumption. For example, the state of
Energy efficiency has proved to be a cost-effective strategy for building economies without necessarily increasing energy consumption. For example, the state of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
began implementing energy-efficiency measures in the mid-1970s, including building code and appliance standards with strict efficiency requirements. During the following years, California's energy consumption has remained approximately flat on a per capita basis while national US consumption doubled. As part of its strategy, California implemented a "loading order" for new energy resources that puts energy efficiency first, renewable electricity supplies second, and new fossil-fired power plants last. States such as Connecticut and New York have created quasi-public Green Banks
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combina ...
to help residential and commercial building-owners finance energy efficiency upgrades that reduce emissions and cut consumers' energy costs.
Lovin's Rocky Mountain Institute
RMI (Rocky Mountain Institute) is an organization in the United States co-founded by Amory Lovins dedicated to research, publication, consulting, and lecturing in the field of sustainability, with a focus on profitable innovations for energy a ...
points out that in industrial settings, "there are abundant opportunities to save 70% to 90% of the energy and cost for lighting, fan, and pump systems; 50% for electric motors; and 60% in areas such as heating, cooling, office equipment, and appliances." In general, up to 75% of the electricity used in the US today could be saved with efficiency measures that cost less than the electricity itself, the same holds true for home settings. The US Department of Energy has stated that there is potential for energy saving in the magnitude of 90 Billion kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bil ...
by increasing home energy efficiency.
Other studies have emphasized this. A report published in 2006 by the McKinsey Global Institute, asserted that "there are sufficient economically viable opportunities for energy-productivity improvements that could keep global energy-demand growth at less than 1 percent per annum"—less than half of the 2.2 percent average growth anticipated through 2020 in a business-as-usual scenario. Energy productivity, which measures the output and quality of goods and services per unit of energy input, can come from either reducing the amount of energy required to produce something, or from increasing the quantity or quality of goods and services from the same amount of energy.
The Vienna Climate Change Talks 2007 Report, under the auspices of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, clearly shows "that energy efficiency can achieve real emission reductions at low cost."
International standards ISO17743 and ISO17742 provide a documented methodology for calculating and reporting on energy savings and energy efficiency for countries and cities.
The energy intensity of a country or region, the ratio of energy use to Gross Domestic Product or some other measure of economic output", differs from its energy efficiency. Energy intensity is affected by climate, economic structure (e.g. services vs manufacturing), trade, as well as the energy efficiency of buildings, vehicles, and industry.
Benefits
From the point of view of an energy consumer, the main motivation of energy efficiency is often simply saving money by lowering the cost of purchasing energy. Additionally, from anenergy policy
Energy policy is the manner in which a given entity (often governmental) has decided to address issues of energy development including energy conversion, distribution and use as well as reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in order to cont ...
point of view, there has been a long trend in a wider recognition of energy efficiency as the "first fuel", meaning the ability to replace or avoid the consumption of actual fuels. In fact, International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, wit ...
has calculated that the application of energy efficiency measures in the years 1974-2010 has succeeded in avoiding more energy consumption in its member states than is the consumption of any particular fuel, including oil, coal and natural gas.International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, wit ...
Report on Multiple Benefits of Energy Efficiency
. OECD, Paris, 2014. Moreover, it has long been recognized that energy efficiency brings other benefits additional to the reduction of energy consumption. Some estimates of the value of these other benefits, often called multiple benefits, co-benefits, ancillary benefits or non-energy benefits, have put their summed value even higher than that of the direct energy benefits. These multiple benefits of energy efficiency include things such as reduced climate change impact, reduced air pollution and improved health, improved indoor conditions, improved energy security and reduction of the price risk for energy consumers. Methods for calculating the monetary value of these multiple benefits have been developed, including e.g. the choice experiment method for improvements that have a subjective component (such as aesthetics or comfort) and Tuominen-Seppänen method for price risk reduction. When included in the analysis, the economic benefit of energy efficiency investments can be shown to be significantly higher than simply the value of the saved energy.
Appliances
Modern appliances, such as, freezers, ovens, stoves, dishwashers, clothes washers and dryers, use significantly less energy than older appliances. Installing a clothesline will significantly reduce one's energy consumption as their dryer will be used less. Current energy-efficient refrigerators, for example, use 40 percent less energy than conventional models did in 2001. Following this, if all households in Europe changed their more than ten-year-old appliances into new ones, 20 billion kWh of electricity would be saved annually, hence reducing CO2 emissions by almost 18 billion kg. In the US, the corresponding figures would be 17 billion kWh of electricity and CO2. According to a 2009 study fromMcKinsey & Company
McKinsey & Company is a global management consulting firm founded in 1926 by University of Chicago professor James O. McKinsey, that offers professional services to corporations, governments, and other organizations. McKinsey is the oldest and ...
the replacement of old appliances is one of the most efficient global measures to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. Modern power management systems also reduce energy usage by idle appliances by turning them off or putting them into a low-energy mode after a certain time. Many countries identify energy-efficient appliances using energy input labeling.
The impact of energy efficiency on peak demand depends on when the appliance is used. For example, an air conditioner uses more energy during the afternoon when it is hot. Therefore, an energy-efficient air conditioner will have a larger impact on peak demand than off-peak demand. An energy-efficient dishwasher, on the other hand, uses more energy during the late evening when people do their dishes. This appliance may have little to no impact on peak demand.
Over the period 2001-2021, tech companies have replaced the traditional silicon switch in an electric circuit with quicker gallium nitride transistors to make new gadgets as energy efficient as feasible. Gallium nitride transistors are, however, more costly. This is a significant change in lowering the carbon footprint
A carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, place or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e). Greenhouse gases, including the carbon-containing gases carb ...
.
Building design
 Buildings are an important field for energy efficiency improvements around the world because of their role as a major energy consumer. However, the question of energy use in buildings is not straightforward as the indoor conditions that can be achieved with energy use vary a lot. The measures that keep buildings comfortable, lighting, heating, cooling and ventilation, all consume energy. Typically the level of energy efficiency in a building is measured by dividing energy consumed with the floor area of the building which is referred to as specific energy consumption or energy use intensity:
:
However, the issue is more complex as building materials have embodied energy in them. On the other hand, energy can be recovered from the materials when the building is dismantled by reusing materials or burning them for energy. Moreover, when the building is used, the indoor conditions can vary resulting in higher and lower quality indoor environments. Finally, overall efficiency is affected by the use of the building: is the building occupied most of the time and are spaces efficiently used — or is the building largely empty? It has even been suggested that for a more complete accounting of energy efficiency, specific energy consumption should be amended to include these factors:
:
Thus a balanced approach to energy efficiency in buildings should be more comprehensive than simply trying to minimize energy consumed. Issues such as quality of indoor environment and efficiency of space use should be factored in. Thus the measures used to improve energy efficiency can take many different forms. Often they include passive measures that inherently reduce the need to use energy, such as better insulation. Many serve various functions improving the indoor conditions as well as reducing energy use, such as increased use of natural light.
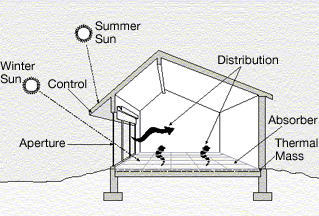
A building's location and surroundings play a key role in regulating its temperature and illumination. For example, trees, landscaping, and hills can provide shade and block wind. In cooler climates, designing northern hemisphere buildings with south facing windows and southern hemisphere buildings with north facing windows increases the amount of sun (ultimately heat energy) entering the building, minimizing energy use, by maximizing passive solar heating. Tight building design, including energy-efficient windows, well-sealed doors, and additional thermal insulation of walls, basement slabs, and foundations can reduce heat loss by 25 to 50 percent.
Dark roofs may become up to 39 °C (70 °F) hotter than the most reflective white surfaces. They transmit some of this additional heat inside the building. US Studies have shown that lightly colored roofs use 40 percent less energy for cooling than buildings with darker roofs. White roof systems save more energy in sunnier climates. Advanced electronic heating and cooling systems can moderate energy consumption and improve the comfort of people in the building.
Proper placement of windows and skylights as well as the use of architectural features that reflect light into a building can reduce the need for artificial lighting. Increased use of natural and task lighting has been shown by one study to increase productivity in schools and offices. Compact fluorescent lamps use two-thirds less energy and may last 6 to 10 times longer than
Buildings are an important field for energy efficiency improvements around the world because of their role as a major energy consumer. However, the question of energy use in buildings is not straightforward as the indoor conditions that can be achieved with energy use vary a lot. The measures that keep buildings comfortable, lighting, heating, cooling and ventilation, all consume energy. Typically the level of energy efficiency in a building is measured by dividing energy consumed with the floor area of the building which is referred to as specific energy consumption or energy use intensity:
:
However, the issue is more complex as building materials have embodied energy in them. On the other hand, energy can be recovered from the materials when the building is dismantled by reusing materials or burning them for energy. Moreover, when the building is used, the indoor conditions can vary resulting in higher and lower quality indoor environments. Finally, overall efficiency is affected by the use of the building: is the building occupied most of the time and are spaces efficiently used — or is the building largely empty? It has even been suggested that for a more complete accounting of energy efficiency, specific energy consumption should be amended to include these factors:
:
Thus a balanced approach to energy efficiency in buildings should be more comprehensive than simply trying to minimize energy consumed. Issues such as quality of indoor environment and efficiency of space use should be factored in. Thus the measures used to improve energy efficiency can take many different forms. Often they include passive measures that inherently reduce the need to use energy, such as better insulation. Many serve various functions improving the indoor conditions as well as reducing energy use, such as increased use of natural light.
A building's location and surroundings play a key role in regulating its temperature and illumination. For example, trees, landscaping, and hills can provide shade and block wind. In cooler climates, designing northern hemisphere buildings with south facing windows and southern hemisphere buildings with north facing windows increases the amount of sun (ultimately heat energy) entering the building, minimizing energy use, by maximizing passive solar heating. Tight building design, including energy-efficient windows, well-sealed doors, and additional thermal insulation of walls, basement slabs, and foundations can reduce heat loss by 25 to 50 percent.
Dark roofs may become up to 39 °C (70 °F) hotter than the most reflective white surfaces. They transmit some of this additional heat inside the building. US Studies have shown that lightly colored roofs use 40 percent less energy for cooling than buildings with darker roofs. White roof systems save more energy in sunnier climates. Advanced electronic heating and cooling systems can moderate energy consumption and improve the comfort of people in the building.
Proper placement of windows and skylights as well as the use of architectural features that reflect light into a building can reduce the need for artificial lighting. Increased use of natural and task lighting has been shown by one study to increase productivity in schools and offices. Compact fluorescent lamps use two-thirds less energy and may last 6 to 10 times longer than incandescent light bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
s. Newer fluorescent lights produce a natural light, and in most applications they are cost effective, despite their higher initial cost, with payback periods as low as a few months. LED lamps use only about 10% of the energy an incandescent lamp requires.
Effective energy-efficient building design can include the use of low cost passive infra reds to switch-off lighting when areas are unoccupied such as toilets, corridors or even office areas out-of-hours. In addition, lux levels can be monitored using daylight sensors linked to the building's lighting scheme to switch on/off or dim the lighting to pre-defined levels to take into account the natural light and thus reduce consumption. Building management systems link all of this together in one centralised computer to control the whole building's lighting and power requirements.
In an analysis that integrates a residential bottom-up simulation with an economic multi-sector model, it has been shown that variable heat gains caused by insulation and air-conditioning efficiency can have load-shifting effects that are not uniform on the electricity load. The study also highlighted the impact of higher household efficiency on the power generation capacity choices that are made by the power sector.
The choice of which space heating or cooling technology to use in buildings can have a significant impact on energy use and efficiency. For example, replacing an older 50% efficient natural gas furnace with a new 95% efficient one will dramatically reduce energy use, carbon emissions, and winter natural gas bills. Ground source heat pumps can be even more energy-efficient and cost-effective. These systems use pumps and compressors to move refrigerant fluid around a thermodynamic cycle in order to "pump" heat against its natural flow from hot to cold, for the purpose of transferring heat into a building from the large thermal reservoir contained within the nearby ground. The end result is that heat pumps typically use four times less electrical energy to deliver an equivalent amount of heat than a direct electrical heater does. Another advantage of a ground source heat pump is that it can be reversed in summertime and operate to cool the air by transferring heat from the building to the ground. The disadvantage of ground source heat pumps is their high initial capital cost, but this is typically recouped within five to ten years as a result of lower energy use.
Smart meter
A smart meter is an electronic device that records information such as consumption of electric energy, voltage levels, current, and power factor. Smart meters communicate the information to the consumer for greater clarity of consumption be ...
s are slowly being adopted by the commercial sector to highlight to staff and for internal monitoring purposes the building's energy usage in a dynamic presentable format. The use of power quality analysers can be introduced into an existing building to assess usage, harmonic distortion, peaks, swells and interruptions amongst others to ultimately make the building more energy-efficient. Often such meters communicate by using wireless sensor networks.
Green Building XML is an emerging scheme, a subset of the Building Information Modeling efforts, focused on green building design and operation. It is used as input in several energy simulation engines. But with the development of modern computer technology, a large number of building performance simulation tools are available on the market. When choosing which simulation tool to use in a project, the user must consider the tool's accuracy and reliability, considering the building information they have at hand, which will serve as input for the tool. Yezioro, Dong and Leite developed an artificial intelligence approach towards assessing building performance simulation results and found that more detailed simulation tools have the best simulation performance in terms of heating and cooling electricity consumption within 3% of mean absolute error.
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is a
green building certification program used worldwide. Developed by the non-profit U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), it includes a set of rating systems for the design, constructio ...
(LEED) is a rating system organized by the US Green Building Council (USGBC) to promote environmental responsibility in building design. They currently offer four levels of certification for existing buildings (LEED-EBOM) and new construction (LEED-NC) based on a building's compliance with the following criteria: Sustainable sites
Sustainable gardening includes the more specific sustainable landscapes, sustainable landscape design, sustainable landscaping, sustainable landscape architecture, resulting in sustainable sites. It comprises a disparate group of Horticulture, hor ...
, water efficiency, energy and atmosphere, materials and resources, indoor environmental quality, and innovation in design. In 2013, USGBC developed the LEED Dynamic Plaque, a tool to track building performance against LEED metrics and a potential path to recertification. The following year, the council collaborated with Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building technologies, performance ma ...
to pull data on energy and water use, as well as indoor air quality from a BAS to automatically update the plaque, providing a near-real-time view of performance. The USGBC office in Washington, D.C. is one of the first buildings to feature the live-updating LEED Dynamic Plaque.
A deep energy retrofit
A Deep energy retrofit (abbreviated as DER) can be broadly categorized as an energy conservation measure in an existing building also leading to an overall improvement in the building performance. While there is no exact definition for a deep ener ...
is a whole-building analysis and construction process that uses to achieve much larger energy savings than conventional energy retrofits. Deep energy retrofits can be applied to both residential and non-residential (“commercial”) buildings. A deep energy retrofit typically results in energy savings of 30 percent or more, perhaps spread over several years, and may significantly improve the building value. The Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The building was designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from " Empire State", the nickname of the ...
has undergone a deep energy retrofit process that was completed in 2013. The project team, consisting of representatives from Johnson Controls, Rocky Mountain Institute
RMI (Rocky Mountain Institute) is an organization in the United States co-founded by Amory Lovins dedicated to research, publication, consulting, and lecturing in the field of sustainability, with a focus on profitable innovations for energy a ...
, Clinton Climate Initiative, and Jones Lang LaSalle will have achieved an annual energy use reduction of 38% and $4.4 million. For example, the 6,500 windows were remanufactured onsite into superwindows which block heat but pass light. Air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling ...
operating costs on hot days were reduced and this saved $17 million of the project's capital cost immediately, partly funding other retrofitting. Receiving a gold Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) rating in September 2011, the Empire State Building is the tallest LEED certified building in the United States.
The Indianapolis City-County Building recently underwent a deep energy retrofit process, which has achieved an annual energy reduction of 46% and $750,000 annual energy saving.
Energy retrofits, including deep, and other types undertaken in residential, commercial or industrial locations are generally supported through various forms of financing or incentives. Incentives include pre-packaged rebates where the buyer/user may not even be aware that the item being used has been rebated or "bought down". "Upstream" or "Midstream" buy downs are common for efficient lighting products. Other rebates are more explicit and transparent to the end user through the use of formal applications. In addition to rebates, which may be offered through government or utility programs, governments sometimes offer tax incentives for energy efficiency projects. Some entities offer rebate and payment guidance and facilitation services that enable energy end use customers tap into rebate and incentive programs.
To evaluate the economic soundness of energy efficiency investments in buildings, cost-effectiveness analysis or CEA can be used. A CEA calculation will produce the value of energy saved, sometimes called '' negawatts'', in $/kWh. The energy in such a calculation is virtual in the sense that it was never consumed but rather saved due to some energy efficiency investment being made. Thus CEA allows comparing the price of negawatts with price of energy such as electricity from the grid or the cheapest renewable alternative. The benefit of the CEA approach in energy systems is that it avoids the need to guess future energy prices for the purposes of the calculation, thus removing the major source of uncertainty in the appraisal of energy efficiency investments.
Industry
Industries use a large amount of energy to power a diverse range of manufacturing and resource extraction processes. Many industrial processes require large amounts of heat and mechanical power, most of which is delivered asnatural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
, petroleum fuels, and electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
. In addition some industries generate fuel from waste products that can be used to provide additional energy.
Because industrial processes are so diverse it is impossible to describe the multitude of possible opportunities for energy efficiency in industry. Many depend on the specific technologies and processes in use at each industrial facility. There are, however, a number of processes and energy services that are widely used in many industries.
Various industries generate steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporizat ...
and electricity for subsequent use within their facilities. When electricity is generated, the heat that is produced as a by-product can be captured and used for process steam, heating or other industrial purposes. Conventional electricity generation is about 30% efficient, whereas combined heat and power (also called co-generation) converts up to 90 percent of the fuel into usable energy.
Advanced boilers and furnaces can operate at higher temperatures while burning less fuel. These technologies are more efficient and produce fewer pollutants.
Over 45 percent of the fuel used by US manufacturers is burnt to make steam. The typical industrial facility can reduce this energy usage 20 percent (according to the US Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United State ...
) by insulating steam and condensate return lines, stopping steam leakage, and maintaining steam traps.
Electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
s usually run at a constant speed, but a variable speed drive
Motor drive means a system that includes a motor. An adjustable speed motor drive means a system that includes a motor that has multiple operating speeds. A variable speed motor drive is a system that includes a motor and is continuously variabl ...
allows the motor's energy output to match the required load. This achieves energy savings ranging from 3 to 60 percent, depending on how the motor is used. Motor coils made of superconducting materials can also reduce energy losses. Motors may also benefit from voltage optimisation.
Industry uses a large number of pumps
A pump is a device that moves fluids ( liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method the ...
and compressors of all shapes and sizes and in a wide variety of applications. The efficiency of pumps and compressors depends on many factors but often improvements can be made by implementing better process control and better maintenance practices. Compressors are commonly used to provide compressed air which is used for sand blasting, painting, and other power tools. According to the US Department of Energy, optimizing compressed air systems by installing variable speed drives, along with preventive maintenance to detect and fix air leaks, can improve energy efficiency 20 to 50 percent.
Transportation

Automobiles
 The estimated energy efficiency for an automobile is 280 Passenger-Mile/106 Btu. There are several ways to enhance a vehicle's energy efficiency. Using improved
The estimated energy efficiency for an automobile is 280 Passenger-Mile/106 Btu. There are several ways to enhance a vehicle's energy efficiency. Using improved aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
to minimize drag can increase vehicle fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, ...
. Reducing vehicle weight can also improve fuel economy, which is why composite materials
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite, which is the common name) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or ...
are widely used in car bodies.
More advanced tires, with decreased tire to road friction and rolling resistance, can save gasoline. Fuel economy can be improved by up to 3.3% by keeping tires inflated to the correct pressure. Replacing a clogged air filter can improve a cars fuel consumption by as much as 10 percent on older vehicles. On newer vehicles (1980s and up) with fuel-injected, computer-controlled engines, a clogged air filter has no effect on mpg but replacing it may improve acceleration by 6-11 percent. Aerodynamics also aid in efficiency of a vehicle. The design of a car impacts the amount of gas needed to move it through air. Aerodynamics involves the air around the car, which can affect the efficiency of the energy expended.
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pr ...
s can increase fuel efficiency by allowing a smaller displacement engine. The 'Engine of the year 2011' is the Fiat TwinAir engine equipped with an MHI turbocharger. "Compared with a 1.2-liter 8v engine, the new 85 HP turbo has 23% more power and a 30% better performance index. The performance of the two-cylinder is not only equivalent to a 1.4-liter 16v engine, but fuel consumption is 30% lower."
Energy-efficient vehicles may reach twice the fuel efficiency of the average automobile. Cutting-edge designs, such as the diesel Mercedes-Benz Bionic
The Mercedes-Benz Bionic is a concept car created by DaimlerChrysler AG under the Mercedes Group. It was first introduced in 2005 at the DaimlerChrysler Innovation Symposium in Washington, D. C. The Bionic is modeled after a type of fish, the ...
concept vehicle have achieved a fuel efficiency as high as , four times the current conventional automotive average.
The mainstream trend in automotive efficiency is the rise of electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes c ...
s (all-electric or hybrid electric). Electric engines have more than double the efficiency of internal combustion engines. Hybrids, like the Toyota Prius
The is a car built by Toyota which has a hybrid drivetrain, combining an internal combustion engine with an electric motor. Initially offered as a four-door sedan, it has been produced only as a five-door liftback since 2003.
In 2007, t ...
, use regenerative braking to recapture energy that would dissipate in normal cars; the effect is especially pronounced in city driving. Plug-in hybrid
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external electric power source, in addition to internally by its on-board internal combustion engin ...
s also have increased battery capacity, which makes it possible to drive for limited distances without burning any gasoline; in this case, energy efficiency is dictated by whatever process (such as coal-burning, hydroelectric, or renewable source) created the power. Plug-ins can typically drive for around purely on electricity without recharging; if the battery runs low, a gas engine kicks in allowing for extended range. Finally, all-electric cars are also growing in popularity; the Tesla Model S sedan is the only high-performance all-electric car currently on the market.
Street lighting
Cities around the globe light up millions of streets with 300 million lights. Some cities are seeking to reducestreet light
A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distributio ...
power consumption by dimming lights during off-peak hours or switching to LED lamps. LED lamps are known to reduce the energy consumption by 50% to 80%.
Aircraft
There are several ways to improve aviation's use of energy through modifications aircraft and air traffic management. Aircraft improve with better aerodynamics, engines and weight. Seat density and cargo load factors contribute to efficiency. Air traffic management systems can allow automation of takeoff, landing, and collision avoidance, as well as within airports, from simple things like HVAC and lighting to more complex tasks such as security and scanning.Alternative fuels
 Alternative fuels, known as non-conventional or advanced
Alternative fuels, known as non-conventional or advanced fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy bu ...
s, are any materials or substances that can be used as fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy bu ...
s, other than conventional fuels. Some well known alternative fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy bu ...
s include biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil ...
, bioalcohol ( methanol, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a h ...
, butanol
Butanol (also called butyl alcohol) is a four-carbon alcohol with a formula of C4 H9 O H, which occurs in five isomeric structures (four structural isomers), from a straight-chain primary alcohol to a branched-chain tertiary alcohol; all are a ...
), chemically stored electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
(batteries and fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
s), hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, non-fossil methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
, non-fossil natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
, vegetable oil
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, ...
, and other biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms biom ...
sources. The production efficiency of these fuels greatly differs.
Energy conservation

Energy conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (f ...
is broader than energy efficiency in including active efforts to decrease energy consumption, for example through behaviour change, in addition to using energy more efficiently. Examples of conservation without efficiency improvements are heating a room less in winter, using the car less, air-drying your clothes instead of using the dryer, or enabling energy saving modes on a computer. As with other definitions, the boundary between efficient energy use and energy conservation can be fuzzy, but both are important in environmental and economic terms. This is especially the case when actions are directed at the saving of fossil fuels. Energy conservation is a challenge requiring policy programmes, technological development and behavior change to go hand in hand. Many energy intermediary organisations, for example governmental or non-governmental organisations on local, regional, or national level, are working on often publicly funded programmes or projects to meet this challenge. Psychologists have also engaged with the issue of energy conservation and have provided guidelines for realizing behavior change to reduce energy consumption while taking technological and policy considerations into account.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) maintains a comprehensive list of apps useful for energy efficiency.
Commercial property managers that plan and manage energy efficiency projects generally use a software platform to perform energy audits and to collaborate with contractors to understand their full range of options. ThDepartment of Energy (DOE) Software Directory
describes EnergyActio software, a cloud based platform designed for this purpose.
Rebound effect
If the demand for energy services remains constant, improving energy efficiency will reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions. However, many efficiency improvements do not reduce energy consumption by the amount predicted by simple engineering models. This is because they make energy services cheaper, and so consumption of those services increases. For example, since fuel efficient vehicles make travel cheaper, consumers may choose to drive farther, thereby offsetting some of the potential energy savings. Similarly, an extensive historical analysis of technological efficiency improvements has conclusively shown that energy efficiency improvements were almost always outpaced by economic growth, resulting in a net increase in resource use and associated pollution. These are examples of the direct rebound effect.The Rebound Effect: an assessment of the evidence for economy-wide energy savings from improved energy efficiencypp. v-vi. Estimates of the size of the rebound effect range from roughly 5% to 40%. The rebound effect is likely to be less than 30% at the household level and may be closer to 10% for transport. A rebound effect of 30% implies that improvements in energy efficiency should achieve 70% of the reduction in energy consumption projected using engineering models. Saunders et al. showed in 2010 that lighting has accounted for about 0.7% of GDP across many societies and hundreds of years, implying a rebound effect of 100%. However, some of the authors argue in a followup paper that increased lighting generally increases economic welfare and has substantial benefits. A 2014 study has shown the rebound effect to be rather low for household lighting, in particular for high use bulbs.
Sustainable energy
Energy efficiency and renewable energy are considered as main elements in sustainableenergy policy
Energy policy is the manner in which a given entity (often governmental) has decided to address issues of energy development including energy conversion, distribution and use as well as reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in order to cont ...
. Both strategies must be developed concurrently in order to stabilize and reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Efficient energy use is essential to slowing the energy demand growth so that rising clean energy supplies can make deep cuts in fossil fuel use. If energy use grows too rapidly, renewable energy development will chase a receding target. Likewise, unless clean energy supplies come online rapidly, slowing demand growth will only begin to reduce total carbon emissions; a reduction in the carbon content of energy sources is also needed. A sustainable energy economy thus requires major commitments to both efficiency and renewables.
By country or region
Europe
 Energy efficiency targets for 2020 and 2030.
The first EU-wide energy efficiency target was set in 1998. Member states agreed to improve energy efficiency by 1 percent a year over twelve years. In addition, legislation about products, industry, transport and buildings has contributed to a general energy efficiency framework. More effort is needed to address heating and cooling: there is more heat wasted during electricity production in Europe than is required to heat all buildings in the continent. All in all, EU energy efficiency legislation is estimated to deliver savings worth the equivalent of up to 326 million tons of oil per year by 2020.
The EU set itself a 20% energy savings target by 2020 compared to 1990 levels, but member states decide individually how energy savings will be achieved. At an EU summit in October 2014, EU countries agreed on a new energy efficiency target of 27% or greater by 2030. One mechanism used to achieve the target of 27% is the 'Suppliers Obligations & White Certificates'. The ongoing debate around the 2016 Clean Energy Package also puts an emphasis on energy efficiency, but the goal will probably remain around 30% greater efficiency compared to 1990 levels. Some have argued that this will not be enough for the EU to meet its Paris Agreement goals of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 40% compared to 1990 levels.
Important organisations and programs:
* Building energy rating
*
Energy efficiency targets for 2020 and 2030.
The first EU-wide energy efficiency target was set in 1998. Member states agreed to improve energy efficiency by 1 percent a year over twelve years. In addition, legislation about products, industry, transport and buildings has contributed to a general energy efficiency framework. More effort is needed to address heating and cooling: there is more heat wasted during electricity production in Europe than is required to heat all buildings in the continent. All in all, EU energy efficiency legislation is estimated to deliver savings worth the equivalent of up to 326 million tons of oil per year by 2020.
The EU set itself a 20% energy savings target by 2020 compared to 1990 levels, but member states decide individually how energy savings will be achieved. At an EU summit in October 2014, EU countries agreed on a new energy efficiency target of 27% or greater by 2030. One mechanism used to achieve the target of 27% is the 'Suppliers Obligations & White Certificates'. The ongoing debate around the 2016 Clean Energy Package also puts an emphasis on energy efficiency, but the goal will probably remain around 30% greater efficiency compared to 1990 levels. Some have argued that this will not be enough for the EU to meet its Paris Agreement goals of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 40% compared to 1990 levels.
Important organisations and programs:
* Building energy rating
* Eco-Design of Energy-Using Products Directive
The European Union's Ecodesign Directive (Directive 2009/125/EC) establishes a framework to set mandatory ecological requirements for energy-using and energy-related products sold in all 27 member states. Its scope currently covers more than 40 pr ...
* Energy efficiency in Europe (study)
* Orgalime
Orgalim (derived originally from the French Organisme de Liaison des Industries Métalliques Européennes) represents Europe's technology industries, comprising 770,000 companies spanning the mechanical, electrical and electronics, and metal techn ...
, the European engineering industries association
Germany
Energy efficiency is central toenergy policy
Energy policy is the manner in which a given entity (often governmental) has decided to address issues of energy development including energy conversion, distribution and use as well as reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in order to cont ...
in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
.
As of late 2015, national policy includes the following efficiency and consumption targets (with actual values for 2014):
Recent progress toward improved efficiency has been steady aside from the financial crisis of 2007–08
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline o ...
.
Some however
 believe energy efficiency is still under-recognised in terms of its contribution to Germany's energy transformation (or ''
believe energy efficiency is still under-recognised in terms of its contribution to Germany's energy transformation (or ''Energiewende
The ''Energiewende'' (; ) is the ongoing transition by Germany to a low carbon, environmentally sound, reliable, and affordable energy supply. The new system intends to rely heavily on renewable energy (particularly wind, photovoltaics, and ...
'').
Efforts to reduce final energy consumption in transport sector have not been successful, with a growth of 1.7% between 2005–2014. This growth is due to both road passenger and road freight transport. Both sectors increased their overall distance travelled to record the highest figures ever for Germany. Rebound effects played a significant role, both between improved vehicle efficiency and the distance travelled, and between improved vehicle efficiency and an increase in vehicle weights and engine power.
On 3 December 2014, the German federal government released its National Action Plan on Energy Efficiency (NAPE).
The areas covered are the energy efficiency of buildings, energy conservation for companies, consumer energy efficiency, and transport energy efficiency. The policy contains both immediate and forward-looking measures. The central short-term measures of NAPE include the introduction of competitive tendering for energy efficiency, the raising of funding for building renovation, the introduction of tax incentives for efficiency measures in the building sector, and the setting up energy efficiency networks together with business and industry. German industry is expected to make a sizeable contribution.
On 12 August 2016, the German government released a green paper on energy efficiency for public consultation (in German).
It outlines the potential challenges and actions needed to reduce energy consumption in Germany over the coming decades. At the document's launch, economics and energy minister Sigmar Gabriel said "we do not need to produce, store, transmit and pay for the energy that we save". The green paper prioritizes the efficient use of energy as the "first" response and also outlines opportunities for sector coupling, including using renewable power for heating and transport. Other proposals include a flexible energy tax which rises as petrol prices fall, thereby incentivizing fuel conservation despite low oil prices.
Poland
In May 2016 Poland adopted a new Act on Energy Efficiency, to enter into force on 1October 2016.Australia
The Australian national government is actively leading the country in efforts to increase their energy efficiency, mainly through the government's Department of Industry and Science. In July 2009, the Council of Australian Governments, which represents the individual states and territories of Australia, agreed to a National Strategy on Energy Efficiency (NSEE). This is a ten-year plan accelerating the implementation of a nationwide adoption of energy-efficient practices and a preparation for the country's transformation into a low carbon future. There are several different areas of energy use addressed within the NSEE. But, the chapter devoted to the approach on energy efficiency that is to be adopted on a national level stresses four points in achieving stated levels of energy efficiency: * To help households and businesses transition to a low carbon future * To streamline the adoption of efficient energy * To make buildings more energy-efficient * For governments to work in partnership and lead the way to energy efficiency The overriding agreement that governs this strategy is the National Partnership Agreement on Energy Efficiency. This document also explains the role of both thecommonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with " republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from th ...
and the individual states and territories in the NSEE, as well provides for the creation of benchmarks and measurement devices which will transparently show the nation's progress in relation to the stated goals, and addresses the need for funding of the strategy in order to enable it to move forward.
Departments and events:
* Department of Climate Change and Energy Efficiency
* Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts
* Sustainable House Day
Sustainable House Day is a national event held annually across Australia, where households open their doors to the public to give interested people the chance to learn about the benefits of energy efficiency, renewable energy and sustainable design ...
Canada
In August 2017, the Government of Canada releaseBuild Smart - Canada's Buildings Strategy
as a key driver of the Pan-Canadian Framework on Clean Growth and Climate Change, Canada's national climate strategy. The Build Smart strategy seeks to dramatically increase the energy-efficiency performance of existing and new Canadian buildings, and establishes five goals to that end: *Federal, provincial, and territorial governments will work to develop and adopt increasingly stringent model building codes, starting in 2020, with the goal that provinces and territories adopt a “ net-zero energy ready” model building code by 2030. *Federal, provincial, and territorial governments will work to develop a model code for existing buildings by 2022, with the goal that provinces and territories adopt the code. *Federal, provincial, and territorial governments will work together with the aim of requiring labelling of building energy use by as early as 2019. *The federal government will set new standards for heating equipment and other key technologies to the highest level of efficiency that is economically and technically achievable. *Provincial and territorial governments will work to sustain and expand efforts to retrofit existing buildings by supporting energy efficiency improvements and by accelerating the adoption of high-efficiency equipment while tailoring their programs to regional circumstances. The strategy details a range of activities the Government of Canada will pursue, and investments it will make, in support of the goals. As of early 2018, only one of Canada's 10 provinces and three territories, British Columbia, has developed a policy in support of federal government's goal to reach net zero energy ready ambitions: the BC Energy Step Code. Local British Columbia governments may use the BC Energy Step Code, if they wish, to incentivize or require a level of energy efficiency in new construction that goes above and beyond the requirements of the base building code. The regulation and standard is designed as a technical roadmap to help the province reach its target that all new buildings will attain a net zero energy ready level of performance by 2032.
United States
The United States is the second-largest single consumer of energy in the world. The U.S. Department of Energy categorizes national energy use in four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial, and industrial. A 2011 Energy Modeling Forum study covering the United States examines how energy efficiency opportunities will shape future fuel and electricity demand over the next several decades. The US economy is already set to lower its energy and carbon intensity, but explicit policies will be necessary to meet climate goals. These policies include: acarbon tax
A carbon tax is a tax levied on the carbon emissions required to produce goods and services. Carbon taxes are intended to make visible the "hidden" social costs of carbon emissions, which are otherwise felt only in indirect ways like more s ...
, mandated standards for more efficient appliances, buildings and vehicles, and subsidies or reductions in the upfront costs of new more energy-efficient equipment.
 Programs and organisations:
* Alliance to Save Energy
* American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy
*
Programs and organisations:
* Alliance to Save Energy
* American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy
* Building Codes Assistance Project
The Building Codes Assistance Project (BCAP) is a non-profit organization that advocates for the adoption, implementation, and advancement of building energy codes. It was established in 1994 as a joint initiative of the Alliance to Save Energy (A ...
* Building Energy Codes Program The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE's) Building Energy Codes Program (BECP) was established in 1991 (originally called the Building Standards and Guidelines Program), with its activities defined by the Energy Conservation and Production Act (EC ...
* Consortium for Energy Efficiency
* Energy Star, from United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
* Industrial Assessment Center
There are 31 Industrial Assessment Centers in the United States as of June 2021. These centers are located at universities across the US, and are funded by the United States Department of Energy (DOE) to spread ideas relating to industrial energy ...
* National Electrical Manufacturers Association
* Rocky Mountain Institute
RMI (Rocky Mountain Institute) is an organization in the United States co-founded by Amory Lovins dedicated to research, publication, consulting, and lecturing in the field of sustainability, with a focus on profitable innovations for energy a ...
See also
* Carbon offset * Data center infrastructure efficiency *Distributed generation
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred t ...
*
* Energy audit
* Energy conservation measures
* Energy conversion efficiency
* Energy efficiency implementation
* Energy recovery
* Energy resilience
*Energy security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to (relatively) cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven ...
* Energy storage as a service (ESaaS)
*EU Energy Efficiency Directive 2012/27/EU
The Energy Efficiency Directive 2012/27/EU (abbreviated EED) is a European Union directive which mandates energy efficiency improvements within the European Union.
It was approved on 25 October 2012 and entered into force on 4 December 201 ...
* European Union energy label
* Performance per watt
* Lee Schipper
*List of energy storage projects
This is a list of energy storage power plants worldwide, other than pumped hydro storage.
Many individual energy storage plants augment electrical grids by capturing excess electrical energy during periods of low demand and storing it in o ...
* List of least carbon efficient power stations
* Peak oil
* Renewable heat
* Standby power
* The Green Deal
*World Energy Engineering Congress The World Energy Engineering Congress (WEEC) is an international energy industry conference and exposition hosted annually by the Association of Energy Engineers.
Professionals in the field of energy engineering from around the world convene annu ...
*Energy Reduction Assets
Energy Reduction Assets (ERAs) are revenue streams that are created by tracking the unspent portion of traditional energy usage.
The reduction of expected energy use is a potential revenue source that may be manipulated to improve business perfor ...
International programs:
* 80 Plus
* 2000-watt society
The 2000-watt society is an environmental vision, first introduced in 1998 by the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zürich (ETH Zurich), which pictures the average First World citizen reducing their overall average primary energy usage ra ...
* IEA Solar Heating & Cooling Implementing Agreement Task 13
* International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, wit ...
* International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and ...
* International Partnership for Energy Efficiency Cooperation
* World Sustainable Energy Days
The World Sustainable Energy Days is an annual sustainability conference held in Austria. It hosts events centred on sustainable energy production and use, which covers energy efficiency and renewable energy sources for buildings, industry and tra ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Efficient Energy Use Energy efficiency Energy policy Industrial ecology Sustainable energy es:Mitigación del cambio climático#Eficiencia energética y conservación