|
Major Hours
In Christianity, the Little Hours or minor hours are the canonical hours other than the three major hours. In the Syriac Orthodox Church and the Indian Orthodox Church, two denominations in Oriental Orthodox Christianity, these fixed prayer times are known as 3rd hour prayer ( Tloth sho`in am, 6th hour prayer ( Sheth sho`in 2 pm, and 9th hour prayer ( Tsha' sho`in pm. In the Catholic Church, since the reform of the Liturgy of the Hours mandated by the Second Vatican Council, they are called the office of readings, morning prayer and evening prayer. The minor hours, so called because their structure is shorter and simpler than that of the major hours, are those celebrated between lauds and vespers (morning and evening prayer) together with compline (night prayer). The major hours are those whose traditional names are matins, lauds and vespers. History From the time of the early Church, the practice of seven fixed prayer times have been taught; in ''Apostolic Tradition'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostolic Tradition
The ''Apostolic Tradition'' (or ''Egyptian Church Order'') is an early Christian treatise which belongs to the genre of the ancient Church Orders. It has been described to be of "incomparable importance as a source of information about church life and liturgy in the third century". Rediscovered in the 19th century, it was given the name of "Egyptian Church Order". In the first half of the 20th century this text was commonly identified with the lost ''Apostolic Tradition'' presumed to have been written by Hippolytus of Rome. Due to this attribution, and the apparent early date of the text, ''Apostolic Tradition'' played a crucial role in the liturgical reforms of many mainstream Christian bodies. The attribution of the text to Hippolytus has since become a subject of continued debate in recent scholarship. If the ''Apostolic Tradition'' is the work of Hippolytus of Rome, it would be dated before 235 AD (when Hippolytus is believed to have suffered martyrdom) and its origin would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICEL
The International Commission on English in the Liturgy (ICEL) is a commission set up by a number of episcopal conferences of English-speaking countries for the purpose of providing English translations of the liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the originals of which are in Latin. Decisions to adopt these translations are made by the episcopal conference of the country concerned,"It is for the competent territorial ecclesiastical authority mentioned in Art. 22, 2, to decide whether, and to what extent, the vernacular language is to be used; their decrees are to be approved, that is, confirmed, by the Apostolic See. And, whenever it seems to be called for, this authority is to consult with bishops of neighbouring regions which have the same language. Translations from the Latin text into the mother tongue intended for use in the liturgy must be approved by the competent territorial ecclesiastical authority mentioned above"''Sacrosanctum Concilium'', Second Vatican Council, Constitut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime (liturgy)
Prime, or the First Hour, is one of the canonical hours of the Divine Office, said at the first hour of daylight (6:00 a.m. at the equinoxes but earlier in summer, later in winter), between the dawn hour of Lauds and the 9 a.m. hour of Terce. It remains part of the Christian liturgies of Eastern Christianity, but in the Latin Rite it was suppressed by the Second Vatican Council. In the Coptic Church, a denomination of Oriental Orthodox Christianity, the office of Prime is prayed at 6 am in eastward direction of prayer by all members in this denomination, both clergy and laity, being one of the seven fixed prayer times. Roman Catholic clergy under obligation to celebrate the Liturgy of the Hours may still fulfil their obligation by using the edition of the Roman Breviary promulgated by Pope John XXIII in 1962, which contains Prime. Like all the liturgical hours, except the Office of Readings, it consists mainly of Psalms. It is one of the Little Hours. Name From the time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–63 (see ''Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites that survived into the 20th century were abandoned voluntarily after the Second Vatican Council. The Roman Rite is now the most widespread liturgical rite not only in the Catholic Church but in Christianity as a whole. The Roman Rite has been adapted through the centuries and the history of its Eucharistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
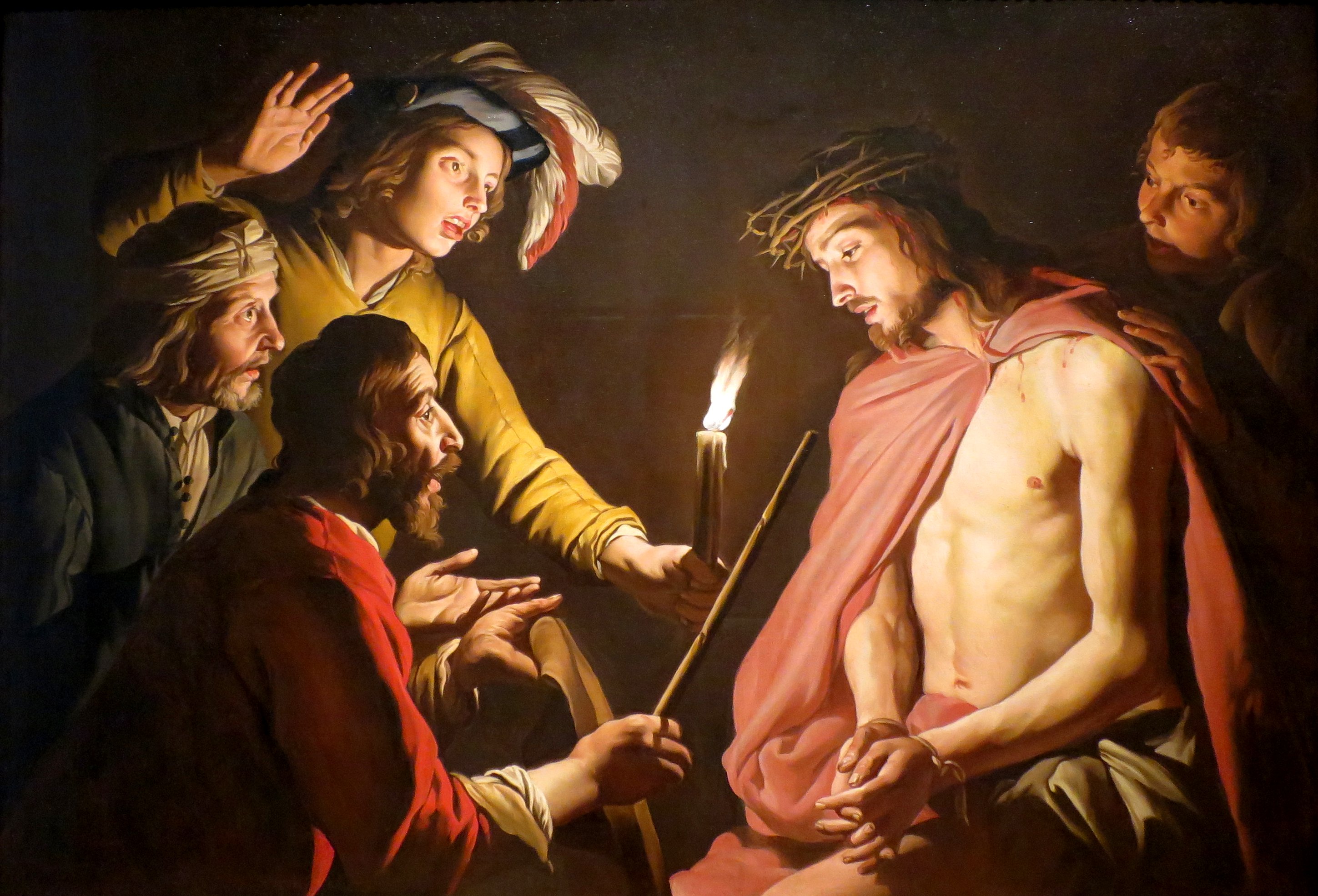
Passion Of Jesus
In Christianity, the Passion (from the Latin verb ''patior, passus sum''; "to suffer, bear, endure", from which also "patience, patient", etc.) is the short final period in the life of Jesus Christ. Depending on one's views, the "Passion" may include, among other events, Jesus' triumphal entry into Jerusalem, his cleansing of the Temple, his anointing, the Last Supper, Jesus' agony in the Garden, his arrest, his Sanhedrin trial, his trial before Pontius Pilate, his crucifixion and his death on Good Friday, his burial, and the resurrection of Jesus. Those parts of the four canonical Gospels that describe these events are known as the "Passion narratives". In some Christian communities, commemoration of the Passion also includes remembrance of the sorrow of Mary, the mother of Jesus, on the Friday of Sorrows. The word ''passion'' has taken on a more general application and now may also apply to accounts of the suffering and death of Christian martyrs, sometimes using the Lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acts Of The Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its message to the Roman Empire. It gives an account of the ministry and activity of Christ's apostles in Jerusalem and other regions, after Christ's death, resurrection, and ascension. Acts and the Gospel of Luke make up a two-part work, Luke–Acts, by the same anonymous author. It is usually dated to around 80–90 AD, although some scholars suggest 90–110. The first part, the Gospel of Luke, tells how God fulfilled his plan for the world's salvation through the life, death, and resurrection of Jesus of Nazareth. Acts continues the story of Christianity in the 1st century, beginning with the ascension of Jesus to Heaven. The early chapters, set in Jerusalem, describe the Day of Pentecost (the coming of the Holy Spirit) and the growth of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, "Historically, the religious and ethnic dimensions of Jewish identity have been closely interwoven. In fact, so closely bound are they, that the traditional Jewish lexicon hardly distinguishes between the two concepts. Jewish religious practice, by definition, was observed exclusively by the Jewish people, and notions of Jewish peoplehood, nation, and community were suffused with faith in the Jewish God, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
None (liturgy)
Nones (), also known as None ( la, Nona, "Ninth"), the Ninth Hour, or the Midafternoon Prayer, is a fixed time of prayer of the Divine Office of almost all the traditional Christian liturgies. It consists mainly of psalms and is said around 3 pm, about the ninth hour after dawn. In the Roman Rite the Nones it is one of the so-called "little hours". In the Oriental Orthodox Churches, such as the Coptic Orthodox Church, Ethiopian Orthodox Church and Indian Orthodox Church, it is one of the seven fixed prayer times to be recited by all Christians. History Origin According to an Ancient Greek and Roman custom, the day was, like the night, divided into four parts, each consisting of three hours. Among the ancients the hour of Nones was regarded as the close of the day's business and the time for the baths and supper. This division of the day was in vogue also among the Jews, from whom the Church borrowed it. In addition to Morning and Evening Prayer to accompany the sacrifices, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sext
Sext, or Sixth Hour, is a canonical hour of the Divine Office of almost all the traditional Christian liturgies. It consists mainly of psalms and is held around noon. Its name comes from Latin and refers to the sixth hour of the day after dawn. With Terce, None and Compline it belongs to the so-called "Little hours". In Oriental Orthodox Christianity and Oriental Protestant Christianity, the office is prayed at 12 pm, being known as Sheth sho`in in the Syriac and Indian traditions; it is prayed facing the eastward direction of prayer by all members in these denominations, both clergy and laity, being one of the seven fixed prayer times. History The ''hora sexta'' of the Romans corresponded closely with our noon. Among the Jews it was already regarded, together with Terce and None, as an hour most favourable to prayer. In the Acts of the Apostles we read that St. Peter went up to the higher parts of the house to pray (). It was the middle of the day, also the usual hour o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terce
Terce is a canonical hour of the Divine Office. It consists mainly of psalms and is held around 9 a.m. Its name comes from Latin and refers to the third hour of the day after dawn. With Sext, None and Compline it belongs to the so-called "Little hours". Origin From the time of the early Church, the practice of seven fixed prayer times have been taught; in '' Apostolic Tradition'', Hippolytus instructed Christians to pray seven times a day "on rising, at the lighting of the evening lamp, at bedtime, at midnight" and "the third, sixth and ninth hours of the day, being hours associated with Christ's Passion." This practice of seven fixed prayer times continues today in many Christian denominations. The origin of Terce, like that of Sext and None, to which it bears a close relationship, dates back to Apostolic times. According to an ancient custom of the Romans and Greeks, the day and night respectively were divided into four parts of about three hours each. The second division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived from the Greek translation, (), meaning "instrumental music" and, by extension, "the words accompanying the music". The book is an anthology of individual Hebrew religious hymns, with 150 in the Jewish and Western Christian tradition and more in the Eastern Christian churches. Many are linked to the name of David, but modern mainstream scholarship rejects his authorship, instead attributing the composition of the psalms to various authors writing between the 9th and 5th centuries BC. In the Quran, the Arabic word ‘Zabur’ is used for the Psalms of David in the Hebrew Bible. Structure Benedictions The Book of Psalms is divided into five sections, each closing with a doxology (i.e., a benediction). These divisions were probably intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

