|
Myocardial Infarction Complications
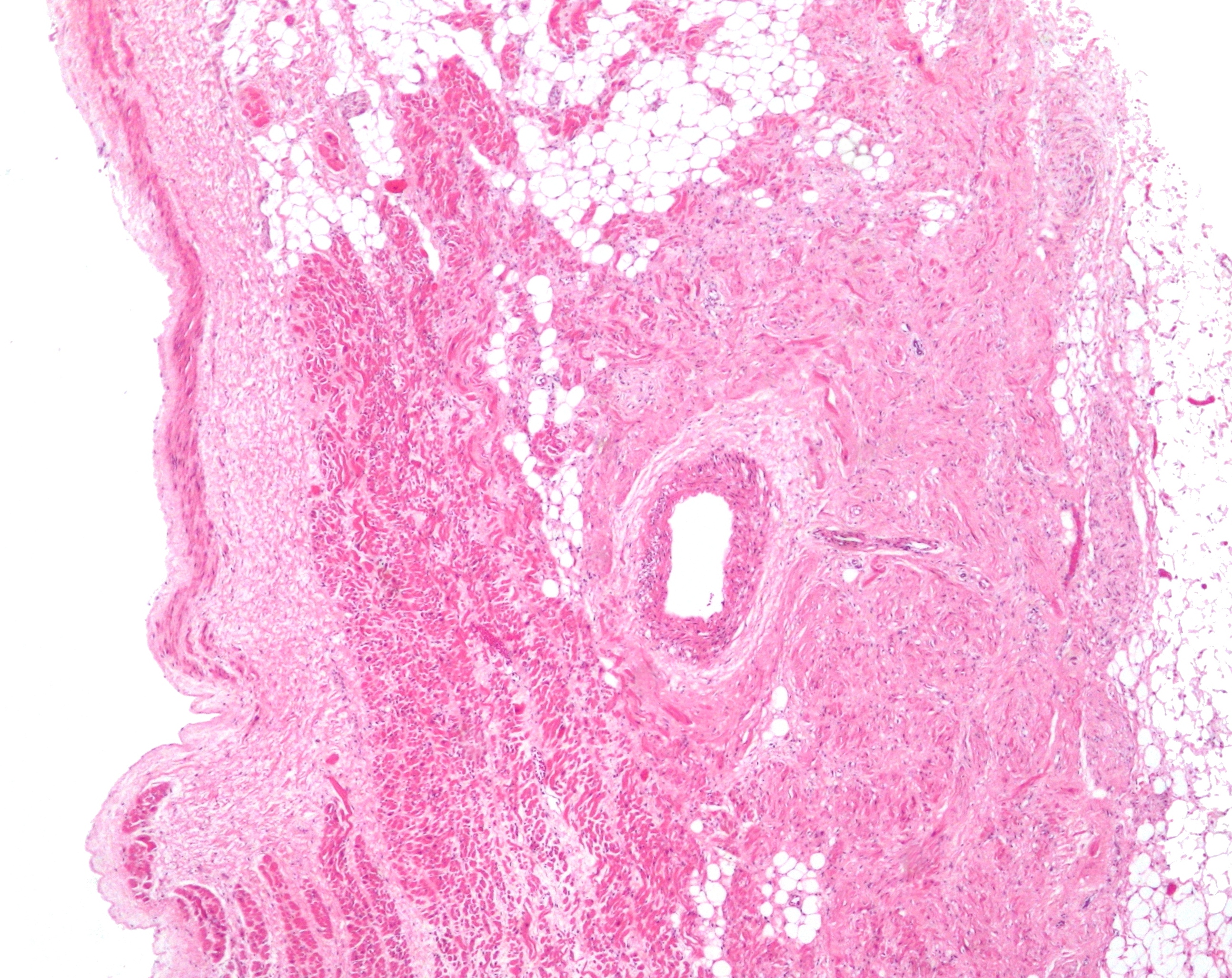
Myocardial infarction complications may occur immediately following a heart attack (in the acute phase), or may need time to develop (a chronic problem). After an infarction, an obvious complication is a second infarction, which may occur in the domain of another atherosclerotic coronary artery, or in the same zone if there are any live cells left in the infarct. Post-myocardial complications occur after a period of ischemia, these changes can be seen in gross tissue changes and microscopic changes. Necrosis begins after 20 minutes of an infarction. Under 4 hours of ischemia, there are no gross or microscopic changes noted.Kumar, V., Abbas, A. K., & Aster, J. C. (2015). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (Ninth edition.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. From 4-24 hours coagulative necrosis begins to be seen, which is characterized by the removal of dead cardiomyocytes through heterolysis and the nucleus through karyorrhexis, karyolysis, and pyknosis. On gross exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Septal Defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes. The membranous portion, which is close to the atrioventricular node, is most commonly affected in adults and older children in the United States. It is also the type that will most commonly require surgical intervention, comprising over 80% of cases. Membranous ventricular septal defects are more common than muscular ventricular septal defects, and are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly. Signs and symptoms Ventricular septal defect is usually symptomless at birth. It usually manifests a few weeks after birth. VSD is an acyanotic congenital heart defect, aka a lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dressler's Syndrome
Dressler syndrome is a secondary form of pericarditis that occurs in the setting of injury to the heart or the pericardium (the outer lining of the heart). It consists of fever, pleuritic pain, pericarditis and/or a pericardial effusion. Dressler syndrome is also known as postmyocardial infarction syndrome and the term is sometimes used to refer to post-pericardiotomy pericarditis. It was first characterized by William Dressler at Maimonides Medical Center in 1956. It should not be confused with the Dressler's syndrome of haemoglobinuria named for Lucas Dressler, who characterized it in 1854. Presentation Dressler syndrome was historically a phenomenon complicating about 7% of myocardial infarctions, but in the era of percutaneous coronary intervention, it is very uncommon. The disease consists of a persistent low-grade fever, chest pain (usually pleuritic), pericarditis (usually evidenced by a pericardial friction rub, chest pain worsening when recumbent, and diffuse ST elev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe when sitting up and more severe when lying down or breathing deeply. Other symptoms of pericarditis can include fever, weakness, palpitations, and shortness of breath. The onset of symptoms can occasionally be gradual rather than sudden. The cause of pericarditis often remains unknown but is believed to be most often due to a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infections such as tuberculosis, uremic pericarditis, heart attack, cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chest trauma. Diagnosis is based on the presence of chest pain, a pericardial rub, specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, and fluid around the heart. A heart attack may produce similar symptoms to pericarditis. Treatment in most cases is with NSAIDs and possibly the ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinoatrial Node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approximately fifteen mm long, three mm wide, and one mm thick, located directly below and to the side of the superior vena cava. These cells can produce an electrical impulse an action potential known as a cardiac action potential that travels through the electrical conduction system of the heart, causing it to contract. In a healthy heart, the SA node continuously produces action potentials, setting the rhythm of the heart (sinus rhythm), and so is known as the heart's natural pacemaker. The rate of action potentials produced (and therefore the heart rate) is influenced by the nerves that supply it. Structure The sinoatrial node is a oval-shaped structure that is approximately fifteen mm long, three mm wide, and one mm thick, located directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Degree Heart Block
Third-degree atrioventricular block (AV block) is a medical condition in which the electrical impulse generated in the sinoatrial node (SA node) in the atrium of the heart can not propagate to the ventricles. Because the impulse is blocked, an accessory pacemaker in the lower chambers will typically activate the ventricles. This is known as an ''escape rhythm''. Since this accessory pacemaker also activates independently of the impulse generated at the SA node, two independent rhythms can be noted on the electrocardiogram (ECG). * The P waves with a regular P-to-P interval (in other words, a sinus rhythm) represent the first rhythm. * The QRS complexes with a regular R-to-R interval represent the second rhythm. The PR interval will be variable, as the hallmark of complete heart block is the lack of any apparent relationship between P waves and QRS complexes. Presentation People with third-degree AV block typically experience severe bradycardia (an abnormally low measured heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conduction System Of The Heart
The cardiac conduction system (CCS) (also called the electrical conduction system of the heart) transmits the signals generated by the sinoatrial node – the heart's pacemaker, to cause the heart muscle to contract, and pump blood through the body's circulatory system. The pacemaking signal travels through the right atrium to the atrioventricular node, along the bundle of His, and through the bundle branches to Purkinje fibers in the walls of the ventricles. The Purkinje fibers transmit the signals more rapidly to stimulate contraction of the ventricles. The conduction system consists of specialized heart muscle cells, situated within the myocardium. There is a skeleton of fibrous tissue that surrounds the conduction system which can be seen on an ECG. Dysfunction of the conduction system can cause irregular heart rhythms including rhythms that are too fast or too slow. Structure Electrical signals arising in the SA node (located in the right atrium) stimulate the atr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
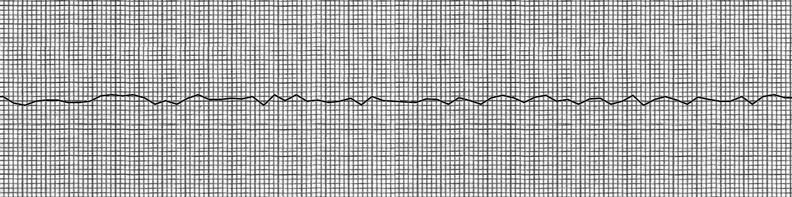
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by sudden cardiac death in the absence of treatment. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10% of people with cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation can occur due to coronary heart disease, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, Brugada syndrome, long QT syndrome, electric shock, or intracranial hemorrhage. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing irregular unformed QRS complexes without any clear P waves. An important differential diagnosis is torsades de pointes. Treatment is with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation. Biphasic defibrillation may be better than monophasic. The medication epinephrine or amiodarone may be given if initial treatments are not effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
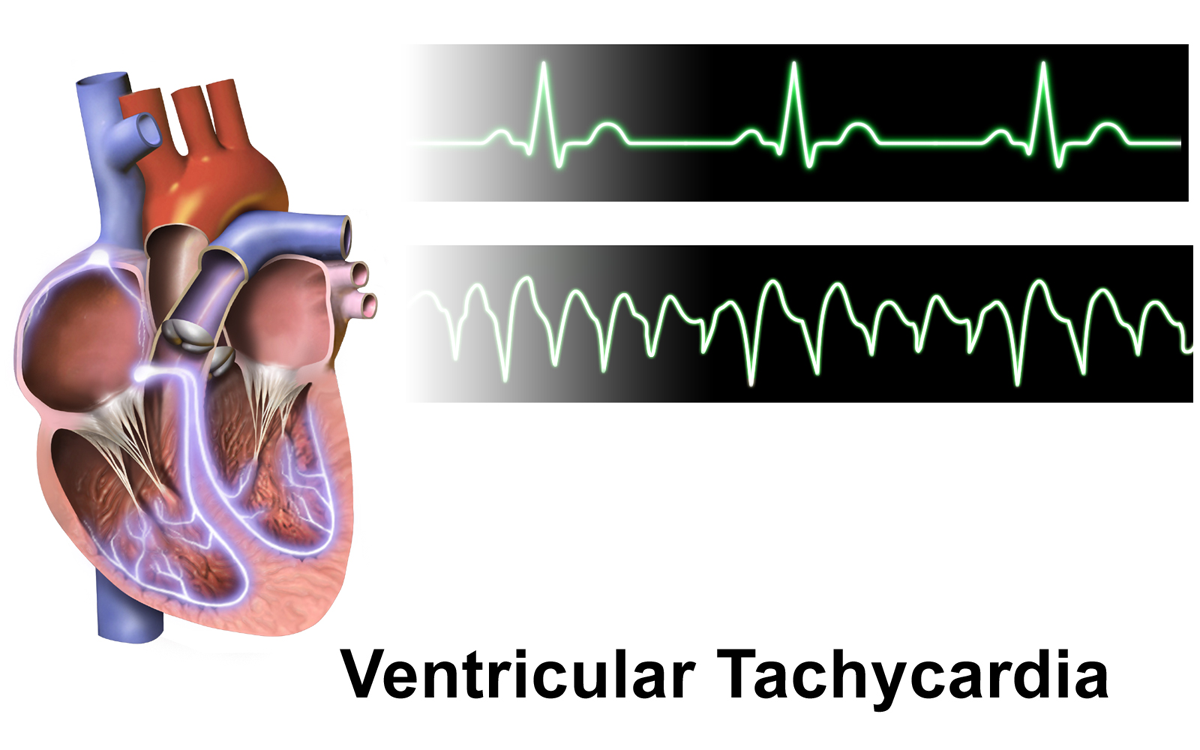
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, or chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte problems, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing a rate of greater than 120 beats per minute and at least three wide QRS complexes in a row. It is classified as non-sustained versus sustained based on whether it lasts le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)