 |
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic
Mothers against decapentaplegic is a protein from the SMAD family that was discovered in ''Drosophila''. During ''Drosophila'' research, it was found that a mutation in the gene in the mother repressed the gene decapentaplegic in the embryo. The phrase "Mothers against" was added as a humorous take-off on organizations opposing various issues e.g. Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD); and based on a tradition of such unusual naming within the gene research community. Several human homologues are known: * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 5 * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 6 * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 9 Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 9 also known as SMAD9, SMAD8, and MADH6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Protein SMAD2 PDB 1dev
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
SMAD (protein)
Smads (or SMADs) comprise a family of structurally similar proteins that are the main signal transducers for receptors of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-B) superfamily, which are critically important for regulating cell development and growth. The abbreviation refers to the homologies to the ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' SMA ("small" worm phenotype) and MAD family ("Mothers Against Decapentaplegic") of genes in Drosophila. There are three distinct sub-types of Smads: receptor-regulated Smads ( R-Smads), common partner Smads (Co-Smads), and inhibitory Smads ( I-Smads). The eight members of the Smad family are divided among these three groups. Trimers of two receptor-regulated SMADs and one co-SMAD act as transcription factors that regulate the expression of certain genes. Sub-types The R-Smads consist of Smad1, Smad2, Smad3, Smad5 and Smad8/9, and are involved in direct signaling from the TGF-B receptor. Smad4 is the only known human Co-Smad, and has the role of partne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, '' D. melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literature. The entire genus, however, contains more than 1,500 species and is very diverse in appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Decapentaplegic
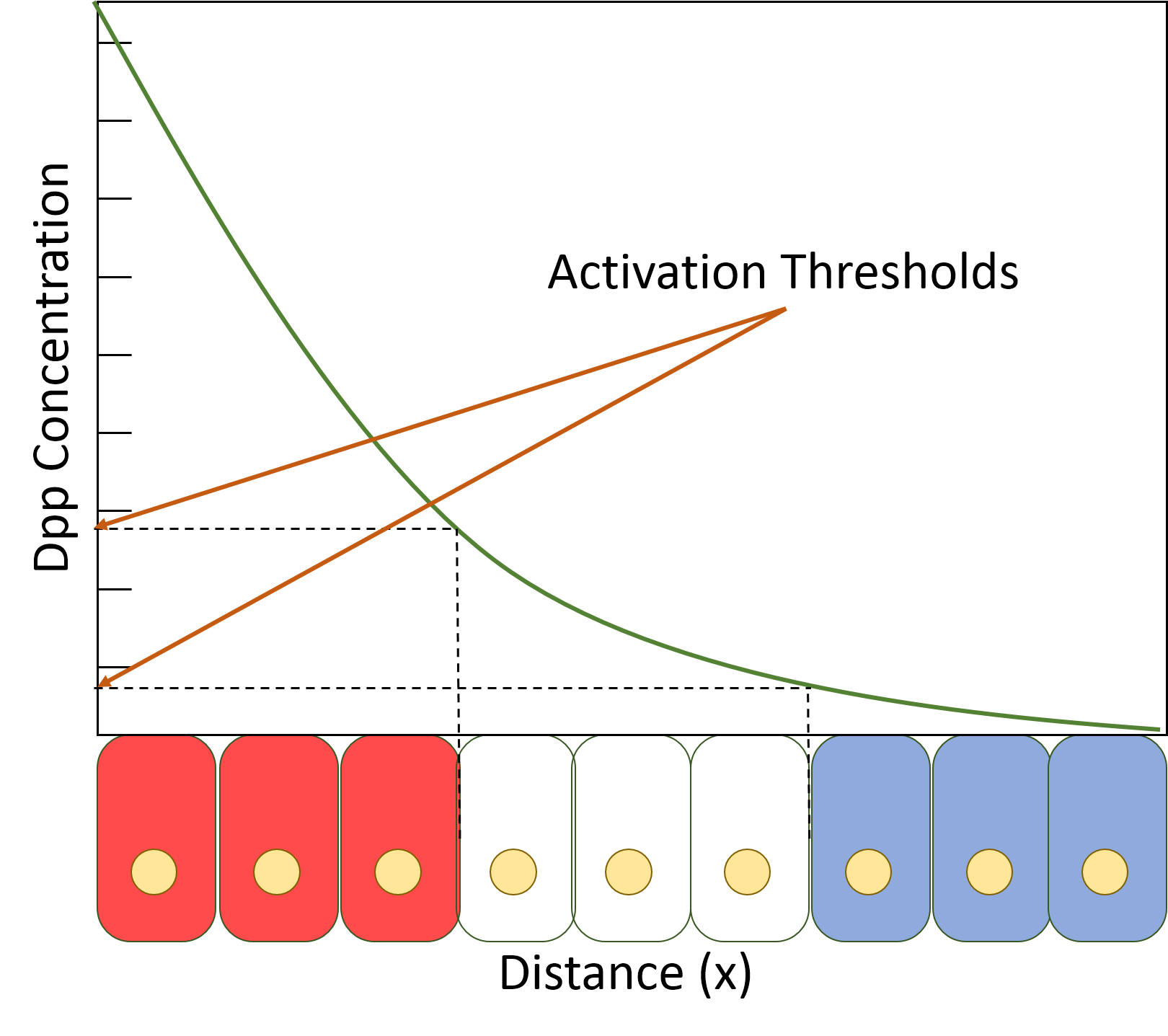
Decapentaplegic (Dpp) is a key morphogen involved in the development of the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and is the first validated secreted morphogen. It is known to be necessary for the correct patterning and development of the early ''Drosophila'' embryo and the fifteen imaginal discs, which are tissues that will become limbs and other organs and structures in the adult fly. It has also been suggested that Dpp plays a role in regulating the growth and size of tissues. Flies with mutations in decapentaplegic fail to form these structures correctly, hence the name (''decapenta''-, fifteen, -''plegic'', paralysis). Dpp is the Drosophila homolog of the vertebrate bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are members of the TGF-β superfamily, a class of proteins that are often associated with their own specific signaling pathway. Studies of Dpp in Drosophila have led to greater understanding of the function and importance of their homologs in vertebrates like humans. Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mothers Against Drunk Driving
Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD) is a non-profit organization in the United States, Canada and Brazil that seeks to stop drunk driving, support those affected by drunk driving, prevent underage drinking, and strive for stricter impaired driving policy, whether that impairment is caused by alcohol or any other drug. The Irving, Texas–based organization was founded on September 5, 1980, in California by Candace Lightner after her 13-year-old daughter, Cari, was killed by a drunk driver. There is at least one MADD office in every state of the United States and at least one in each province of Canada. These offices offer victim services and many resources involving alcohol safety. MADD has claimed that drunk driving has been reduced by half since its founding. Positions According to MADD's website, "The mission of Mothers Against Drunk Driving is to end drunk driving, help fight drugged driving, support the victims of these violent crimes and prevent underage drinking." Generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 1
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 also known as SMAD family member 1 or SMAD1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMAD1'' gene. Nomenclature SMAD1 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the ''Drosophila'' gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the ''C. elegans'' gene Sma. The name is a combination of the two; and based on a tradition of such unusual naming within the gene research community. It was found that a mutation in the 'Drosophila' gene, ''MAD'', in the mother, repressed the gene, '' decapentaplegic'', in the embryo. Mad mutations can be placed in an allelic series based on the relative severity of the maternal effect enhancement of weak dpp alleles, thus explaining the name Mothers against dpp. Function SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. This protein mediates the signals of the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 2
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 also known as SMAD family member 2 or SMAD2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMAD2'' gene. MAD homolog 2 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the ''Drosophila'' gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the ''C. elegans'' gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. Function SMAD2 mediates the signal of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta, and thus regulates multiple cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. This protein is recruited to the TGF-beta receptors through its interaction with the SMAD anchor for receptor activation (SARA) protein. In response to TGF-beta signal, this protein is phosphorylated by the TGF-beta receptors. The phosphorylation induces the dissociation of this protein with SARA and the association with the family member SMAD4. The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 3
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene. SMAD3 is a member of the SMAD family of proteins. It acts as a mediator of the signals initiated by the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) superfamily of cytokines, which regulate cell proliferation, differentiation and death. Based on its essential role in TGF beta signaling pathway, SMAD3 has been related with tumor growth in cancer development. Gene The human SMAD3 gene is located on chromosome 15 on the cytogenic band at 15q22.33. The gene is composed of 9 exons over 129,339 base pairs. It is one of several human homologues of a gene that was originally discovered in the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster''. The expression of SMAD3 has been related to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/ERK pathway), particularly to the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-1 (MEK1). Studies have demonstrated that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 4
SMAD4, also called SMAD family member 4, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4, or DPC4 (Deleted in Pancreatic Cancer-4) is a highly conserved protein present in all metazoans. It belongs to the SMAD family of transcription factor proteins, which act as mediators of TGF-β signal transduction. The TGFβ family of cytokines regulates critical processes during the lifecycle of metazoans, with important roles during embryo development, tissue homeostasis, regeneration, and immune regulation. SMAD 4 belongs to the co-SMAD group (''common mediator'' SMAD), the second class of the SMAD family. SMAD4 is the only known co-SMAD in most metazoans. It also belongs to the Darwin family of proteins that modulate members of the TGFβ protein superfamily, a family of proteins that all play a role in the regulation of cellular responses. Mammalian SMAD4 is a homolog of the ''Drosophila'' protein "Mothers against decapentaplegic" named Medea. SMAD4 interacts with R-Smads, such as SMAD2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 5
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 5 also known as SMAD5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMAD5'' gene. SMAD5, as its name describes, is a homolog of the Drosophila gene: "Mothers against decapentaplegic", based on a tradition of such unusual naming within the gene research community. Sep 26, 2014, Michael White. psmag.com It belongs to the SMAD family of proteins, which belong to the TGFβ superfamily of modulators. Like many other TGFβ family members SMAD5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 6
SMAD family member 6, also known as SMAD6, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMAD6'' gene. SMAD6 is a protein that, as its name describes, is a homolog of the Drosophila gene "mothers against decapentaplegic". It belongs to the SMAD (protein), SMAD family of proteins, which belong to the transforming growth factor beta, TGFβ superfamily of modulators. Like many other TGFβ family members SMAD6 is involved in cell signalling. It acts as a regulator of TGFβ family (such as bone morphogenetic proteins) activity by competing with SMAD4 and preventing the transcription of SMAD4's gene products. There are two known isoforms of this protein. Nomenclature The SMAD proteins are homologs of both the drosophila protein, mothers against decapentaplegic (MAD) and the ''Caenorhabditis elegans, C. elegans'' protein SMA. The name is a combination of the two. During ''Drosophila'' research, it was found that a mutation in the gene ''MAD'' in the mother repressed the gene ''decapen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 7
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 or SMAD7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMAD7'' gene. SMAD7 is a protein that, as its name describes, is a homolog of the Drosophila gene: "Mothers against decapentaplegic". It belongs to the SMAD (protein), SMAD family of proteins, which belong to the transforming growth factor beta, TGFβ superfamily of ligands. Like many other TGFβ family members, SMAD7 is involved in cell signalling. It is a TGFβ type 1 receptor antagonist. It blocks TGFβ1 and activin associating with the receptor, blocking access to SMAD2. It is an inhibitory SMAD (I-SMAD) and is enhanced by SMURF2. Smad7 enhances muscle differentiation. Structure Smad proteins contain two conserved domains. The Mad Homology domain 1 (MH1 domain) is at the N-terminal and the Mad Homology domain 2 (MH2 domain) is at the C-terminal. Between them there is a linker region which is full of regulatory sites. The MH1 domain has DNA binding activity while the MH2 dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |