|
Modern Attempts To Revive The Sanhedrin
Modern attempts to revive the Sanhedrin are the efforts from 1538 until the present day to renew the Sanhedrin which was dissolved in 358 by the edict of the Roman emperor Constantius II. (Though 358 was the last formal meeting, there is no record of when it was actually dissolved and by whom, nor any reference to the last nasi's execution.) The latest effort was in 2004 when a group of seventy-one rabbis claiming to represent varied communities in Israel undertook a ceremony in Tiberias, where the original Sanhedrin was disbanded. That group claimed to re-establish the body, based on the proposal of Maimonides and the Jewish legal rulings of Rabbi Yosef Karo. As of March 2010, that effort is ongoing and is supported by The Temple Institute. Sanhedrin in Judaism The Sanhedrin is traditionally viewed as the last institution which commanded universal authority among the Jewish people in the long chain of tradition from Moses until the present day. Since its dissolution in 358, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
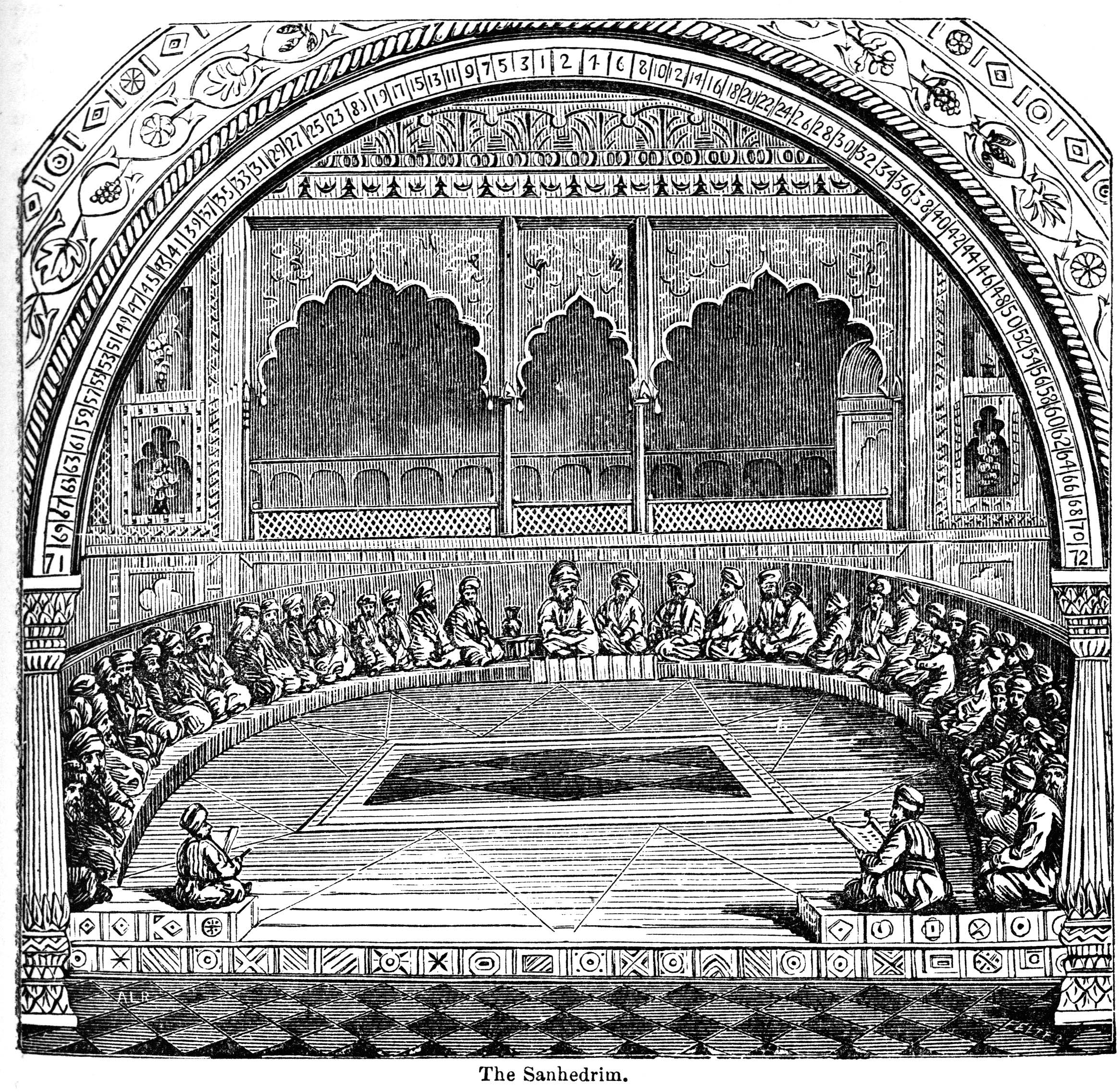
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , ''synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the ''Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was second to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolidation of the empire generated political stability and a vast Roman building program. Vespasian was the first emperor from an equestrian family and only rose later in his lifetime into the senatorial rank as the first member of his family to do so. Vespasian's renown came from his military success; he was legate of Legio II Augusta during the Roman invasion of Britain in 43 and subjugated Judaea during the Jewish rebellion of 66. While Vespasian besieged Jerusalem during the Jewish rebellion, emperor Nero committed suicide and plunged Rome into a year of civil war known as the Year of the Four Emperors. After Galba and Otho perished in quick succession, Vitellius became emperor in Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judah II
Judah II or Nesi'ah I was a Jewish sage who lived in Tiberias in the Land of Israel, in the middle of the third century CE. He is mentioned in the classical works of Judaism's Oral Torah, the Mishnah and Talmud. There he is variously called "Judah," "Judah Nesi'ah" (= "ha-Nasi"), and occasionally "Rabbi" like his grandfather, Judah haNasi. As Judah III is also designated as "Judah Nesi'ah," it is often difficult, sometimes impossible, to determine which one of these patriarchs is referred to. Biography Youth Various stories of Judah's youth, referring to him and his brother Hillel, have been preserved. As youths, Judah and Hillel visited Cabul and Biri, each time behaving in ways which offended the local population. Relations with other scholars He had especially friendly relations with Hoshaiah. Together with Rabbi Joshua ben Levi, he assisted at Laodicea in the reception of a female proselyte into Judaism. Jonathan b. Eleazar was his companion at the baths of Gadara. The rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamaliel III
Gamaliel III ( he, רבן גמליאל ברבי, read as ''Rabban Gamaliel beRabbi'', that is: ''son of Rebbi'', after his father Judah haNasi) was a 3rd-century rabbi (first generation of amoraim). His father appointed him his successor as '' nasi''. Little certain is known about his activities, but it is likely that the revision of the Mishnah was completed during his era. He was the father of Judah II and Hillel (not to be mistaken with Hillel the Elder), and the brother of Shimon ben Judah HaNasi. Teachings The Tosefta contains but one saying of Gamaliel, a paraphrase of Numbers 11:22, in which Moses complains of the unreasonableness of the people's wishes. A baraita contains a halakhic exegesis by him. R. Hoshaiah asks Gamaliel's son, Judah II, concerning a halakhic opinion of his father's. Rabbi Yohanan tells of a question which Gamaliel answered for him. Samuel of Nehardea tells of differences of opinion between Gamaliel and other scholars. Quotes * "Good is the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judah HaNasi
Judah ha-Nasi ( he, יְהוּדָה הַנָּשִׂיא, ''Yəhūḏā hanNāsīʾ''; Yehudah HaNasi or Judah the Prince) or Judah I, was a second-century rabbi (a tanna of the fifth generation) and chief redactor and editor of the ''Mishnah''. He lived from approximately 135 to 217 CE. He was a key leader of the Jewish community during the Roman occupation of Judea. Name and titles The title ''nasi'' was used for presidents of the Sanhedrin. He was the first ''nasi'' to have this title added permanently to his name; in traditional literature he is usually called "Rabbi Yehuda ha-Nasi." Often though (and always in the Mishnah), he is simply called "Rabbi" (), the master par excellence. He is occasionally called "Rabbenu" (= "our master"). He is also called "Rabbenu HaQadosh" (, "our holy Master") due to his deep piety. Biography Youth Judah the Prince was born in 135 CE to Simeon ben Gamliel II. According to the Talmud he was of the Davidic line. He is said to have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepphoris
Sepphoris (; grc, Σέπφωρις, Séphōris), called Tzipori in Hebrew ( he, צִפּוֹרִי, Tzipori),Palmer (1881), p115/ref> and known in Arabic as Saffuriya ( ar, صفورية, Ṣaffūriya) since the 7th century, is an archaeological site located in the central Galilee region of Israel, north-northwest of Nazareth. It lies above sea level and overlooks the Beit Netofa Valley. The site holds a rich and diverse historical and architectural legacy that includes Hellenistic, ancient Jewish, Roman, Byzantine, Early Islamic, Crusader, Mamluk and Ottoman remains. In the Roman period, it was also called ''Diocaesaraea''. In Mandatory Palestine, Saffuriya was a Palestinian Arab town with a population of approximately 5,000 people at the time of its depopulation in 1948. Since Late Antiquity, it was believed to be the birthplace of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and the village where Saints Anna and Joachim are often said to have resided, where today a 5th—century bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beth Shearim
Beit She'arim ( / / Bet Sharei) or Besara ( gr, Βήσαρα) was a Roman-era Jewish village from the 1st century BCE until the 3rd century CE which, at one time, was the seat of the Sanhedrin. In the mid-2nd century, the village briefly became the seat of the rabbinic synod under Rabbi Judah ha-Nasi (compiler of the Mishnah), who was buried in the adjoining necropolis. It is today part of the Beit She'arim National Park. Location The site is situated on the spur of a hill about half a kilometer long and 200 meters wide, and lies in the southern extremity of the Lower Galilee mountains, facing the western end of the Jezreel Valley, east of Daliat el-Carmel, south of Kiryat Tivon, and west of Ramat Yishai. It rises above sea level at its highest point. It is first mentioned by Josephus as Besara where grain from the King's land was stored. Identification For many years the ancient site of ''Beit Shearim'' remained obscure and nearly slipped into oblivion. Some historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimon Ben Gamliel II
Simeon (or Shimon) ben Gamaliel II (Hebrew: ) was a Tanna of the third generation and president of the Great Sanhedrin. He was the son of Gamaliel II. Biography Simeon was a youth in Betar when the Bar Kokhba revolt broke out, but when that fortress was taken by the Romans he managed to escape the massacre. On the restoration of the college at Usha, Simeon was elected its president, this dignity being bestowed upon him not only because he was a descendant of the house of Hillel, but in recognition of his personal worth and influence. There were many children in his family, one-half of whom were instructed in the Torah, and the other half in Greek philosophy. Simeon himself seems to have been trained in Greek philosophy; this probably accounting for his declaring later that the Scriptures might be written only in the original text and in Greek. Simeon appears to have studied natural science as well, for some of his sayings betray a scientific knowledge of the nature of plants a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shefa-'Amr
Shefa-Amr, also Shfar'am ( ar, شفاعمرو, Šafāʻamr, he, שְׁפַרְעָם, Šəfarʻam) is an Arab city in the Northern District of Israel. In it had a population of , with a Sunni Muslim majority and large Christian Arab and Druze minorities. Etymology Palmer writes that the name meant: "The margin or edge of 'Amr. Locally and erroneously supposed to mean the healing of 'Amer ( ed Dhaher)" History Ancient period Walls, installations and pottery sherds from the Early Bronze Age IB and the Middle Bronze Age IIB, Iron, Hellenistic and Roman periods have been excavated at Shefa-ʻAmr. Shefa-Amr is first mentioned under the name ''Shefar'am'' ( he, שפרעם) in the Tosefta (Tractate Mikvaot 6:1), followed by the Talmud redacted in 500 CE where it is mentioned in several places, in Tractate ''Avodah Zarah'' 8b and ''Rosh Hashanah'' 31b, ''et al.'' Settlement has existed there without interruption since the Roman period, when it was one of the cities mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimon Ben Gamliel
Simeon ben Gamliel (I) ( or רשב"ג הראשון; c. 10 BCE – 70 CE) was a '' Tanna'' sage and leader of the Jewish people. He served as nasi of the Great Sanhedrin at Jerusalem during the outbreak of the First Jewish–Roman War, succeeding his father in the same office after his father's death in 52 CE and just before the destruction of the Second Temple. The great-grandson of Hillel the Elder, he was considered to be a direct descendant of King David.(Hebrew) He was a contemporary of the high priests Ḥanan ben Ḥanan and Yehoshua ben Gamla. He is one of the Ten Martyrs mentioned in Jewish liturgy. According to the ''Iggeret of Rabbi Sherira Gaon'' he was beheaded, along with Rabbi Ishmael ben Elisha the High Priest, prior to the Temple's destruction, although the historian Josephus Flavius mentions only the execution of Ishmael in Cyrene during the First Jewish–Roman War (ca. 66-68 CE). The account is mentioned in both Tractate Semachot ch 8, and in Avot de-Rabb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usha (ancient)
Usha () was a city in the Western part of Galilee. The Arab village of Hawsha later occupied the ruins of the old site. The modern kibbutz of Usha, Israel is located nearby to the ruins. History The site came to renown in the 2nd century (c. 135), after the Hadrianic persecutions, when the Sanhedrin, or rabbinic court, was moved from Yavne in Judea to Usha, and then from Usha back to Yavne, and a second time from Yavne to Usha.Simon, Maurice, ed. (1990). ''Hebrew-English Edition of the Babylonian Talmud (Seder Moed), Rosh Hashanah, Beẓah, Sheḳalim''. The Soncino Press: London, s.v. ''Rosh Hashanah'' 31b (note 6, citing Horowitz, ''Palestine'', p.34) The Sanhedrin is thought to have continued there until it was dissolved during the reign of Verus, and re-established in Shefar'am under Marcus Aurelius. The final settlement in Usha indicates the ultimate spiritual supremacy of Galilee over Judea, the latter having become depopulated after the Second Jewish Revolt. Usha was al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasi (Hebrew Title)
( ''nāśīʾ'') is a Hebrew title meaning "prince" in Biblical Hebrew, "Prince f the Sanhedrin">Sanhedrin.html" ;"title="f the Sanhedrin">f the Sanhedrin in Mishnaic Hebrew, or "President (government title), president" in Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Modern Hebrew. Usage Genesis and ancient Israel The noun ''nasi'' (including its grammatical variations), occurs 132 times in the Masoretic Text of the Hebrew Bible, and in English is usually translated "prince," occasionally "captain." The first use is for the twelve "princes" who will descend from Ishmael, in the Book of Genesis , and the second use, in , is the Hethites recognising Abraham as "a godly prince" (' ). In the Book of Leviticus (), in the rites of sacrifices for leaders who err, there is the special offering made by a "nasi". In the Book of Numbers (), the leader of each tribe is referred to as a ''nasi'', and each one brings a gift to the Tabernacle. In , occurring 38 years later in the Biblical story, the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |