|
Misorientation
In materials science, misorientation is the difference in crystallographic orientation between two crystallites in a polycrystalline material. In crystalline materials, the orientation of a crystallite is defined by a transformation from a sample reference frame (i.e. defined by the direction of a rolling or extrusion process and two orthogonal directions) to the local reference frame of the crystalline lattice, as defined by the basis of the unit cell. In the same way, misorientation is the transformation necessary to move from one local crystal frame to some other crystal frame. That is, it is the distance in orientation space between two distinct orientations. If the orientations are specified in terms of matrices of direction cosines and , then the misorientation operator going from to can be defined as follows: :\begin & g_B = \Delta g_ g_A \\ & \Delta g_ = g_B g_A^ \end where the term is the reverse operation of , that is, transformation from crystal frame back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
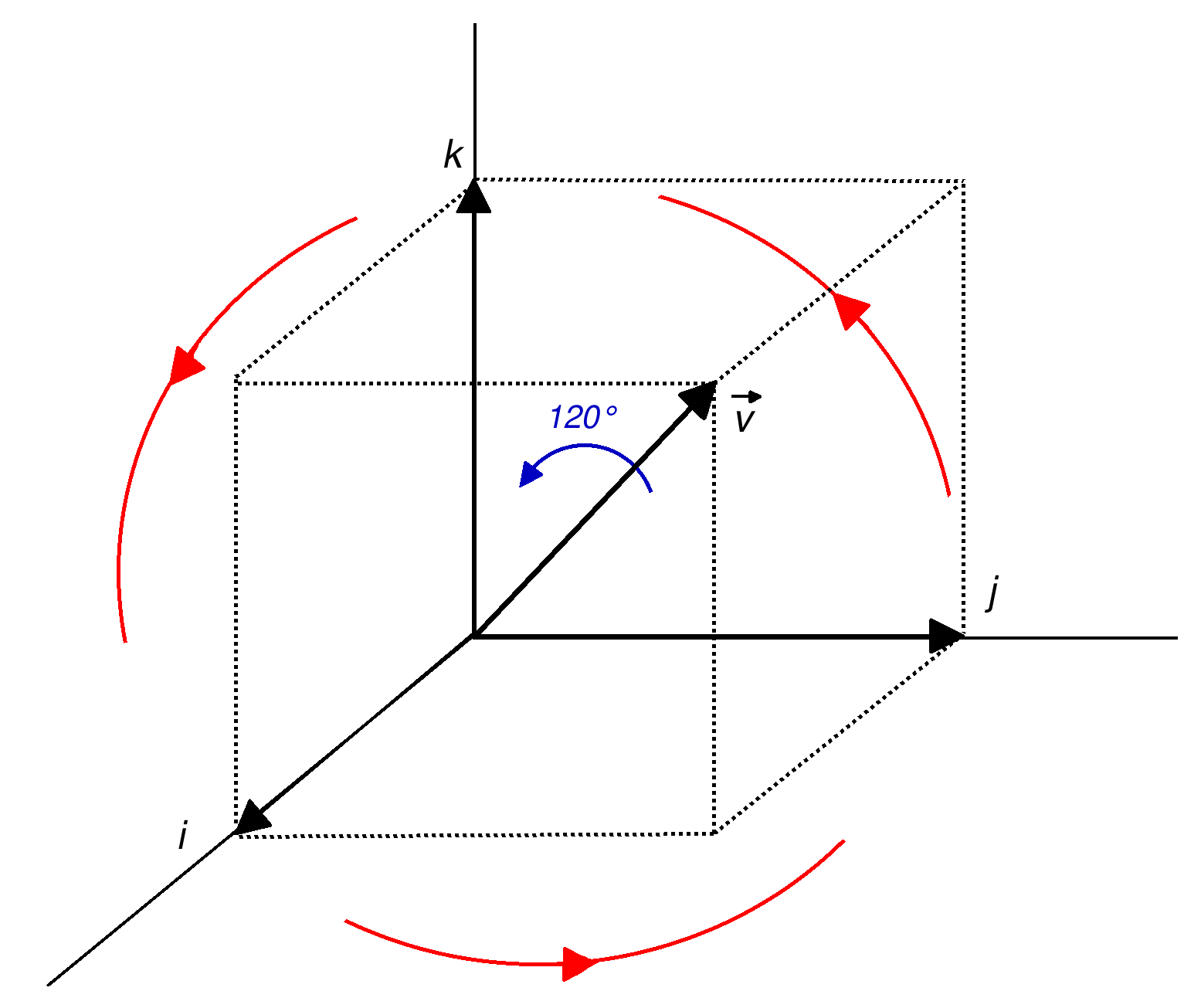
Axis Angle
An axis (: axes) may refer to: Mathematics *A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular: ** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system *** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names for the coordinate axes of a Cartesian coordinate system ** Axis of rotation ** Axis of symmetry ** Axis of a conic section Politics *Axis powers of World War II, 1936–1945. *Axis of evil (first used in 2002), U.S. President George W. Bush's description of Iran, Iraq, and North Korea *Axis of Resistance (first used in 2002), the Shia alliance of Iran, Syria, and Hezbollah *Axis of Upheaval (first used in 2024), foreign policy neologism of the Anti-western collaboration between Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea * Jakarta-Pyongyang-Peking Axis, diplomatic alignment and alliance between Indonesia, China, and North Korea during Sukarno's Presidency *Political spectrum, sometimes called an axis Science *Axis (anatomy), the second cervica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reza Abbaschian
Reza Abbaschian is an Iranian/American engineer, currently the William R. Johnson, Jr. Family Professor, Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering and the former Dean of the Bourns College of Engineering and, also formerly the Vladimir Grodsky Professor of Materials Science at University of Florida. In 2006, he was elected to the American Association for the Advancement of Science, The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society and ASM, the latter of which he was a former president. Abbaschian is considered pivotal in establishing a relationship with Winston Chung, which led to a $10 million donation to the college. Abbascian was recognized with the 2017 AIME Honorary Membership Award for "pioneering contributions in solidification processing, materials education and leadership in materials science and engineering worldwide". Education *Ph.D. in Materials Science and Engineering from the University of California, Berkeley *M.S. in metallurgical engineering from Michigan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orientation Matrix
In geometry, the orientation, attitude, bearing, direction, or angular position of an object – such as a line, plane or rigid body – is part of the description of how it is placed in the space it occupies. More specifically, it refers to the imaginary rotation that is needed to move the object from a reference placement to its current placement. A rotation may not be enough to reach the current placement, in which case it may be necessary to add an imaginary translation to change the object's position (or linear position). The position and orientation together fully describe how the object is placed in space. The above-mentioned imaginary rotation and translation may be thought to occur in any order, as the orientation of an object does not change when it translates, and its position does not change when it rotates. Euler's rotation theorem shows that in three dimensions any orientation can be reached with a single rotation around a fixed axis. This gives one common way of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackenzie Plot
Mackenzie, Mckenzie, MacKenzie, or McKenzie may refer to: People * Mackenzie (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) * Mackenzie (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * Clan Mackenzie, a Scottish clan Places Cities, towns and roads Australia * Mackenzie, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane * Mackenzie, Queensland (Central Highlands), a locality in the Central Highlands Region * Lake McKenzie, a perched lake in Queensland Canada * Mackenzie (provincial electoral district), a former constituency in British Columbia * Mackenzie, British Columbia, near Williston Lake in east central British Columbia * Mackenzie, Ontario, on Thunder Bay in west central Ontario * Mackenzie Mountains, a mountain range in northern Canada * District of Mackenzie, a former administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories ''Alberta'' * Mackenzie County, a specialized municipality in northwestern Alberta * Mackenzie Highway, in Alber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Harmonics
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. The table of spherical harmonics contains a list of common spherical harmonics. Since the spherical harmonics form a complete set of orthogonal functions and thus an orthonormal basis, every function defined on the surface of a sphere can be written as a sum of these spherical harmonics. This is similar to periodic functions defined on a circle that can be expressed as a sum of circular functions (sines and cosines) via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by (spatial) angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for irreducible representations of SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orientation Distribution Function
In materials science and related fields, crystallographic texture is the distribution of crystallographic orientations of a polycrystalline sample. A sample in which these orientations are fully random or is amorphous and thus no crystallographic planes, is said to have no texture. If the crystallographic orientations are not random, but have some preferred orientation, then the sample may have a weak, moderate or strong texture. The degree is dependent on the percentage of crystals having the preferred orientation. Texture is seen in almost all engineered materials, and can have a great influence on materials properties. The texture forms in materials during thermo-mechanical processes, for example during production processes e.g. rolling. Consequently, the rolling process is often followed by a heat treatment to reduce the amount of unwanted texture. Controlling the production process in combination with the characterization of texture and the material's microstructure help to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MDF Rodrigues AA5083
MDF may refer to: Computing * Master Database File, a Microsoft SQL Server file type * ''MES Development Framework'', a .NET framework for building manufacturing execution system applications * ''Message Development Framework'', a collection of models, methods and tools used by Health Level 7 v3.0 methodology * Media Descriptor File, a proprietary disc image file format developed for Alcohol 120% * Measurement Data Format, one of the data formats defined by the Association for Standardisation of Automation and Measuring Systems (ASAM) * Multiple Domain Facility; see Logical partition Medicine * Map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy, a genetic disease affecting the cornea * ''Mean Diastolic Filling'' of the heart * Myocardial depressant factor, a low-molecular-weight peptide released from the pancreas into the blood in mammals during various shock states Organizations * Hungarian Democratic Forum (Hungarian: ''Magyar Demokrata Fórum''), a political party * Maraland Democratic F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
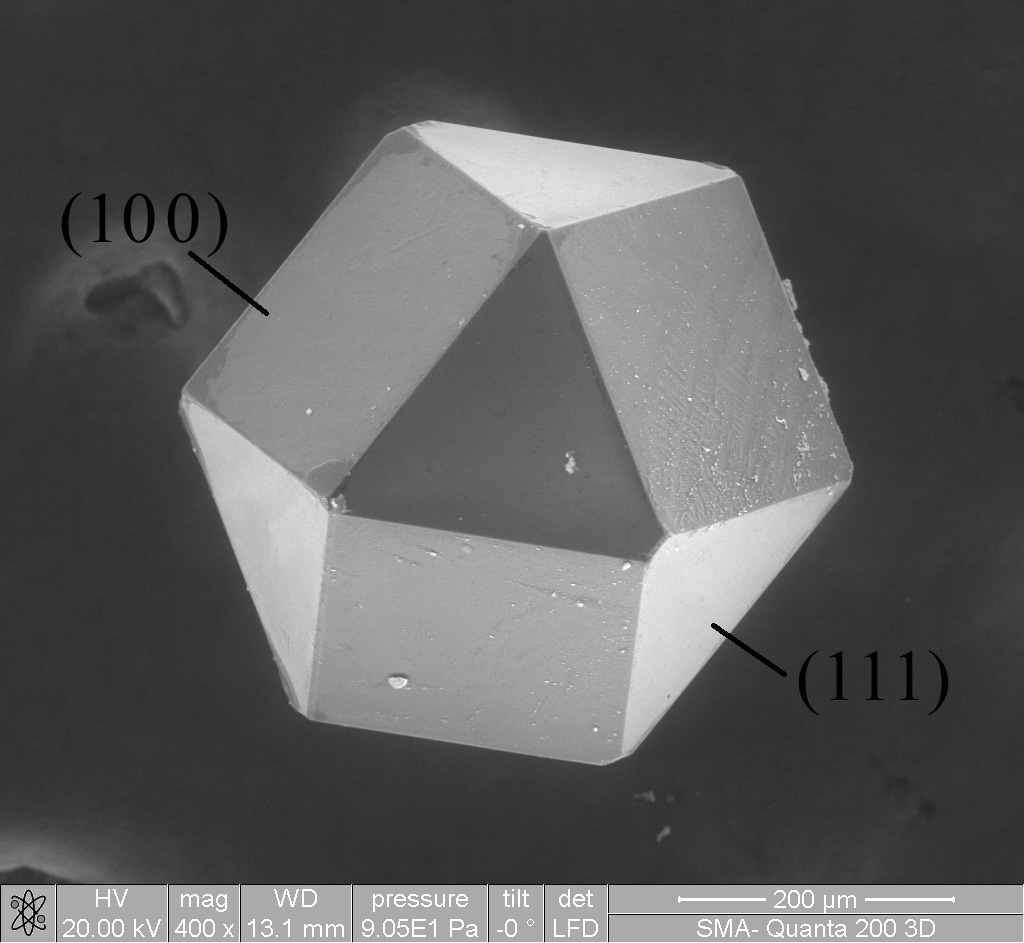
Crystal Symmetry
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternions And Spatial Rotation
unit vector, Unit quaternions, known as versor, ''versors'', provide a convenient mathematics, mathematical notation for representing spatial Orientation (geometry), orientations and rotations of elements in three dimensional space. Specifically, they encode information about an Axis–angle representation, axis-angle rotation about an arbitrary axis. Rotation and orientation quaternions have applications in computer graphics, Presented at SIGGRAPH '85. computer vision, robotics, navigation, molecular dynamics, flight dynamics, orbital mechanics of satellites, and Texture (crystalline), crystallographic texture analysis. When used to represent rotation, unit quaternions are also called rotation quaternions as they represent the 3D rotation group. When used to represent an Orientation (geometry), orientation (rotation relative to a reference coordinate system), they are called orientation quaternions or attitude quaternions. A spatial rotation around a fixed point of \theta radians ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler Angles
The Euler angles are three angles introduced by Leonhard Euler to describe the Orientation (geometry), orientation of a rigid body with respect to a fixed coordinate system.Novi Commentarii academiae scientiarum Petropolitanae 20, 1776, pp. 189–207 (E478PDF/ref> They can also represent the orientation of a mobile frame of reference in physics or the orientation of a general Basis (linear algebra), basis in three dimensional linear algebra. Classic Euler angles usually take the inclination angle in such a way that zero degrees represent the vertical orientation. Alternative forms were later introduced by Peter Guthrie Tait and George H. Bryan intended for use in aeronautics and engineering in which zero degrees represent the horizontal position. Chained rotations equivalence Euler angles can be defined by elemental geometry or by composition of rotations (i.e. chained rotations). The geometrical definition demonstrates that three consecutive ''elemental rotations'' (rotatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |