|
Mike Fossum
Michael Edward Fossum (born December 19, 1957, in Sioux Falls, South Dakota) is a former American astronaut, engineer, and thChief Operating Officer of Texas A&M University at Galveston He flew into space on board the NASA Space Shuttle missions STS-121 and STS-124 and served as a mission specialist of Expedition 28 and commander of Expedition 29 aboard the International Space Station. Air Force Fossum was involved with the United States Air Force during his undergraduate years at Texas A&M and served as commander of Squadron 3 in the Corps of Cadets. He graduated in mechanical engineering in 1980. He received his master's in physical science (space science) from the University of Houston. He was selected to attend Air Force Test Pilot School from which he flew 34 different types of aircraft. . He left active duty for the Air Force Reserve in 1992 to work for NASA and retired as a colonel in the USAFR in 2010. NASA The first time Fossum became interested in being an astronaut w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
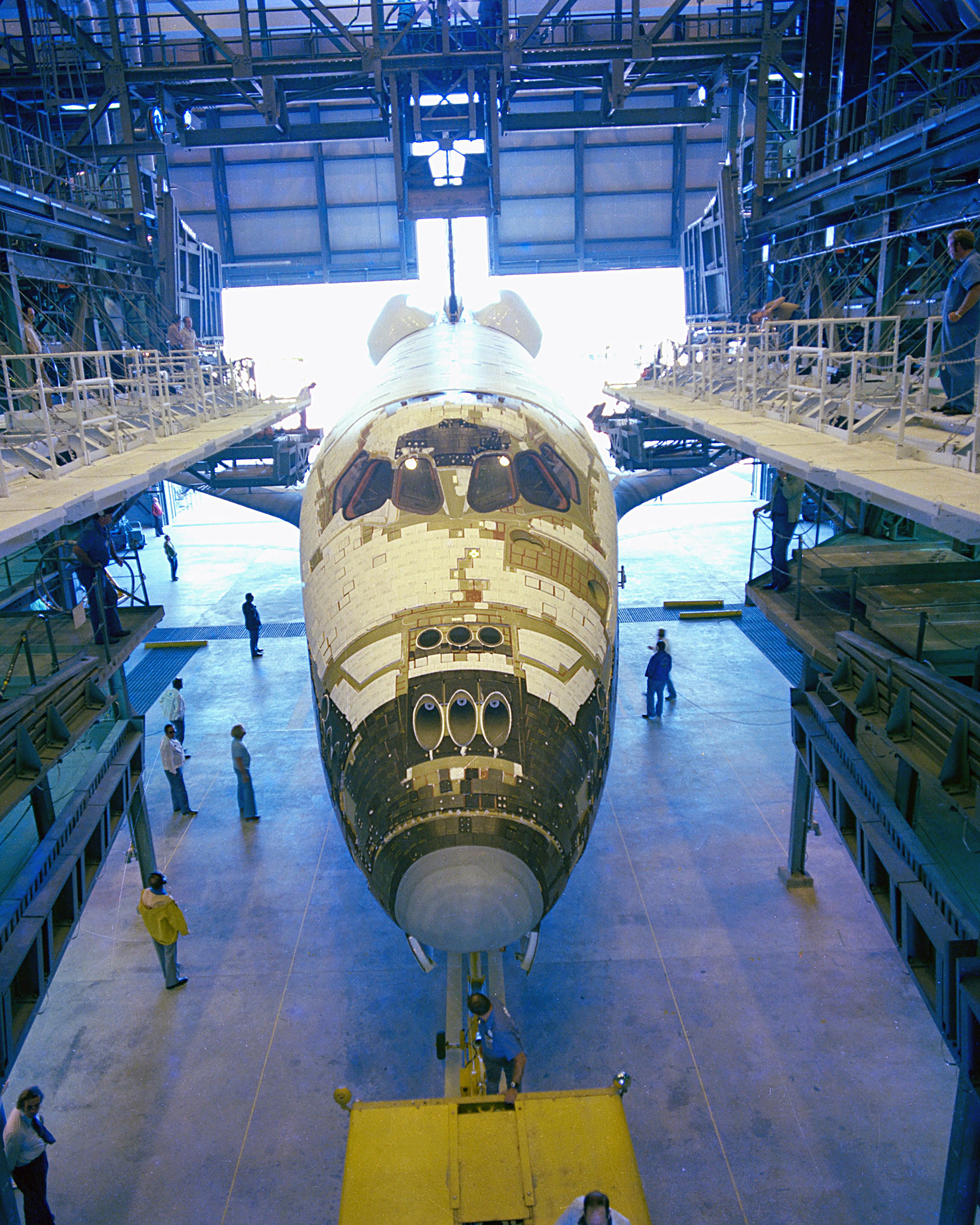
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first ( STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (ISS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piers Sellers
Piers John Sellers (11 April 1955 – 23 December 2016) was a British-American meteorologist, NASA astronaut and Director of the Earth Science Division at NASA/GSFC. He was a veteran of three Space Shuttle missions. Sellers attended Cranbrook School, Cranbrook, Kent, United Kingdom, until 1973, and achieved a bachelor's degree in ecological science from the University of Edinburgh in 1976. In 1981 he gained a doctorate in biometeorology from the University of Leeds. In 2011, Sellers retired from the NASA Astronaut Corps. Before joining the astronaut corps, Sellers worked at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center on research into how the Earth's biosphere and atmosphere interact. This work involved climate system computer modelling and field work utilising aircraft, satellites and ground support input. Personal life Sellers was born in Crowborough, Sussex, the second born of five boys for mother Lindsey. His education started at Tyttenhanger Lodge Pre-preparatory School in Seaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacewalk
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable atmosphere of Earth, Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environmental support. EVA includes ''spacewalks'' and Moon, lunar or planetary surface exploration (commonly known from 1969 to 1972 as ''moonwalks''). In a stand-up EVA (SEVA), an astronaut stands through an open hatch but does not fully leave the spacecraft. EVA has been conducted by the Soviet Union/Russia, the United States, Canada, the European Space Agency and China. On March 18, 1965, Alexei Leonov became the first human to perform a spacewalk, exiting the Voskhod 2 capsule for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to perform a moonwalk, outside his lunar lander on Apollo 11 for 2 hours and 31 minutes. On the last three Moon missions, astronauts also performed deep-space EVAs on the return to Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossum And Sellers On Spacewalk , sports club from Bærum, Norway
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Fossum may refer to: Places * Fossum, Akershus, Norway * Fossum, Oslo, Norway * Fossum, Telemark, Norway * Fossum Bridge, Østfold, Norway * Fossum Township, Minnesota, United States Other uses * Fossum (surname) * Fossum IF Fossum Idrettsforening is a Norwegian sports club from Fossum, Grini, Østerås and Eiksmarka in Bærum. It has sections for cross-country skiing, biathlon, ski jumping, alpine skiing, Nordic combined, orienteering, and football, and was found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-38
The X-38 was an experimental re-entry vehicle designed by NASA to research a possible emergency crew return vehicle (CRV) for the International Space Station (ISS). The 1995–2002 program also developed concepts for a crew return vehicle design that could be modified for other uses, such as a possible joint U.S. and international human spacecraft that could be launched on the French Ariane 5 booster. The program would eventually develop a total of three test prototype flight demonstrators for the proposed Crew Return Vehicle, each having incremental improvements on its predecessor. All three were wingless lifting body vehicles used in drop tests. The X-38 program was canceled in 2002 due to budget cuts. History The maximum crew size for the ISS is dependent on crew rescue capacity. Since it is imperative that the crew members be able to return to Earth in case of an unexpected emergency, a Crew Return Vehicle able to hold up to seven crew members was initially planned by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Test Engineer
A flight test engineer (FTE) is an engineer involved in the flight testing of prototype aircraft or aircraft systems. Overview The flight test engineer generally has overall responsibility for the planning of a specific flight test phase, which includes preparing the test plans in conjunction with other analytical and/or systems engineers, overseeing the buildup of the aircraft to the proper configuration, working with the flight test instrumentation engineer to ensure the sensors and recording systems are installed for required data parameters, and preparing the maneuver-by-maneuver plan for each test flight (enshrined typically in a higher level document called a "test plan" and then an operational document usually called the "test cards"). The FTE and the experimental test pilot are jointly responsible for the safety of the test flying. The FTE is also responsible for the overall analysis of the data acquired during a test flight. Finally, the flight test engineer will coordinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
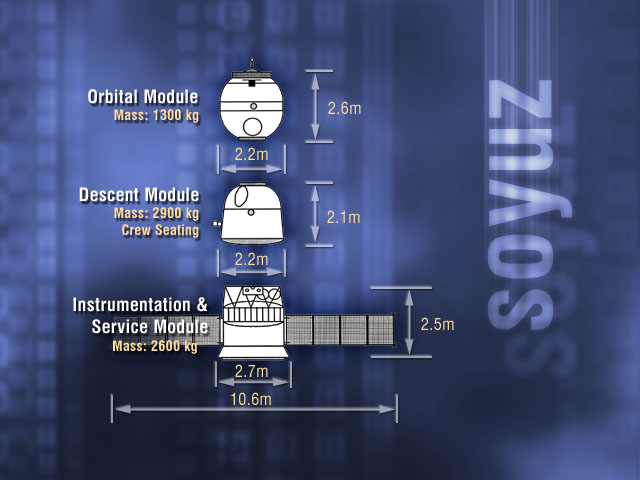
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Space Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight (originally named the Manned Spacecraft Center), where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late US president and Texas native, Lyndon B. Johnson, by an act of the United States Senate on February 19, 1973. It consists of a complex of 100 buildings constructed on in the Clear Lake Area of Houston, which acquired the official nickname "Space City" in 1967. The center is home to NASA's astronaut corps, and is responsible for training astronauts from both the US and its international partners. It houses the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, which has provided the flight control function for every NASA human spaceflight since Gemini 4 (including Apollo, Skylab, Apollo–Soyuz, and Space Shuttle). It is popularly known by its radio call signs "Mission Control" and "Houston". The original Manned Spacecraft Center grew out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
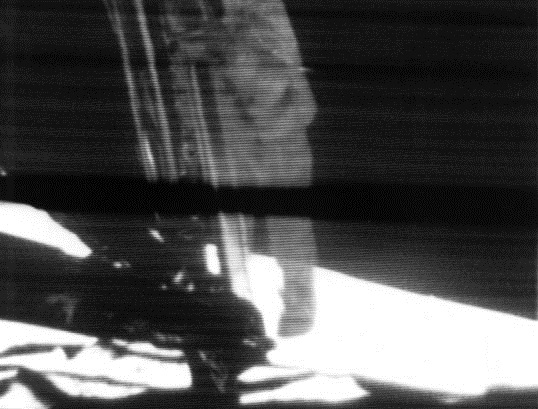
Moon Landing
A Moon landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon. This includes both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was the Soviet Union's Luna 2, on 13 September 1959. The United States' Apollo 11 was the first crewed mission to land on the Moon, on 20 July 1969. There were six crewed U.S. landings between 1969 and 1972, and numerous uncrewed landings, with no soft landings happening between 22 August 1976 and 14 December 2013. The United States is the only country to have successfully conducted crewed missions to the Moon, with the last departing the lunar surface in December 1972. All soft landings took place on the near side of the Moon until 3 January 2019, when the Chinese Chang'e 4 spacecraft made the first landing on the far side of the Moon. Uncrewed landings After the unsuccessful attempt by Luna 1 to land on the Moon in 1959, the Soviet Union performed the first hard Moon landing – "hard" meaning the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 11
Apollo 11 (July 16–24, 1969) was the American spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and lunar module pilot Buzz Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module ''Eagle'' on July 20, 1969, at 20:17 UTC, and Armstrong became the first person to step onto the Moon's surface six hours and 39 minutes later, on July 21 at 02:56 UTC. Aldrin joined him 19 minutes later, and they spent about two and a quarter hours together exploring the site they had named Tranquility Base upon landing. Armstrong and Aldrin collected of lunar material to bring back to Earth as pilot Michael Collins flew the Command Module ''Columbia'' in lunar orbit, and were on the Moon's surface for 21 hours, 36 minutes before lifting off to rejoin ''Columbia''. Apollo 11 was launched by a Saturn V rocket from Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island, Florida, on July 16 at 13:32 UTC, and it was the fifth crewed mission of NASA's Apollo program. The Apollo spacecraft had three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |