|
Microviridin
The microviridins are a class of serine protease inhibitor (biology), protease inhibitors produced by various genera of cyanobacteria. Recent genome mining has shown that the gene cluster, biosynthetic gene cluster responsible for microviridin biosynthesis is much more prevalent, found in many species of Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria) and Bacteriodota (formerly Bacteriodetes). Microviridins are members of the Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides, RiPP family of natural products. The first microviridin was isolated from ''Microcystis viridis'' (NIES-102) and its structure was reported in 1990. Microviridins are characterized by a tricyclic depsipeptide structure resulting from the enzymatic activity of two dedicated ATP-grasp ligases, which form two lactone and one lactam rings in the core region of the precursor peptide. Toxicity Microviridin J has been found to disrupt molting in the invertebrate ''Daphnia, Daphnia pulicaria'', probably as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microviridin B
The microviridins are a class of serine protease inhibitor (biology), protease inhibitors produced by various genera of cyanobacteria. Recent genome mining has shown that the gene cluster, biosynthetic gene cluster responsible for microviridin biosynthesis is much more prevalent, found in many species of Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria) and Bacteriodota (formerly Bacteriodetes). Microviridins are members of the Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides, RiPP family of natural products. The first microviridin was isolated from ''Microcystis viridis'' (NIES-102) and its structure was reported in 1990. Microviridins are characterized by a tricyclic depsipeptide structure resulting from the enzymatic activity of two dedicated ATP-grasp ligases, which form two lactone and one lactam rings in the core region of the precursor peptide. Toxicity Microviridin J has been found to disrupt molting in the invertebrate ''Daphnia, Daphnia pulicaria'', probably as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protease Inhibitor (biology)
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases (enzymes that aid the breakdown of proteins). Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins. In medicine, ''protease inhibitor'' is often used interchangeably with alpha 1-antitrypsin (A1AT, which is abbreviated PI for this reason). A1AT is indeed the protease inhibitor most often involved in disease, namely in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Classification Protease inhibitors may be classified either by the type of protease they inhibit, or by their mechanism of action. In 2004 Rawlings and colleagues introduced a classification of protease inhibitors based on similarities detectable at the level of amino acid sequence. This classification initially identified 48 families of inhibitors that could be grouped into 26 related superfamily (or clans) by their structure. According to the MEROPS database there are now 81 families of inhibitors. These fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not usually scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Sericytochromatia, the proposed name of the paraphyletic and most basal group, is the ancestor of both the non-photosynthetic group Melainabacteria and the photosynthetic cyanobacteria, also called Oxyphotobacteria. Cyanobacteria use photosynthetic pigments, such as carotenoids, phycobilins, and various forms of chlorophyll, which absorb energy from light. Unlike heterotrophic prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have internal membranes. These are flattened sacs called thylakoids where photosynthesis is performed. Phototrophic eukaryotes such as green plants perform photosynthesis in plast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Cluster
A gene family is a set of homologous genes within one organism. A gene cluster is a group of two or more genes found within an organism's DNA that encode similar polypeptides, or proteins, which collectively share a generalized function and are often located within a few thousand base pairs of each other. The size of gene clusters can vary significantly, from a few genes to several hundred genes. Portions of the DNA sequence of each gene within a gene cluster are found to be identical; however, the resulting protein of each gene is distinctive from the resulting protein of another gene within the cluster. Genes found in a gene cluster may be observed near one another on the same chromosome or on different, but homologous chromosomes. An example of a gene cluster is the Hox gene, which is made up of eight genes and is part of the Homeobox gene family. Formation Historically, four models have been proposed for the formation and persistence of gene clusters. Gene duplication and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as ''Escherichia'', '' Salmonella'', ''Vibrio'', ''Yersinia'', ''Legionella'', and many others.Slonczewski JL, Foster JW, Foster E. Microbiology: An Evolving Science 5th Ed. WW Norton & Company; 2020. Others are free-living (nonparasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation. Carl Woese established this grouping in 1987, calling it informally the "purple bacteria and their relatives". Because of the great diversity of forms found in this group, it was later informally named Proteobacteria, after Proteus, a Greek god of the sea capable of assuming many different shapes (not after the Proteobacteria genus ''Proteus''). In 2021 the Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomally Synthesized And Post-translationally Modified Peptides
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs), also known as ribosomal natural products, are a diverse class of natural products of ribosomal origin. Consisting of more than 20 sub-classes, RiPPs are produced by a variety of organisms, including prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea, and they possess a wide range of biological functions. As a consequence of the falling cost of genome sequencing and the accompanying rise in available genomic data, scientific interest in RiPPs has increased in the last few decades. Because the chemical structures of RiPPs are more closely predictable from genomic data than are other natural products (e.g. alkaloids, terpenoids), their presence in sequenced organisms can, in theory, be identified rapidly. This makes RiPPs an attractive target of modern natural product discovery efforts. Definition RiPPs consist of any peptides (i.e. molecular weight below 10 kDa) that are ribosomally-produced and undergo some degree of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystis
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming ''Microcystis aeruginosa''. Many members of a ''Microcystis'' community can produce neurotoxins and hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Communities are often a mix of toxin-producing and nonproducing isolates. Etymology The genus ''Microcystis'' derives from the Greek ''mikros'' (small) + ''kystis'' (bladder) Physical characteristics As the etymological derivation implies, ''Microcystis'' is characterized by small cells (a few micrometre, micrometers in diameter), possessing gas-filled vesicles (also lacking individual sheaths). The cells are usually organized into colonies (aggregations of which are visible with the naked eye) that begin in a spherical shape, losing coherence to become perforated or irregularly shaped over time. These colonies are bound by a thick mucilage composed of complex polysaccharide compounds, including xylose, mannose, glucose, fuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depsipeptide
A depsipeptide is a peptide in which one or more of its amide, -C(O)NHR-, groups are replaced by the corresponding ester, -C(O)OR, Many depsipeptides have both peptide and ester linkages. Elimination of the N–H group in a peptide structure results in a decrease of H-bonding capability, which is responsible for secondary structure and folding patterns of peptides, thus inducing structural deformation of the helix and b-sheet structures. Because of decreased resonance delocalization in esters relative to amides, depsipeptides have lower rotational barriers for cis-trans isomerization and therefore they have more flexible structures than their native analogs. They are mainly found in marine and microbial natural products. Depsipeptide natural products 222px, Enterochelin is a depsipeptide that is an iron-transporter. Several depsipeptides have been found to exhibit anti-cancer properties. A depsipeptide enzyme inhibitor includes romidepsin, a member of the bicyclic peptide class, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
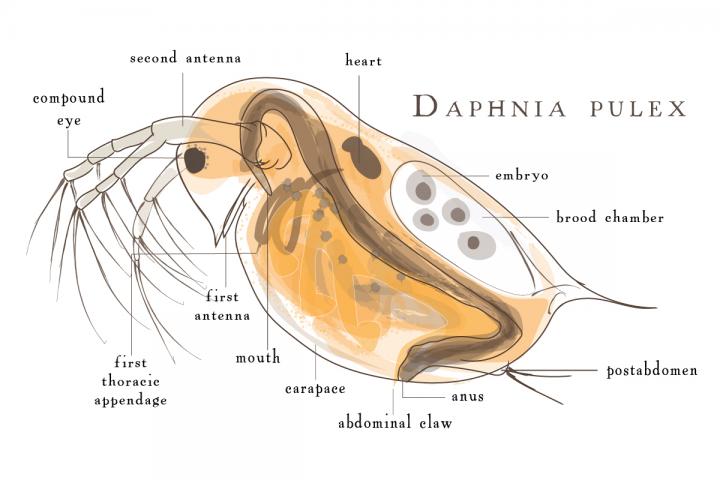
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotoxin
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they exponential growth, reproduce exponentially to form Algal bloom, blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanopeptolin
Cyanopeptolins (CPs) are a class of oligopeptides produced by Microcystis and Planktothrix algae strains, and can be neurotoxic. The production of cyanopeptolins occurs through nonribosomal peptides synthases (NRPS). Chemistry CPs are, in general, a six-residue peptide formed into a ring by a beta-lactone bridge, making them chemically depsipeptides (peptidolactones). The first position is usually threonine, which links to one or two residues via an ester bound on the beta-hydroxyl group; the third position is conserved to be 3-amino-6-hydroxy-2-piperidone (Ahp) or a derivative. All other positions are highly variable. There is not a single, unified nomenclature, for CPs. Names such as CP1020 and CP1138 refer to the molar mass. Others, such as aeruginopeptins, micropeptins, microcystilide, nostopeptins, and oscillapeptins, refer to the organism the substance is originally found in. Factors affecting production Increased water temperatures, because of climate change and eutrophica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |