|
Metalog Distribution
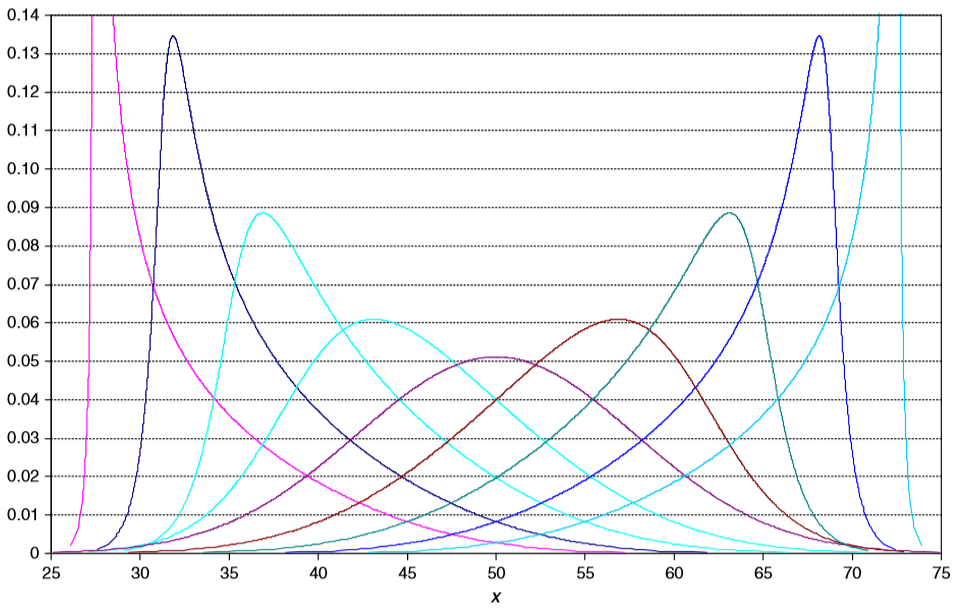
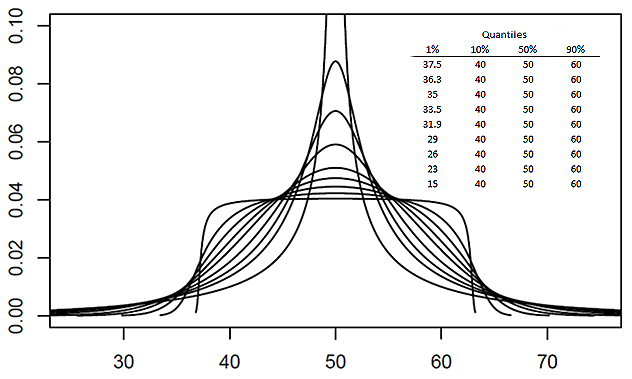
The metalog distribution is a flexible continuous probability distribution designed for ease of use in practice. Together with its transforms, the metalog family of continuous distributions is unique because it embodies ''all'' of following properties: virtually unlimited shape flexibility; a choice among unbounded, semi-bounded, and bounded distributions; ease of fitting to data with linear least squares; simple, closed-form quantile function (inverse CDF) equations that facilitate simulation; a simple, closed-form PDF; and Bayesian updating in closed form in light of new data. Moreover, like a Taylor series, metalog distributions may have any number of terms, depending on the degree of shape flexibility desired and other application needs. Applications where metalog distributions can be useful typically involve fitting empirical data, simulated data, or expert-elicited quantiles to smooth, continuous probability distributions. Fields of application are wide-ranging, and inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantile-parameterized Distribution
Quantile-parameterized distributions (QPDs) are probability distributions that are directly parameterized by data. They were motivated by the need for easy-to-use continuous probability distributions flexible enough to represent a wide range of uncertainties, such as those commonly encountered in business, economics, engineering, and science. Because QPDs are directly parameterized by data, they have the practical advantage of avoiding the intermediate step of parameter estimation, a time-consuming process that typically requires non-linear iterative methods to estimate probability-distribution parameters from data. Some QPDs have virtually unlimited shape flexibility and closed-form moments as well. History The development of quantile-parameterized distributions was inspired by the practical need for flexible continuous probability distributions that are easy to fit to data. Historically, the Pearson and Johnson families of distributions have been used when shape flexibility is ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Uniform Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of symmetric probability distributions. The distribution describes an experiment where there is an arbitrary outcome that lies between certain bounds. The bounds are defined by the parameters, ''a'' and ''b'', which are the minimum and maximum values. The interval can either be closed (e.g. , b or open (e.g. (a, b)). Therefore, the distribution is often abbreviated ''U'' (''a'', ''b''), where U stands for uniform distribution. The difference between the bounds defines the interval length; all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. It is the maximum entropy probability distribution for a random variable ''X'' under no constraint other than that it is contained in the distribution's support. Definitions Probability density function The probability density function of the continuous uniform distribution is: : f(x)=\begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Regression
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is called '' simple linear regression''; for more than one, the process is called multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, where multiple correlated dependent variables are predicted, rather than a single scalar variable. In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimated from the data. Such models are called linear models. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, linear regression focuses on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Least Squares
Linear least squares (LLS) is the least squares approximation of linear functions to data. It is a set of formulations for solving statistical problems involved in linear regression, including variants for ordinary (unweighted), weighted, and generalized (correlated) residuals. Numerical methods for linear least squares include inverting the matrix of the normal equations and orthogonal decomposition methods. Main formulations The three main linear least squares formulations are: * Ordinary least squares (OLS) is the most common estimator. OLS estimates are commonly used to analyze both experimental and observational data. The OLS method minimizes the sum of squared residuals, and leads to a closed-form expression for the estimated value of the unknown parameter vector ''β'': \hat = (\mathbf^\mathsf\mathbf)^ \mathbf^\mathsf \mathbf, where \mathbf is a vector whose ''i''th element is the ''i''th observation of the dependent variable, and \mathbf is a matrix whose ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by an ''upwards continuous'' ''monotonic increasing'' cumulative distribution function F : \mathbb R \rightarrow ,1/math> satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from minus infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable X takes on a value less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Analysis
Decision analysis (DA) is the discipline comprising the philosophy, methodology, and professional practice necessary to address important decisions in a formal manner. Decision analysis includes many procedures, methods, and tools for identifying, clearly representing, and formally assessing important aspects of a decision; for prescribing a recommended course of action by applying the maximum expected-utility axiom to a well-formed representation of the decision; and for translating the formal representation of a decision and its corresponding recommendation into insight for the decision maker, and other corporate and non-corporate stakeholders. History In 1931, mathematical philosopher Frank Ramsey pioneered the idea of subjective probability as a representation of an individual’s beliefs or uncertainties. Then, in the 1940s, mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern developed an axiomatic basis for utility theory as a way of expressing an individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurtosis
In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis (from el, κυρτός, ''kyrtos'' or ''kurtos'', meaning "curved, arching") is a measure of the "tailedness" of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. Like skewness, kurtosis describes a particular aspect of a probability distribution. There are different ways to quantify kurtosis for a theoretical distribution, and there are corresponding ways of estimating it using a sample from a population. Different measures of kurtosis may have different interpretations. The standard measure of a distribution's kurtosis, originating with Karl Pearson, is a scaled version of the fourth moment of the distribution. This number is related to the tails of the distribution, not its peak; hence, the sometimes-seen characterization of kurtosis as "peakedness" is incorrect. For this measure, higher kurtosis corresponds to greater extremity of deviations (or outliers), and not the configuration of data near the mean. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skewness
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean. The skewness value can be positive, zero, negative, or undefined. For a unimodal distribution, negative skew commonly indicates that the ''tail'' is on the left side of the distribution, and positive skew indicates that the tail is on the right. In cases where one tail is long but the other tail is fat, skewness does not obey a simple rule. For example, a zero value means that the tails on both sides of the mean balance out overall; this is the case for a symmetric distribution, but can also be true for an asymmetric distribution where one tail is long and thin, and the other is short but fat. Introduction Consider the two distributions in the figure just below. Within each graph, the values on the right side of the distribution taper differently from the values on the left side. These tapering sides are called ''tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the ''arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the ''sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the ''population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions of mean are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Lloyd Johnson
Norman Lloyd Johnson (9 January 1917, Ilford, Essex, England – 18 November 2004, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, United States) was a professor of statistics and author or editor of several standard reference works in statistics and probability theory. Education Johnson attended Ilford County High School, and went on to University College London, where he obtained a B.Sc. in mathematics 1936 and a B.Sc. and M.Sc. in statistics in 1937 and 1938. Career On qualification in 1938, Johnson was appointed Assistant Lecturer in the Department of Statistics at UCL. During World War II, he served under his former Professor Egon Pearson as an Experimental Officer with the Ordnance Board. He returned to the Statistics Department at UCL in 1945 and stayed there until 1962, as Assistant Lecturer, Lecturer and then Reader. In 1948 he was awarded a Ph.D. in Statistics for his work on the Johnson system of frequency curves. In 1949 he became a Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries. Two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the ''F''-distribution or F-ratio, also known as Snedecor's ''F'' distribution or the Fisher–Snedecor distribution (after Ronald Fisher and George W. Snedecor) is a continuous probability distribution that arises frequently as the null distribution of a test statistic, most notably in the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and other ''F''-tests. Definition The F-distribution with ''d''1 and ''d''2 degrees of freedom is the distribution of : X = \frac where S_1 and S_2 are independent random variables with chi-square distributions with respective degrees of freedom d_1 and d_2. It can be shown to follow that the probability density function (pdf) for ''X'' is given by : \begin f(x; d_1,d_2) &= \frac \\ pt&=\frac \left(\frac\right)^ x^ \left(1+\frac \, x \right)^ \end for real ''x'' > 0. Here \mathrm is the beta function. In many applications, the parameters ''d''1 and ''d''2 are positive integers, but the distribution is well-def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |