|
MESSENGER
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging", and a reference to the messenger god Mercury from Roman mythology. ''MESSENGER'' was launched aboard a Delta II rocket in August 2004. Its path involved a complex series of flybys – the spacecraft flew by Earth once, Venus twice, and Mercury itself three times, allowing it to decelerate relative to Mercury using minimal fuel. During its first flyby of Mercury in January 2008, ''MESSENGER'' became the second mission, after Mariner 10 in 1975, to reach Mercury. ''MESSENGER'' entered orbit around Mercury on March 18, 2011, becoming the first spacecraft to do so. It successfully completed its primary mission in 2012. Following two mission extensions, the spacecraft used the last of its maneuvering propellant to deo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESSENGER Probe
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging", and a reference to the messenger god Mercury from Roman mythology. ''MESSENGER'' was launched aboard a Delta II rocket in August 2004. Its path involved a complex series of flybys – the spacecraft flew by Earth once, Venus twice, and Mercury itself three times, allowing it to decelerate relative to Mercury using minimal fuel. During its first flyby of Mercury in January 2008, ''MESSENGER'' became the second mission, after Mariner 10 in 1975, to reach Mercury. ''MESSENGER'' entered orbit around Mercury on March 18, 2011, becoming the first spacecraft to do so. It successfully completed its primary mission in 2012. Following two mission extensions, the spacecraft used the last of its maneuvering propellant to deorbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the Sun. Its orbit around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the shortest of all the Sun's planets. It is named after the Roman god ' ( Mercury), god of commerce, messenger of the gods, and mediator between gods and mortals, corresponding to the Greek god Hermes (). Like Venus, Mercury orbits the Sun within Earth's orbit as an inferior planet, and its apparent distance from the Sun as viewed from Earth never exceeds 28°. This proximity to the Sun means the planet can only be seen near the western horizon after sunset or the eastern horizon before sunrise, usually in twilight. At this time, it may appear as a bright star-like object, but is more difficult to observe than Venus. From Earth, the planet telescopically displays the complete range of phases, similar to Venus and the Moon, which recurs over its synodic period of approximately 116 days. The synodic proximity of Mercury to Earth makes Mercury most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
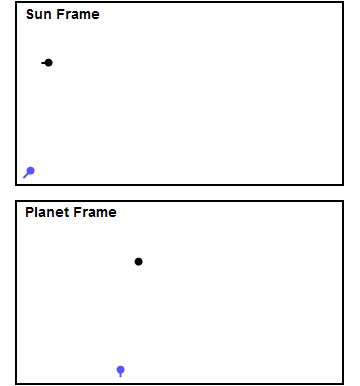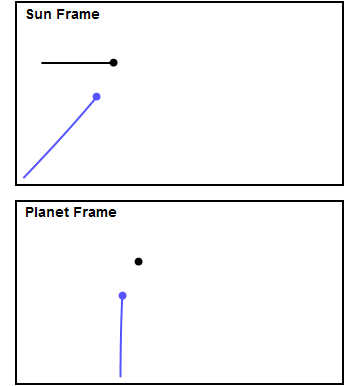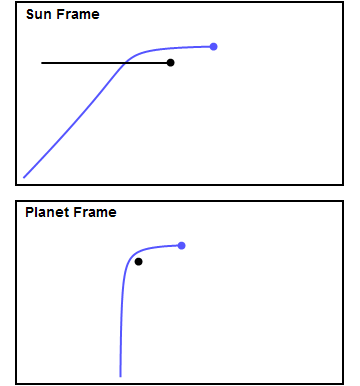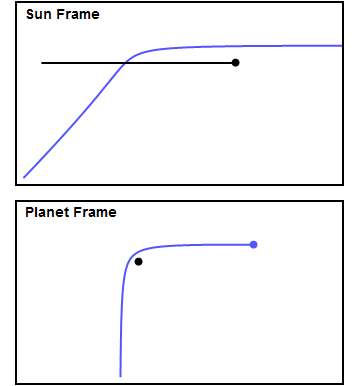
Hermiocentric Orbit
Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the Sun. Its orbit around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the shortest of all the Sun's planets. It is named after the Roman god ' (Mercury), god of commerce, messenger of the gods, and mediator between gods and mortals, corresponding to the Greek god Hermes (). Like Venus, Mercury orbits the Sun within Earth's orbit as an inferior planet, and its apparent distance from the Sun as viewed from Earth never exceeds 28°. This proximity to the Sun means the planet can only be seen near the western horizon after sunset or the eastern horizon before sunrise, usually in twilight. At this time, it may appear as a bright star-like object, but is more difficult to observe than Venus. From Earth, the planet telescopically displays the complete range of phases, similar to Venus and the Moon, which recurs over its synodic period of approximately 116 days. The synodic proximity of Mercury to Earth makes Mercury most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury's Magnetic Field
Mercury's magnetic field is approximately a magnetic dipole (meaning the field has only two magnetic poles) apparently global, on planet Mercury. Data from ''Mariner 10'' led to its discovery in 1974; the spacecraft measured the field's strength as 1.1% that of Earth's magnetic field. The origin of the magnetic field can be explained by dynamo theory. The magnetic field is strong enough near the bow shock to slow the solar wind, which induces a magnetosphere. Strength The magnetic field is about 1.1% as strong as Earth's. At the Hermean equator, the relative strength of the magnetic field is around 300 nT, which is weaker than that of Jupiter's moon Ganymede. Mercury's magnetic field is weaker than Earth's because its core had cooled and solidified more quickly than Earth's. Although Mercury's magnetic field is much weaker than Earth's magnetic field, it is still strong enough to deflect the solar wind, inducing a magnetosphere. Because Mercury's magnetic field is weak whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
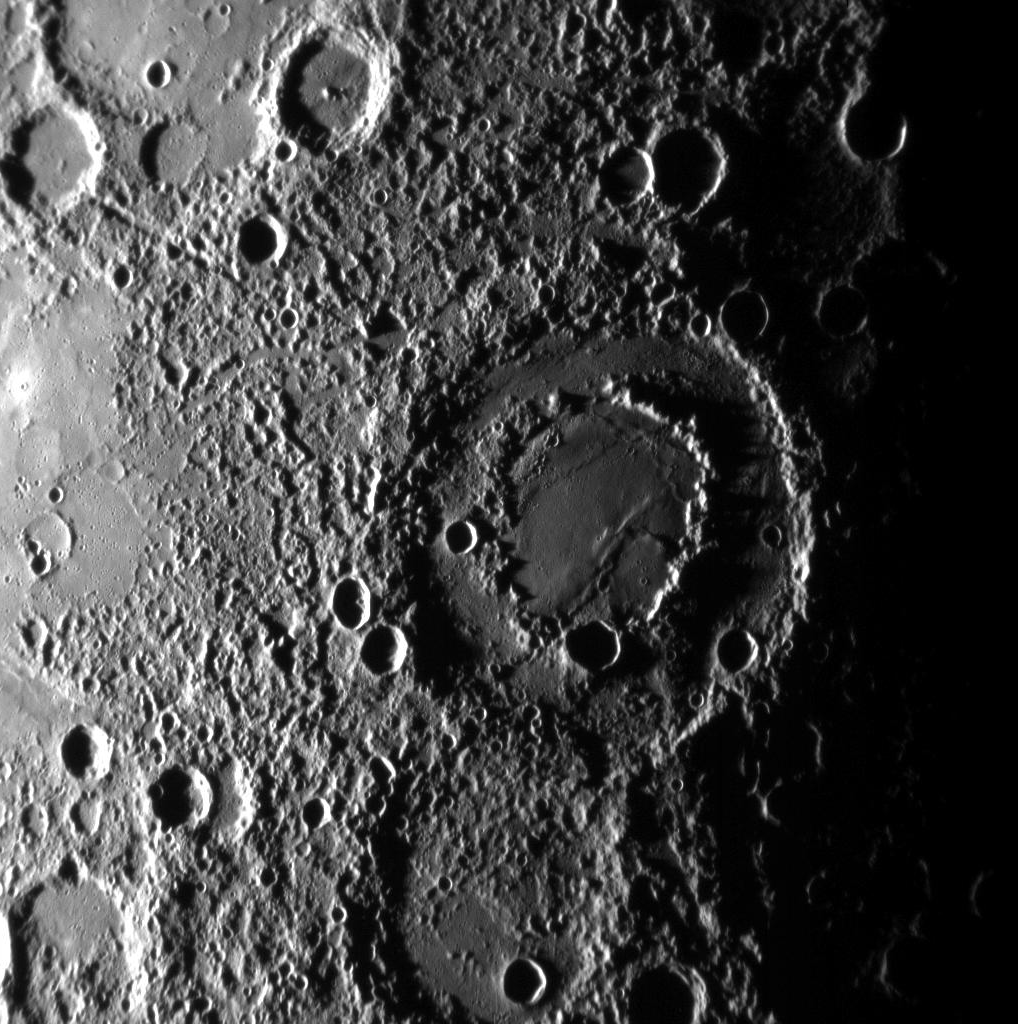
Geology Of Mercury
The geology of Mercury is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mercury. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. Historically, Mercury has been the least understood of all the terrestrial planets in the Solar System. This stems largely from its proximity to the Sun which makes reaching it with spacecraft technically challenging and Earth-based observations difficult. For decades, the principal source of geologic information about Mercury came from the 2,700 images taken by the Mariner 10 spacecraft during three flybys of the planet from 1974 to 1975. These images covered about 45% of the planet’s surface, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Assist
In orbital mechanics and aerospace engineering, a gravitational slingshot, gravity assist maneuver, or swing-by is the use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense. Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and velocity by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon and it was used by interplanetary probes from Mariner 10 onward, including the two Voyager probes' notable flybys of Jupiter and Saturn. Explanation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sean Solomon
Sean Carl Solomon (born October 24, 1945) is the director of the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University, where he is also the William B. Ransford Professor of Earth and Planetary Science. Before moving to Columbia in 2012, he was the director of the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism at the Carnegie Institute in Washington, D.C. His research area is in geophysics, including the fields of planetary geology, seismology, marine geophysics, and geodynamics. Solomon is the principal investigator on the NASA MESSENGER mission to Mercury. He is also a team member on the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory mission and the Plume-Lithosphere Undersea Melt Experiment (PLUME). Education Solomon was born in Los Angeles, California on October 24, 1945. Solomon received his B.S. from the California Institute of Technology, and his Ph.D. in geophysics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1971. Career From 1972 through 1992 he was an assistant, asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Aeronautics And Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never far from the Sun, either as morning star or evening star. Aside from the Sun and Moon, Venus is the brightest natural object in Earth's sky, capable of casting visible shadows on Earth at dark conditions and being visible to the naked eye in broad daylight. Venus is the second largest terrestrial object of the Solar System. It has a surface gravity slightly lower than on Earth and has a very weak induced magnetosphere. The atmosphere of Venus, mainly consists of carbon dioxide, and is the densest and hottest of the four terrestrial planets at the surface. With an atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface of about 92 times the sea level pressure of Earth and a mean temperature of , the carbon dioxide gas at Venus's surface is in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion. The Solar System has at least eight planets: the terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets each rotate around an axis tilted with respect to its orbital pole. All of them possess an atmosphere, although that of Mercury is tenuous, and some share such features as ice caps, seasons, volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology. Apart from Venus and Mars, the Solar System planets generate magnetic fields, and all except Venus and Mercury have natural satellites. The giant planets bear plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station is the primary launch site for the Space Force's Eastern RangeCAST 1999, p. 1-12. with three launch pads currently active (Space Launch Complexes 37B, 40, and 41). The facility is south-southeast of NASA's Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, with the two linked by bridges and causeways. The Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Skid Strip provides a runway close to the launch complexes for military airlift aircraft delivering heavy and outsized payloads to the Cape. A number of American space exploration pioneers were launched from CCSFS, including the first U.S. Earth satellite (1958), first U.S. astronaut (1961), first U.S. astronaut in orbit (1962), first two-man U.S. spacecraft (1965), first U.S. unmanned lunar lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |