|
Meadow Jumping Mouse
The meadow jumping mouse (''Zapus hudsonius'') is the most widely distributed mouse in the family Zapodidae. Its range extends from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Great Plains west, and from the arctic tree lines in Canada and Alaska to the north, and Georgia, Alabama, Arizona, and New Mexico to the south. In mid-2014, the New Mexico subspecies of the meadow jumping mouse, ''Zapus hudsonius luteus'', was listed as an endangered species under the federal Endangered Species Act.Meadow jumping mouse is not ‘resilient’ Albuquerque Journal, July 4, 2014 Albuquerque Journal, June 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
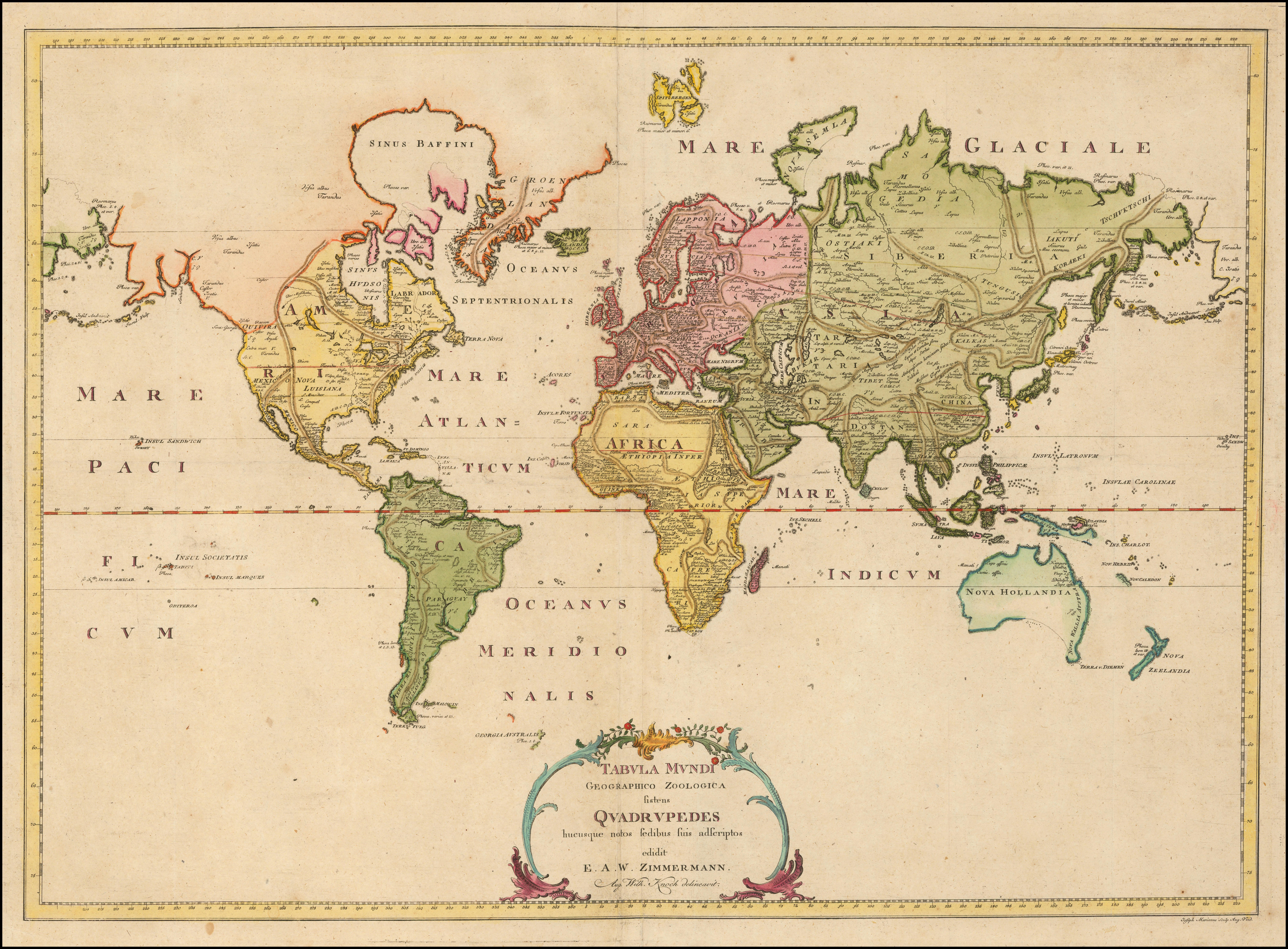
Eberhard August Wilhelm Von Zimmermann
Eberhardt August Wilhelm von Zimmermann (August 17, 1743, Uelzen – July 4, 1815, Braunschweig) was a German geographer and zoologist. He studied natural philosophy and mathematics in Leiden, Halle an der Saale, Halle, Berlin, and Göttingen, and in 1766 was appointed professor of mathematics and natural sciences at the TU Braunschweig, Collegium Carolinum in Braunschweig. One of his pupils was mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. From 1789 onward, he served as aulic councillor in Braunschweig. at Deutsche BiographieThibaut - Zycha, Volume 10 by K. G. Saur Verlag GmbH & Company, Walter De Gruyter Incorporated During his career, he travelled widely throughout Europe — Livon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrion Beetle
Silphidae is a family of beetles that are known commonly as large carrion beetles, carrion beetles or burying beetles. There are two subfamilies: Silphinae and Nicrophorinae. Nicrophorines are sometimes known as sexton beetles. The number of species is relatively small at around two hundred. They are more diverse in the temperate region although a few tropical endemics are known. Both subfamilies feed on decaying organic matter such as dead animals. The subfamilies differ in which uses parental care and which types of carcasses they prefer. Silphidae are considered to be of importance to forensic entomologists because when they are found on a decaying body they are used to help estimate a post-mortem interval. Taxonomy, evolution, and etymology The family Silphidae belongs to the order Coleoptera. They are commonly referred to as carrion beetles or burying beetles and are usually associated with carrion, fungi, and dung. In the past, members of the family Agyrtidae were included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Bugs
Coccinellidae () is a widespread family of small beetles ranging in size from . They are commonly known as ladybugs in North America and ladybirds in Great Britain. Some entomologists prefer the names ladybird beetles or lady beetles as they are not true bugs. Many of the species have conspicuous aposematic colours and patterns, such as red with black spots, that warn potential predators that they are distasteful. The majority of the more than 6,000 described species are generally considered beneficial insects, because many prey on herbivorous hemipterans such as aphids or scale insects, which are agricultural pests. Many coccinellids lay their eggs directly in aphid and scale insect colonies, ensuring their larvae have an immediate food source. However, some species such as the herbivorous Mexican bean beetle are agricultural pests. Etymology The name ''coccinellids'', created by Pierre André Latreille, is derived from the Latin word ''coccineus'' meaning "scarlet". The na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material. A large percentage of herbivores have mutualistic gut flora that help them digest plant matter, which is more difficult to digest than animal prey. This flora is made up of cellulose-digesting protozoans or bacteria. Etymology Herbivore is the anglicized form of a modern Latin coinage, ''herbivora'', cited in Charles Lyell's 1830 ''Principles of Geology''.J.A. Simpson and E.S.C. Weiner, eds. (2000) ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. 8, p. 155. Richard Owen employed the anglicized term in an 1854 work on fossil teeth and skeletons. ''Herbivora'' is derived from Latin ''herba' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granivore
Seed predation, often referred to as granivory, is a type of plant-animal interaction in which granivores (seed predators) feed on the seeds of plants as a main or exclusive food source,Hulme, P.E. and Benkman, C.W. (2002) "Granivory", pp. 132–154 in ''Plant animal Interactions: An Evolutionary Approach'', ed. C.M. Herrera and O. Pellmyr. Oxford: Blackwell. . in many cases leaving the seeds damaged and not viable. Granivores are found across many families of vertebrates (especially mammals and birds) as well as invertebrates (mainly insects); thus, seed predation occurs in virtually all terrestrial ecosystems. Seed predation is commonly divided into two distinctive temporal categories, pre-dispersal and post-dispersal predation, which affect the fitness of the parental plant and the dispersed offspring (the seed), respectively. Mitigating pre- and post-dispersal predation may involve different strategies. To counter seed predation, plants have evolved both physical defenses (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most commonly occurs during winter months. Although traditionally reserved for "deep" hibernators such as rodents, the term has been redefined to include animals such as bears and is now applied based on active metabolic suppression rather than any absolute decline in body temperature. Many experts believe that the processes of daily torpor and hibernation form a continuum and utilise similar mechanisms. The equivalent during the summer months is aestivation. Hibernation functions to conserve energy when sufficient food is not available. To achieve this energy saving, an endothermic animal decreases its metabolic rate and thereby its body temperature. Hibernation may last days, weeks, or months—depending on the species, ambient temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
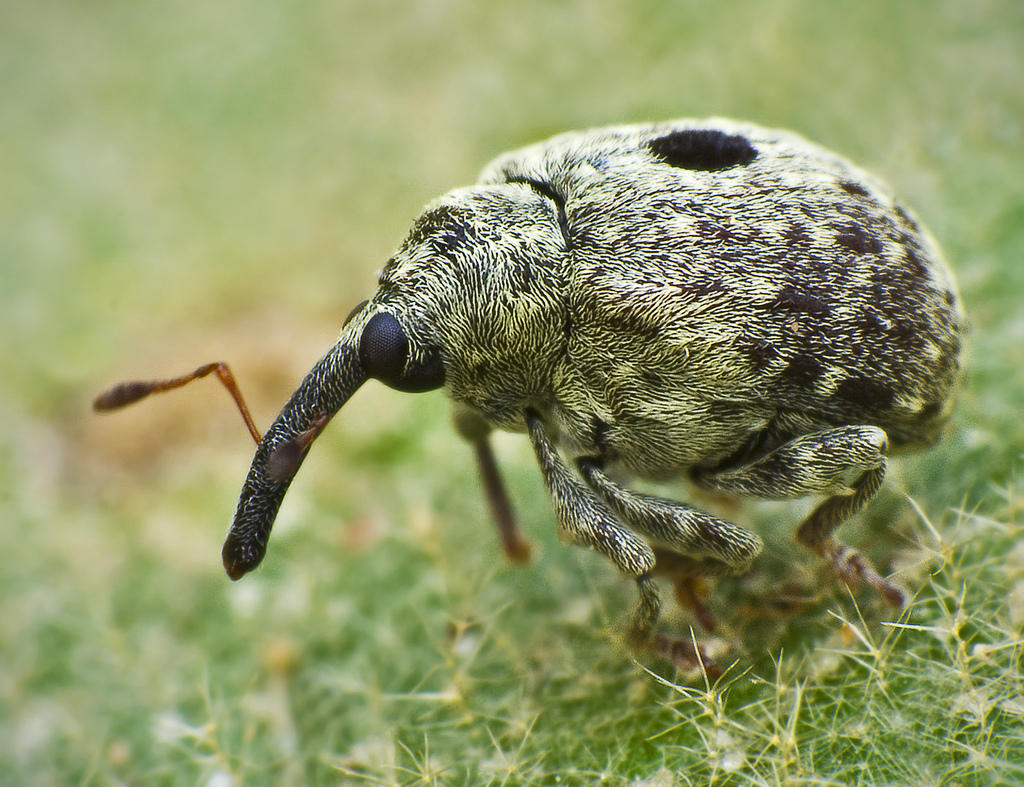
Curculionidae
The Curculionidae are a family of weevils, commonly called snout beetles or true weevils. They are one of the largest animal families, with 6,800 genera and 83,000 species described worldwide. They are the sister group to the family Brentidae. They include the bark beetles as the subfamily Scolytinae, which are modified in shape in accordance with their wood-boring lifestyle. They do not much resemble other weevils, so they were traditionally considered a distinct family, Scolytidae. The family also includes the ambrosia beetles, of which the present-day subfamily Platypodinae was formerly considered the distinct family Platypodidae. Description Adult Curculionidae can be recognised by the well-developed, downwards-curved snout (rostrum) possessed by many species, though the rostrum is sometimes short (e.g. Entiminae). They have elbowed antennae that end in clubs, and the first antennal segment often fits into a groove in the side of the rostrum. The body tends to be robus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carabidae
Ground beetles are a large, cosmopolitan family of beetles, the Carabidae, with more than 40,000 species worldwide, around 2,000 of which are found in North America and 2,700 in Europe. As of 2015, it is one of the 10 most species-rich animal families. They belong to the Adephaga. Members of the family are primarily carnivorous, but some members are phytophagous or omnivorous. Description and ecology Although their body shapes and coloring vary somewhat, most are shiny black or metallic and have ridged wing covers (elytra). The elytra are fused in some species, particularly the large Carabinae, rendering the beetles unable to fly. The species ''Mormolyce phyllodes'' is known as violin beetle due to their peculiarly shaped elytra. All carabids except the quite primitive flanged bombardier beetles (Paussinae) have a groove on their fore leg tibiae bearing a comb of hairs used for cleaning their antennae. Defensive secretions Typical for the ancient beetle suborder Adephaga to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite. Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed senses of hearing, smell, and specially adapted eyesight. Some animals, such as cats and ferrets, have eyes that can adapt to both low-level and bright day levels of illumination (see metaturnal). Others, such as bushbabies and (some) bats, can function only at night. Many nocturnal creatures including tarsiers and some owls have large eyes in comparison with their body size to compensate for the lower light levels at night. More specifically, they have been found to have a larger cornea relative to their eye size than diurnal creatures to increase their : in the low-light conditions. Nocturnality helps wasps, such as ''Apoica flavissima'', avoid hunting in intense sunlight. Diurnal animals, including squirrels and songbirds, are active du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_grazing_-_20050809.jpg)





