|
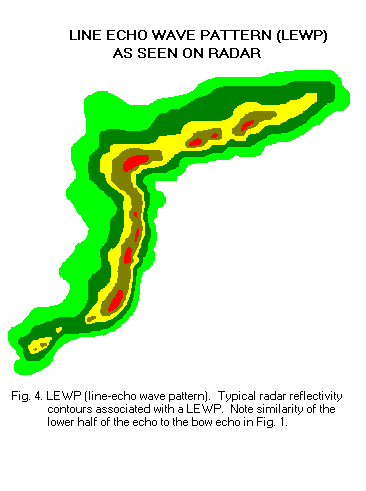
Line Echo Wave Pattern
A line echo wave pattern (LEWP) is a weather radar formation in which a single line of thunderstorms presenting multiple bow echoes forms south (or equatorward) of a mesoscale low-pressure area with a rotating "head". LEWP often are associated with a multiple-bow serial derecho and often produce tornadoes, some of which can be strong. The existence of a LEWP on radar means that a serial derecho has developed or is likely to develop soon, much as a hook echo indicates the same for a tornado. Formation A LEWP, according to the NWS, is defined as "a squall line that has developed into a wave-like pattern due to acceleration at one end of the line and deceleration along the portion immediately adjacent." A LEWP is an extension of the concept of the bow echo, which usually indicates a powerful convective windstorm. Areas hit by the apices of bows often see the worst weather, with the highest winds and very heavy rain. However, if the sides of the bows reach enough of an orientati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Echo Wave Pattern
A line echo wave pattern (LEWP) is a weather radar formation in which a single line of thunderstorms presenting multiple bow echoes forms south (or equatorward) of a mesoscale low-pressure area with a rotating "head". LEWP often are associated with a multiple-bow serial derecho and often produce tornadoes, some of which can be strong. The existence of a LEWP on radar means that a serial derecho has developed or is likely to develop soon, much as a hook echo indicates the same for a tornado. Formation A LEWP, according to the NWS, is defined as "a squall line that has developed into a wave-like pattern due to acceleration at one end of the line and deceleration along the portion immediately adjacent." A LEWP is an extension of the concept of the bow echo, which usually indicates a powerful convective windstorm. Areas hit by the apices of bows often see the worst weather, with the highest winds and very heavy rain. However, if the sides of the bows reach enough of an orientati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squall Line
A squall line, or more accurately a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS), is a line of thunderstorms, often forming along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front (which often are accompanied by abrupt and gusty wind shifts). Linear thunderstorm structures often contain heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and occasionally tornadoes or waterspouts. Particularly strong straight-line winds can occur where the linear structure forms into the shape of a bow echo. Tornadoes can occur along waves within a line echo wave pattern (LEWP), where mesoscale low-pressure areas are present. Some bow echoes can grow to become derechos as they move swiftly across a large area. On the back edge of the rainband associated with mature squall lines, a wake low can be present, on very rare occasions associated with a heat burst. Theory Polar front theory was developed by Jacob Bjerknes, derived from a dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derecho
A ''derecho'' (, from es, derecho, link=no , 'straight') is a widespread, long-lived, straight-line wind storm that is associated with a fast-moving group of severe thunderstorms known as a mesoscale convective system. Derechos can cause hurricanic and tornadic-force winds, heavy rains, and flash floods. In many cases, convection-induced winds take on a bow echo (backward "C") form of squall line, often forming beneath an area of diverging upper tropospheric winds, and in a region of both rich low-level moisture and warm-air advection. Derechos move rapidly in the direction of movement of their associated storms, similar to an outflow boundary (gust front), except that the wind remains sustained for a greater period of time (often increasing in strength after onset), and may exceed hurricane-force. A derecho-producing convective system may remain active for many hours and, occasionally, over multiple days. A warm-weather phenomenon, derechos occur mostly in summer, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Meteorology
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the intensity of the precipitation. Both types of data can be analyzed to determine the structure of storms and their potential to cause severe weather. During World War II, radar operators discovered that weather was causing echoes on their screen, masking potential enemy targets. Techniques were developed to filter them, but scientists began to study the phenomenon. Soon after the war, surplus radars were used to detect precipitation. Since then, weather radar has evolved on its own and is now used by national weather services, research departments in universities, and in television stations' weather departments. Raw images are routinely used and specialize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear-inflow Jet
The rear-inflow jet is a component of bow echoes in a mesoscale convective system that aids in creating a stronger cold pool and downdraft. The jet forms as a response to a convective circulation having upshear tilt and horizontal pressure gradients. The cold pool that comes from the outflow of a storm forms an area of high pressure at the surface. In response to the surface high and warmer temperatures aloft due to convection, a mid-level mesolow forms behind the leading edge of the storm. With a mid-level area of low pressure, air is drawn in under the trailing stratiform region of precipitation. As air is drawn in on the rear side of the storm, it begins to descend as it approaches the front line of the cells. Before reaching the leading edge, the jet descends to the surface as a strong downdraft, creating straight-line winds. Any mature mesoscale convective system is capable of developing its own rear-inflow jet, but questions remain as to what influences the strength of the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolow
A squall is a sudden, sharp increase in wind speed lasting minutes, as opposed to a wind gust, which lasts for only seconds. They are usually associated with active weather, such as rain showers, thunderstorms, or heavy snow. Squalls refer to the increase of the sustained winds over that time interval, as there may be higher gusts during a squall event. They usually occur in a region of strong sinking air or cooling in the mid-atmosphere. These force strong localized upward motions at the leading edge of the region of cooling, which then enhances local downward motions just in its wake. Etymology There are different versions of the word's origins: * By one version, the word appears to be Nordic in origin, but its etymology is considered obscure. It probably has its roots in the word ''skvala'' an Old Norse word meaning literally ''to squeal''. * By another version, it is an alteration of ''squeal'' influenced by ''bawl''. Character of the wind The term "squall" is used to refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoscale Convective Vortex
A mesovortex is a small-scale rotational feature found in a Thunderstorm, convective storm, such as a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS, i.e. squall line), a supercell, or the eyewall of a tropical cyclone. Mesovortices range in diameter from tens of miles to a mile or less and can be immensely intense. Eyewall mesovortex An ''eyewall mesovortex'' is a small-scale rotational feature found in an eyewall of an intense tropical cyclone. Eyewall mesovortices are similar, in principle, to small "suction vortices" often observed in Multiple vortex tornado, multiple-vortex tornadoes. In these vortices, wind speed can be up to 10% higher than in the rest of the eyewall. Eyewall mesovortices are most common during periods of intensification in tropical cyclones. Eyewall mesovortices often exhibit unusual behavior in tropical cyclones. They usually revolve around the low pressure center, but sometimes they remain stationary. Eyewall mesovortices have even been documented to cross the eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoscale Convective Complex
A mesoscale convective complex (MCC) is a unique kind of mesoscale convective system which is defined by characteristics observed in infrared satellite imagery. They are long-lived, often form nocturnally, and commonly contain heavy rainfall, wind, hail, lightning, and possibly tornadoes. Size A mesoscale convective complex has either an area of cloud top of 100,000 km2 or greater with temperature less than or equal to −32 °C, or an area of cloud top of 50,000 km2 with temperature less than or equal to −52 °C. Size definitions must be met for 6 hours or greater. Its maximum extent is defined as when cloud shield reaches maximum area. Its eccentricity (minor axis/major axis) is greater than or equal to 0.7 at maximum extent. Development MCCs commonly develop from the merging of thunderstorms into a squall line which eventually meet the MCC criteria. Furthermore, some MCC formation can be tracked from the plains in Colorado back to the Rocky Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoscale Convective System
A mesoscale convective system (MCS) is a complex of thunderstorms that becomes organized on a scale larger than the individual thunderstorms but smaller than extratropical cyclones, and normally persists for several hours or more. A mesoscale convective system's overall cloud and precipitation pattern may be round or linear in shape, and include weather systems such as tropical cyclones, squall lines, lake-effect snow events, polar lows, and mesoscale convective complexes (MCCs), and generally forms near weather fronts. The type that forms during the warm season over land has been noted across North and South America, Europe, and Asia, with a maximum in activity noted during the late afternoon and evening hours. Forms of MCS that develop within the tropics use either the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) or monsoon troughs as a focus for their development, generally within the warm season between spring and fall. One exception is that of lake-effect snow bands, which form d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convective Storm Detection
Convective storm detection is the meteorological observation, and short-term prediction, of deep moist convection (DMC). DMC describes atmospheric conditions producing single or clusters of large vertical extension clouds ranging from cumulus congestus to cumulonimbus, the latter producing thunderstorms associated with lightning and thunder. Those two types of clouds can produce severe weather at the surface and aloft. The ability to discern the presence of deep moist convection in a storm significantly improves meteorologists' capacity to predict and monitor associated phenomena such as tornadoes, large hail, strong winds, and heavy rain leading to flash flooding. It relies on direct eyewitness observations, for example from storm spotters; and on remote sensing, especially weather radar. Some in situ measurements are used for direct detection as well, notably, wind speed reports from surface observation stations. It is part of the ''integrated warning system'', consisting of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook Echo
A hook echo is a pendant or hook-shaped weather radar signature as part of some supercell thunderstorms. It is found in the lower portions of a storm as air and precipitation flow into a mesocyclone, resulting in a curved feature of reflectivity. The echo is produced by rain, hail, or even debris being wrapped around the supercell. It is one of the classic hallmarks of tornado-producing supercells. The National Weather Service may consider the presence of a hook echo coinciding with a tornado vortex signature as sufficient to justify issuing a tornado warning. History Because of the unpredictable and potentially catastrophic nature of tornadoes, the possibility of detecting tornadoes via radar was discussed in the meteorological community in the earliest days of meteorological radar.Huff, F.A., H.W. Hiser, and S.G. Bigler, 1954Study of an Illinois tornado using radar, synoptic weather and field survey data Report of Investigation 22, Champaign, IL, pp. 73 The first association bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields. Flash floods may also occur after the collapse of a natural ice or debris dam, or a human structure such as a man-made dam, as occurred before the Johnstown Flood of 1889. Flash floods are distinguished from regular floods by having a timescale of fewer than six hours between rainfall and the onset of flooding. Flash floods are a significant hazard, causing more fatalities in the U.S. in an average year than lightning, tornadoes, or hurricanes. Flash floods can also deposit large quantities of sediments on floodplains and can be destructive of vegetation cover not adapted to frequent flood conditions. Causes Flash floods most often occur in dry areas that have recently received precipitation, but they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_eye_close-up.jpg)