|
Levitating
Levitation (from Latin ''levitas'' "lightness") is the process by which an object is held aloft in a stable position, without mechanical support via any physical contact. Levitation is accomplished by providing an upward force that counteracts the pull of gravity (in relation to gravity on earth), plus a smaller stabilizing force that pushes the object toward a home position whenever it is a small distance away from that home position. The force can be a fundamental force such as magnetic or electrostatic, or it can be a reactive force such as optical, buoyant, aerodynamic, or hydrodynamic. Levitation excludes floating at the surface of a liquid because the liquid provides direct mechanical support. Levitation excludes hovering flight by insects, hummingbirds, helicopters, rockets, and balloons because the object provides its own counter-gravity force. Physics Levitation (on Earth or any planetoid) requires an upward force that cancels out the weight of the object, so that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
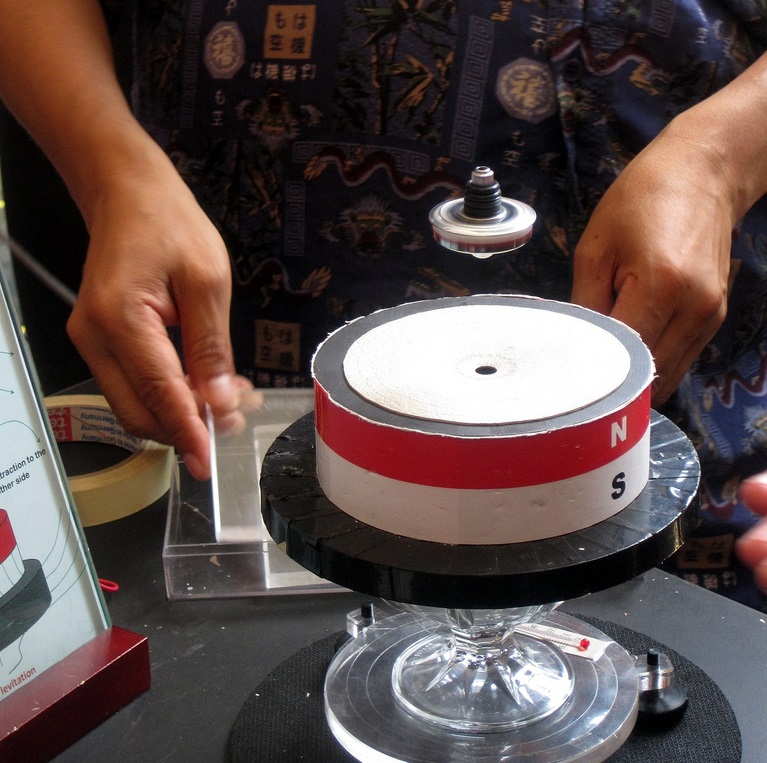
Diamagnetic Levitation
Magnetic levitation (maglev) or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is levitation, suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. Lorentz force, Magnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational force and any other forces. The two primary issues involved in magnetic levitation are ''lifting forces'': providing an upward force sufficient to counteract gravity, and ''stability'': ensuring that the system does not spontaneously slide or flip into a configuration where the lift is neutralized. Magnetic levitation is used for maglev trains, Induction heating, contactless melting, magnetic bearings and for product display purposes. Lift Magnetic materials and systems are able to attract or repel each other with a force dependent on the magnetic field and the area of the magnets. For example, the simplest example of lift would be a simple dipole magnet positioned in the magnetic fields of another dipole magnet, oriented with like poles faci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dua Lipa
Dua Lipa ( , ; born ) is an English and Albanian singer and songwriter. Possessing a mezzo-soprano vocal range, she is known for her signature disco- pop sound. Lipa has received numerous accolades, including six Brit Awards, three Grammy Awards, two MTV Europe Music Awards, an MTV Video Music Award, two Billboard Music Awards, an American Music Award, and two ''Guinness World Records''. " No Lie" and "New Rules", each have over 1 billion views on YouTube, with "New Rules" having reached over 2.7 billion views. After working as a model, she signed with Warner Bros. Records in 2014 and released her eponymous debut album in 2017. The album peaked at number three on the UK Albums Chart and yielded eight singles, including " Be the One", " IDGAF", and the UK number-one single "New Rules", which also peaked at number six in the US. The album has been certified platinum in numerous countries worldwide and won Lipa the Brit Awards for British Female Solo Artist and British B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoyant Levitation
Levitation (from Latin ''levitas'' "lightness") is the process by which an object is held aloft in a stable position, without mechanical support via any physical contact. Levitation is accomplished by providing an upward force that counteracts the pull of gravity (in relation to gravity on earth), plus a smaller stabilizing force that pushes the object toward a home position whenever it is a small distance away from that home position. The force can be a fundamental force such as magnetic or electrostatic, or it can be a reactive force such as optical, buoyant, aerodynamic, or hydrodynamic. Levitation excludes floating at the surface of a liquid because the liquid provides direct mechanical support. Levitation excludes hovering flight by insects, hummingbirds, helicopters, rockets, and balloons because the object provides its own counter-gravity force. Physics Levitation (on Earth or any planetoid) requires an upward force that cancels out the weight of the object, so that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maglev
Maglev (derived from '' magnetic levitation''), is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of electromagnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage of the lack of friction. Such trains rise approximately off the track. There are both high speed, intercity maglev systems (over ), and low speed, urban maglev systems ( to ) being built and under construction and development. With maglev technology, the train travels along a guideway of electromagnets which control the train's stability and speed. While the propulsion and levitation require no moving parts, the bogies can move in relation to the main body of the vehicle and some technologies require support by retractable wheels at low speeds under . This compares with electric multiple units that may have several dozen parts per bogie. Maglev trains can therefore in some cases be quieter and smoother than conventional trains and have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
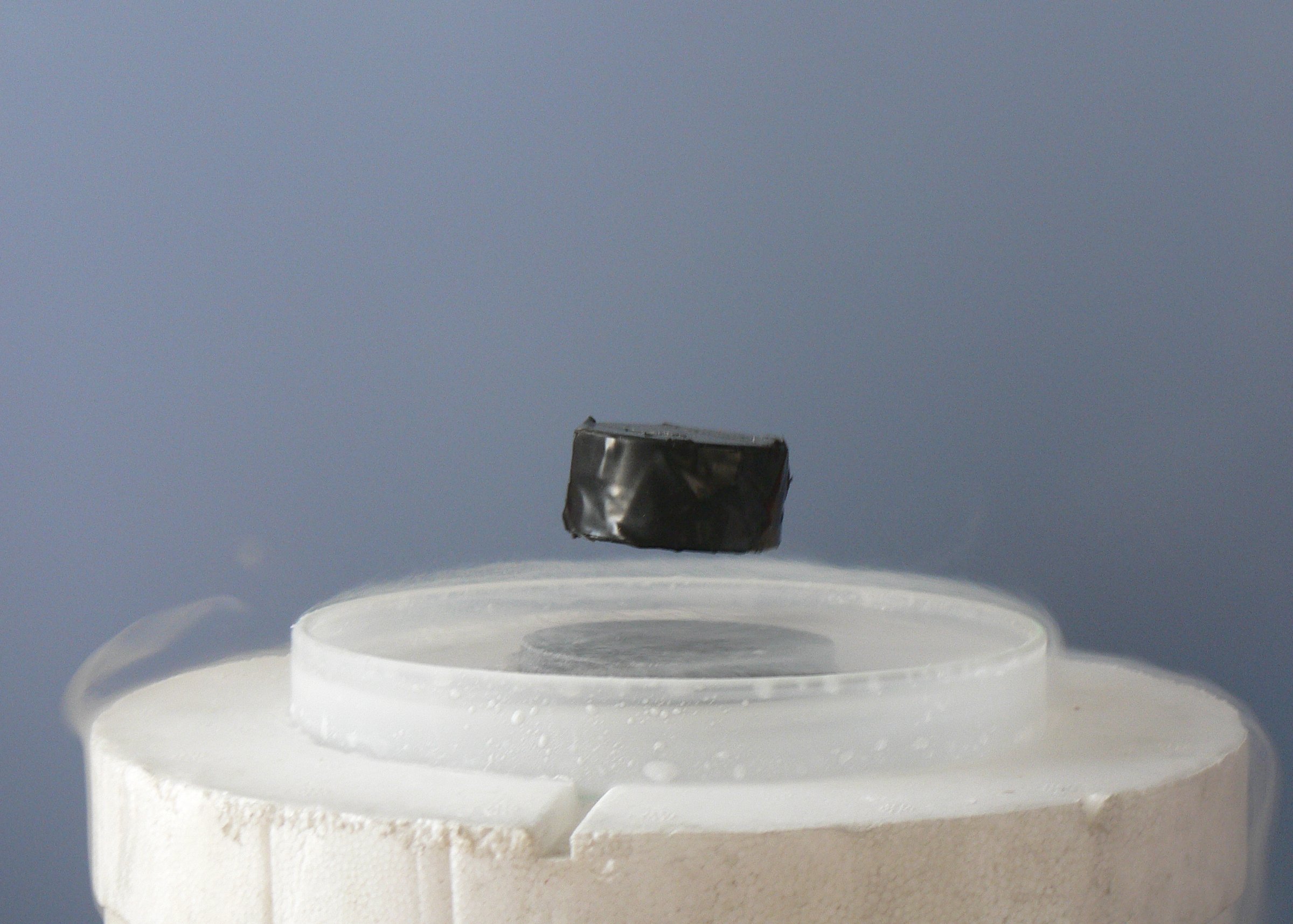
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screening Current
The Meissner effect (or Meissner–Ochsenfeld effect) is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state when it is cooled below the critical temperature. This expulsion will repel a nearby magnet. The German physicists Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered this phenomenon in 1933 by measuring the magnetic field distribution outside superconducting tin and lead samples. The samples, in the presence of an applied magnetic field, were cooled below their superconducting transition temperature, whereupon the samples cancelled nearly all interior magnetic fields. They detected this effect only indirectly because the magnetic flux is conserved by a superconductor: when the interior field decreases, the exterior field increases. The experiment demonstrated for the first time that superconductors were more than just perfect conductors and provided a uniquely defining property of the superconductor state. The ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitation
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coandă Effect
The Coandă effect ( or ) is the tendency of a fluid jet to stay attached to a convex surface. ''Merriam-Webster'' describes it as "the tendency of a jet of fluid emerging from an orifice to follow an adjacent flat or curved surface and to entrain fluid from the surroundings so that a region of lower pressure develops." It is named after Romanian inventor Henri Coandă, who was the first to recognize the practical application of the phenomenon in aircraft design around 1910. It was first documented explicitly in two patents issued in 1936. Discovery An early description of this phenomenon was provided by Thomas Young in a lecture given to The Royal Society in 1800: A hundred years later, Henri Coandă identified an application of the effect during experiments with his Coandă-1910 aircraft, which mounted an unusual engine he designed. The motor-driven turbine pushed hot air rearward, and Coandă noticed that the airflow was attracted to nearby surfaces. In 1934 Coandă obt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six naturally occurring noble gases are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn). Oganesson (Og) is a synthetically produced highly radioactive element. Although IUPAC has used the term "noble gas" interchangeably with "group 18" and thus included oganesson, it may not be significantly chemically noble and is predicted to break the trend and be reactive due to relativistic effects. Because of the extremely short 0.7 ms half-life of its only known isotope, its chemistry has not yet been investigated. For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
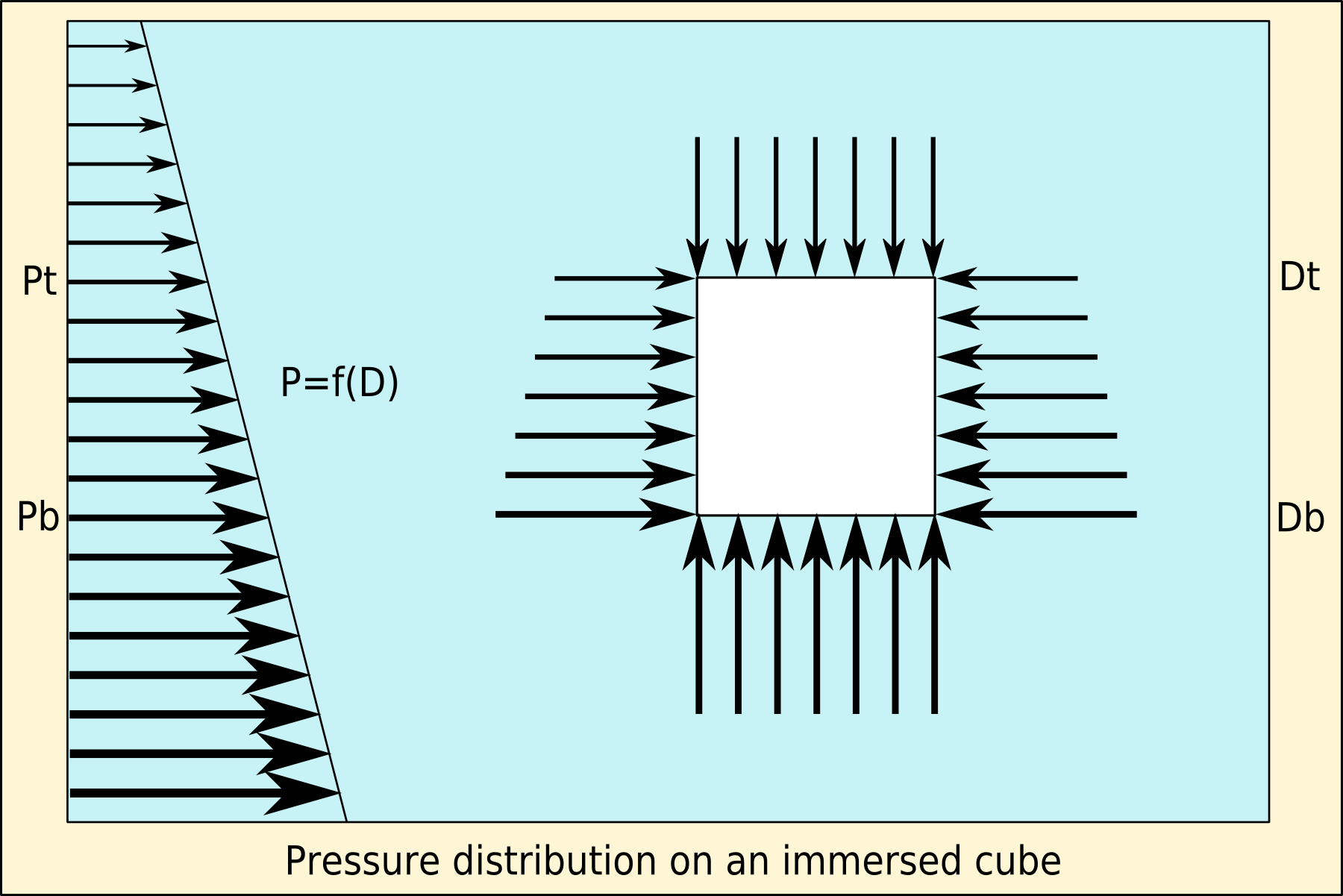
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
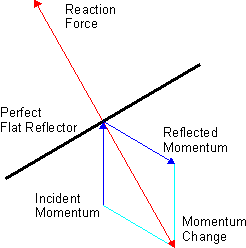
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |