|
Lemniscate Of Gerono
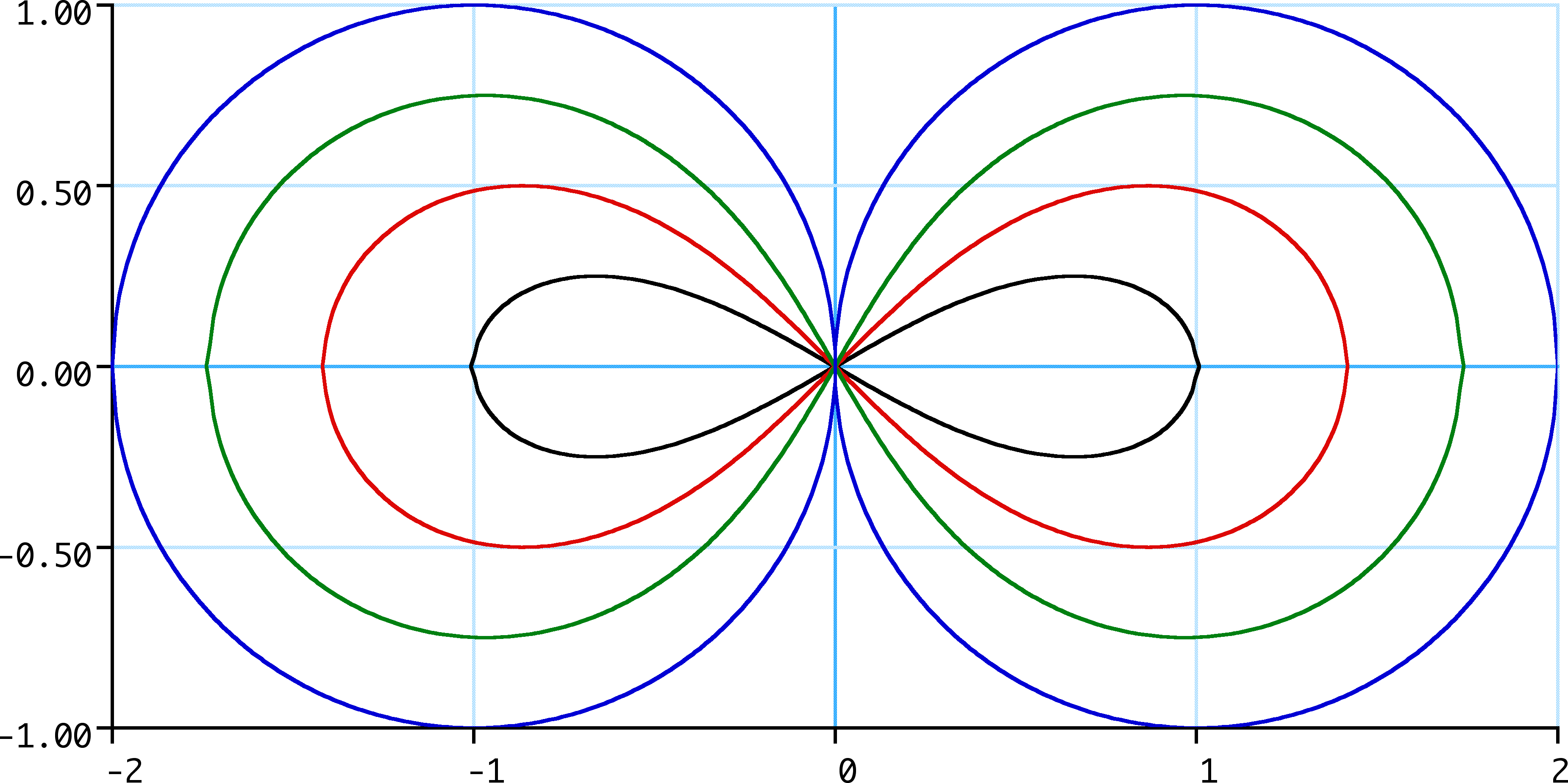
In algebraic geometry, the lemniscate of Gerono, or lemniscate of Huygens, or figure-eight curve, is a plane algebraic curve of degree four and genus zero and is a lemniscate In algebraic geometry, a lemniscate is any of several figure-eight or -shaped curves. The word comes from the Latin "''lēmniscātus''" meaning "decorated with ribbons", from the Greek λημνίσκος meaning "ribbons",. or which alternative ... curve shaped like an \infty symbol, or figure eight. It has equation :x^4-x^2+y^2 = 0. It was studied by Camille-Christophe Gerono. Parameterization Because the curve is of genus zero, it can be parametrized by rational functions; one means of doing that is :x = \frac,\ y = \frac. Another representation is :x = \cos \varphi,\ y = \sin\varphi\,\cos\varphi = \sin(2\varphi)/2 which reveals that this lemniscate is a special case of a Lissajous figure. Dual curve The dual curve (see Plücker formula), pictured below, has therefore a somewhat different char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Geometry
Algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics, classically studying zeros of multivariate polynomials. Modern algebraic geometry is based on the use of abstract algebraic techniques, mainly from commutative algebra, for solving geometrical problems about these sets of zeros. The fundamental objects of study in algebraic geometry are algebraic varieties, which are geometric manifestations of solutions of systems of polynomial equations. Examples of the most studied classes of algebraic varieties are: plane algebraic curves, which include lines, circles, parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, cubic curves like elliptic curves, and quartic curves like lemniscates and Cassini ovals. A point of the plane belongs to an algebraic curve if its coordinates satisfy a given polynomial equation. Basic questions involve the study of the points of special interest like the singular points, the inflection points and the points at infinity. More advanced questions involve the topology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Curve
In mathematics, an affine algebraic plane curve is the zero set of a polynomial in two variables. A projective algebraic plane curve is the zero set in a projective plane of a homogeneous polynomial in three variables. An affine algebraic plane curve can be completed in a projective algebraic plane curve by homogenizing its defining polynomial. Conversely, a projective algebraic plane curve of homogeneous equation can be restricted to the affine algebraic plane curve of equation . These two operations are each inverse to the other; therefore, the phrase algebraic plane curve is often used without specifying explicitly whether it is the affine or the projective case that is considered. More generally, an algebraic curve is an algebraic variety of dimension one. Equivalently, an algebraic curve is an algebraic variety that is birationally equivalent to an algebraic plane curve. If the curve is contained in an affine space or a projective space, one can take a projection for su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Genus
In algebraic geometry, the geometric genus is a basic birational invariant of algebraic varieties and complex manifolds. Definition The geometric genus can be defined for non-singular complex projective varieties and more generally for complex manifolds as the Hodge number (equal to by Serre duality), that is, the dimension of the canonical linear system plus one. In other words for a variety of complex dimension it is the number of linearly independent holomorphic -forms to be found on .Danilov & Shokurov (1998), p. 53/ref> This definition, as the dimension of : then carries over to any base field, when is taken to be the sheaf of Kähler differentials and the power is the (top) exterior power, the canonical line bundle. The geometric genus is the first invariant of a sequence of invariants called the plurigenera. Case of curves In the case of complex varieties, (the complex loci of) non-singular curves are Riemann surfaces. The algebraic definition of genus ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemniscate
In algebraic geometry, a lemniscate is any of several figure-eight or -shaped curves. The word comes from the Latin "''lēmniscātus''" meaning "decorated with ribbons", from the Greek λημνίσκος meaning "ribbons",. or which alternatively may refer to the wool from which the ribbons were made. Curves that have been called a lemniscate include three quartic plane curves: the hippopede or lemniscate of Booth, the lemniscate of Bernoulli, and the lemniscate of Gerono. The study of lemniscates (and in particular the hippopede) dates to ancient Greek mathematics, but the term "lemniscate" for curves of this type comes from the work of Jacob Bernoulli in the late 17th century. History and examples Lemniscate of Booth The consideration of curves with a figure-eight shape can be traced back to Proclus, a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher and mathematician who lived in the 5th century AD. Proclus considered the cross-sections of a torus by a plane parallel to the axis of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinity
Infinity is that which is boundless, endless, or larger than any natural number. It is often denoted by the infinity symbol . Since the time of the ancient Greeks, the philosophical nature of infinity was the subject of many discussions among philosophers. In the 17th century, with the introduction of the infinity symbol and the infinitesimal calculus, mathematicians began to work with infinite series and what some mathematicians (including l'Hôpital and Bernoulli) regarded as infinitely small quantities, but infinity continued to be associated with endless processes. As mathematicians struggled with the foundation of calculus, it remained unclear whether infinity could be considered as a number or magnitude and, if so, how this could be done. At the end of the 19th century, Georg Cantor enlarged the mathematical study of infinity by studying infinite sets and infinite numbers, showing that they can be of various sizes. For example, if a line is viewed as the set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille-Christophe Gerono
Camille-Christophe Gerono (1799 in Paris, France – 1891 in Paris) was a French mathematician. He concerned himself above all with geometry. The Lemniscate of Gerono or ''figure-eight curve'' was named after him. With Olry Terquem, he was founding co-editor in 1842 of the scientific journal ''Nouvelles Annales de Mathématiques The ''Nouvelles Annales de Mathématiques'' (subtitled ''Journal des candidats aux écoles polytechnique et normale'') was a French scientific journal in mathematics. It was established in 1842 by Olry Terquem and Camille-Christophe Gerono, and ...''.. References 1799 births 1891 deaths 19th-century French mathematicians {{France-mathematician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissajous Figure
A Lissajous curve , also known as Lissajous figure or Bowditch curve , is the graph of a system of parametric equations : x=A\sin(at+\delta),\quad y=B\sin(bt), which describe the superposition of two perpendicular oscillations in x and y directions of different angular frequency (''a'' and ''b).'' The resulting family of curves was investigated by Nathaniel Bowditch in 1815, and later in more detail in 1857 by Jules Antoine Lissajous (for whom it has been named). Such motions may be considered as a particular of kind of complex harmonic motion. The appearance of the figure is sensitive to the ratio . For a ratio of 1, when the frequencies match a=b, the figure is an ellipse, with special cases including circles (, radians) and lines (). A small change to one of the frequencies will mean the x oscillation after one cycle will be slightly out of synchronization with the y motion and so the ellipse will fail to close and trace a curve slightly adjacent during the next orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Curve
In projective geometry, a dual curve of a given plane curve is a curve in the dual projective plane consisting of the set of lines tangent to . There is a map from a curve to its dual, sending each point to the point dual to its tangent line. If is algebraic then so is its dual and the degree of the dual is known as the ''class'' of the original curve. The equation of the dual of , given in line coordinates, is known as the ''tangential equation'' of . Duality is an involution: the dual of the dual of is the original curve . The construction of the dual curve is the geometrical underpinning for the Legendre transformation in the context of Hamiltonian mechanics. Equations Let be the equation of a curve in homogeneous coordinates on the projective plane. Let be the equation of a line, with being designated its line coordinatesin a dual projective plane. The condition that the line is tangent to the curve can be expressed in the form which is the tangential equation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plücker Formula
In mathematics, a Plücker formula, named after Julius Plücker, is one of a family of formulae, of a type first developed by Plücker in the 1830s, that relate certain numeric invariants of algebraic curves to corresponding invariants of their dual curves. The invariant called the genus, common to both the curve and its dual, is connected to the other invariants by similar formulae. These formulae, and the fact that each of the invariants must be a positive integer, place quite strict limitations on their possible values. Plücker invariants and basic equations A curve in this context is defined by a non-degenerate algebraic equation in the complex projective plane. Lines in this plane correspond to points in the dual projective plane and the lines tangent to a given algebraic curve ''C'' correspond to points in an algebraic curve ''C''* called the dual curve. In the correspondence between the projective plane and its dual, points on ''C'' correspond to lines tangent ''C''*, so t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Publications
Dover Publications, also known as Dover Books, is an American book publisher founded in 1941 by Hayward and Blanche Cirker. It primarily reissues books that are out of print from their original publishers. These are often, but not always, books in the public domain. The original published editions may be scarce or historically significant. Dover republishes these books, making them available at a significantly reduced cost. Classic reprints Dover reprints classic works of literature, classical sheet music, and public-domain images from the 18th and 19th centuries. Dover also publishes an extensive collection of mathematical, scientific, and engineering texts. It often targets its reprints at a niche market, such as woodworking. Starting in 2015, the company branched out into graphic novel reprints, overseen by Dover acquisitions editor and former comics writer and editor Drew Ford. Most Dover reprints are photo facsimiles of the originals, retaining the original paginatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |