|
Lateral Cord
The lateral cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by the anterior divisions of the upper (C5-C6) and middle trunks (C7). Its name comes from it being lateral to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the brachial plexus are the posterior cord and medial cord. The lateral cord gives rise to the following nerves from proximal to distal: *lateral pectoral nerve (C5-C7) *musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C7) *lateral head of median nerve (C5-C7) [other part of median nerve comes from medial cord The medial cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by of the anterior division of the lower trunk (C8-T1). Its name comes from it being medial to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the brachial plexus ar ...] Additional images File:Slide10EEEE.JPG, Lateral cord File:Slide1cord.JPG, Brachial plexus.Deep dissection. Nerves of the upper limb {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachial Plexus
The brachial plexus is a network () of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve ( C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit, it supplies afferent and efferent nerve fibers the to chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand. Structure The brachial plexus is divided into five ''roots'', three ''trunks'', six ''divisions'' (three anterior and three posterior), three ''cords'', and five ''branches''. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, that leave the plexus at various points along its length. A common structure used to identify part of the brachial plexus in cadaver dissections is the M or W shape made by the musculocutaneous nerve, lateral cord, median nerve, medial cord, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Pectoral Nerve
The lateral pectoral nerve (also known as the lateral anterior thoracic nerve) arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the C5-7. It passes across the axillary artery and vein, pierces the clavipectoral (coracoclavicular) fascia, and enters the deep surface of the pectoralis major to innervate it. Function The lateral pectoral nerve provides motor innervation to the pectoralis major muscle. Although this nerve is described as mostly motor, it also has been considered to carry proprioceptive and nociceptive fibers. It arises either from the lateral cord or directly from the anterior divisions of the upper and middle trunks of the brachial plexus. This is unlike the medial pectoral nerve, which derives from the medial cord (or directly from the anterior division of the lower trunk). It splits into four to seven branches that pierce the clavipectoral fascia to innervate the entire pectoralis major or its superior portion. The medial and lateral pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
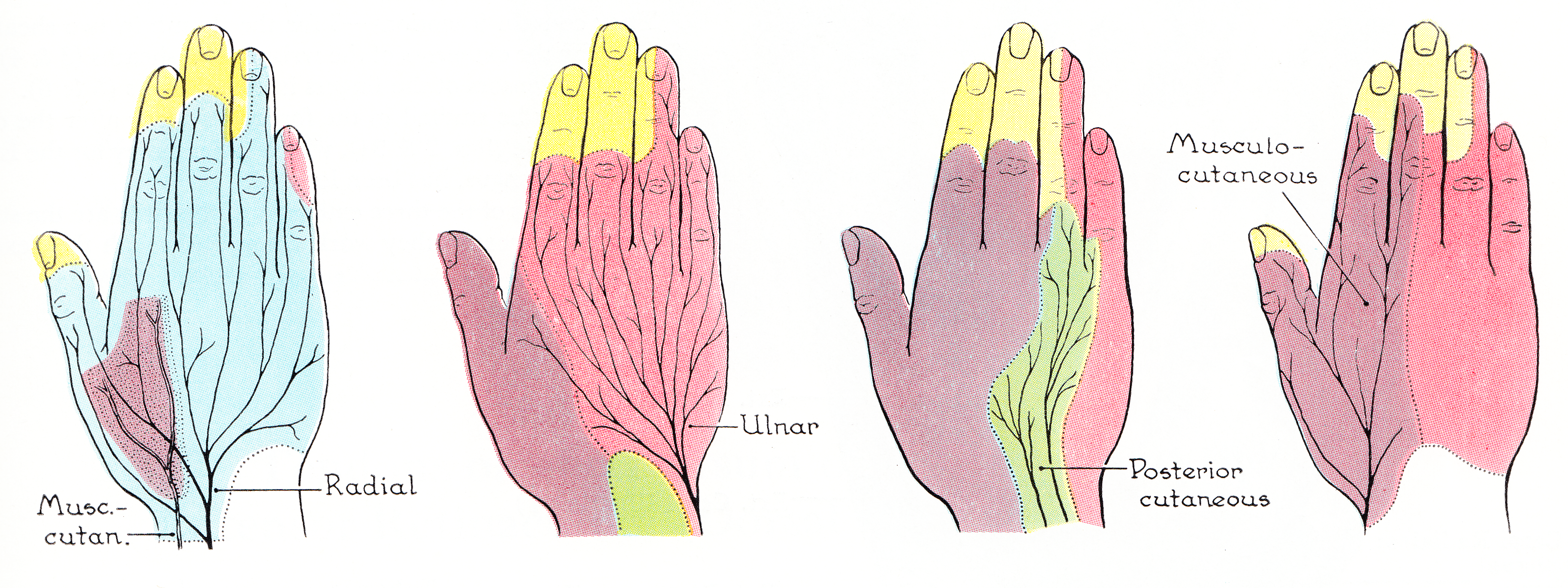
Musculocutaneous Nerve
The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, opposite the lower border of the pectoralis major, its fibers being derived from C5, C6 and C7. Structure The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of the arm, and terminates at 2 cm above elbow as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus with root value of C5 to C7 of the spinal cord. It follows the course of the third part of the axillary artery (part of the axillary artery distal to the pectoralis minor) laterally and enters the frontal aspect of the arm where it penetrates the coracobrachialis muscle. It then passes downwards and laterally between the biceps brachii (above) and the brachialis muscles (below), to the lateral side of the arm; at 2 cm above the elbow it pierces the deep fascia lateral to the tendon of the biceps brachii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C5-C7 (lateral cord) and C8 and T1 (medial cord). The median nerve is the only nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the disability that results from the median nerve being pressed in the carpal tunnel. Structure The median nerve arises from the branches from lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of arm, forearm, and hand, and terminates by supplying the muscles of the hand. Arm After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brachial ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery. After passing the lower margin of teres major it becomes the brachial artery. Structure The axillary artery is often referred to as having three parts, with these divisions based on its location relative to the Pectoralis minor muscle, which is superficial to the artery. * First part – the part of the artery superior to the pectoralis minor * Second part – the part of the artery posterior to the pectoralis minor * Third part – the part of the artery inferior to the pectoralis minor. Relations The axillary artery is accompanied by the axillary vein, which lies medial to the artery, along its length. In the axilla, the axillary artery is surrounded by the brachial plexus. The second part of the axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorly by the imaginary plane between the superior borders of the first rib, clavicle and scapula (above which are considered part of the neck), medially by the serratus anterior muscle and thoracolumbar fascia, anteriorly by the pectoral muscles and posteriorly by the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscle. The soft skin covering the lateral axilla contains many hair and sweat glands. In humans, the formation of body odor happens mostly in the axilla. These odorant substances have been suggested by some to serve as pheromones, which play a role related to mate selection, although this is a controversial topic within the scientific community. The underarms seem more important than the pubic area for emitting body odor, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cord
The posterior cord is a part of the brachial plexus The brachial plexus is a network () of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve ( C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in th .... It consists of contributions from all of the roots of the brachial plexus. The posterior cord gives rise to the following nerves: Additional images File:PLEXUS BRACHIALIS.jpg, Brachial plexus File:Slide12OOO.JPG, Posterior cord File:Slide1SSS.JPG, Posterior cord File:Slide1cord.JPG, Brachial plexus.Deep dissection. File:Slide1ecc.JPG, Brachial plexus.Deep dissection.Anterolateral view References MBBS resources http://mbbsbasic.googlepages.com/ External links * - "Axilla, dissection, anterior view" Nerves of the upper limb {{neuroscience-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Cord
The medial cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by of the anterior division of the lower trunk (C8-T1). Its name comes from it being medial to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the brachial plexus are the posterior cord and lateral cord. The medial cord gives rise to the following nerves from proximal to distal: *medial pectoral nerve (C8-T1) *medial brachial cutaneous nerve (T1) *medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C8-T1) *medial head of median nerve (C8-T1) [other part of median nerve comes from lateral cord The lateral cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by the anterior divisions of the upper (C5-C6) and middle trunks (C7). Its name comes from it being lateral to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the br ...] *ulnar nerve (C8-T1, occasionally C7) Additional images File:PLEXUS BRACHIALIS.jpg, Brachial plexus References Nerves of the upper limb {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |