|
Kane (instrument)
The is a type of dish-shaped bell from Japan. The is often found in traditional Japanese music or Min'yō. Although sometimes suspended from a bar, it is more common for a musician to hold the bell in place with one hand beat it with the other using a special mallet, often made from bone. The ''kane'' makes three distinct sounds: ''chon'' - hitting the middle; ''chi'' - hitting the inside edge; and ''ki'' - reversing the stroke. This kind of onomatopoeic mnemonic or ''shouga'' is common in Japanese music. There are several sizes of ''kane'', such as the ''atarigane'' or the ''surigane''. ''Kane'' are also used in Buddhist or Shinto ceremonies. In temples, they may be used to signify time or alert people to certain events. See also *Bonshō , also known as or are large bells found in Buddhist temples throughout Japan, used to summon the monks to prayer and to demarcate periods of time. Rather than containing a clapper, are struck from the outside, using either a hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Japanese Words And Phrases ...
{{Commons Words and phrases by language Words Words Words A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell (instrument)
A bell is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be made by an internal "clapper" or "uvula", an external hammer, or—in small bells—by a small loose sphere enclosed within the body of the bell (jingle bell). Bells are usually cast from bell metal (a type of bronze) for its resonant properties, but can also be made from other hard materials. This depends on the function. Some small bells such as ornamental bells or cowbells can be made from cast or pressed metal, glass or ceramic, but large bells such as a church, clock and tower bells are normally cast from bell metal. Bells intended to be heard over a wide area can range from a single bell hung in a turret or bell-gable, to a musical ensemble such as an English ring of bells, a carillon or a Russian zvon which are tuned to a common scale and instal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Kane Bell
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Japanese Music
Traditional Japanese music is the folk or traditional music of Japan. Japan's Ministry of Education classifies as a category separate from other traditional forms of music, such as (court music) or (Buddhist chanting), but most ethnomusicologists view , in a broad sense, as the form from which the others were derived. Outside of ethnomusicology, however, usually refers to Japanese music from around the 17th to the mid-19th century. Within this framework, there are three types of traditional music in Japan: theatrical, court music, and instrumental. Theatrical Japan has several theatrical forms of drama in which music plays a significant role. The main forms are kabuki and Noh. Noh or music is a type of theatrical music used in Noh theatre. Noh music is played by an instrumental ensemble called . The instruments used are the stick drum, a large hourglass-shaped drum called the , a smaller hourglass-shaped drum called the , and a bamboo flute called the . The ensemble is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Min'yō
, ''Nihon min'yō'', Japanese ''min'yō'' or Japanese folk music is a genre of traditional Japanese music. Characteristics Styles Many ''min'yō'' are connected to forms of work or to specific trades and were originally sung between work or for specific jobs. Other ''min'yō'' function simply as entertainment, as dance accompaniment, or as a components of religious rituals. ''Min'yō'' are also distinct depending on the area of Japan, with each area boasting its own favorite songs and styles. The songs found in the far northern island of Hokkaidō and sung by the Ainu people are usually excluded from the category of min'yō. In the far south, (especially Okinawa) distinct genres of min'yō, differing in scale structure, language and textual forms, have developed as well. Instruments Most Japanese folk songs related to work were originally sung unaccompanied, either solo, or by groups (heterophonically). Some songs exhibit the same sort of "call and response" chant often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. There is no central authority in control of Shinto, with much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the . The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshiped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common rituals include the dances, rites of pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
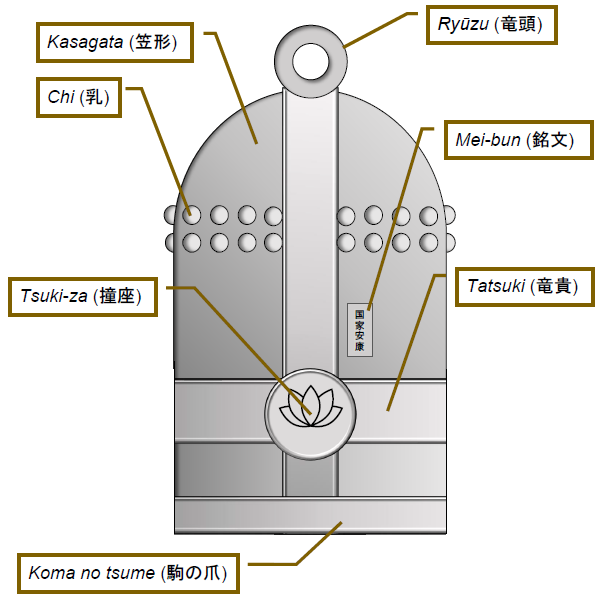
Bonshō
, also known as or are large bells found in Buddhist temples throughout Japan, used to summon the monks to prayer and to demarcate periods of time. Rather than containing a clapper, are struck from the outside, using either a handheld mallet or a beam suspended on ropes. The bells are usually made from bronze, using a form of expendable mould casting. They are typically augmented and ornamented with a variety of bosses, raised bands and inscriptions. The earliest of these bells in Japan date to around 600 CE, although the general design is of much earlier Chinese origin and shares some of the features seen in ancient Chinese bells. The bells' penetrating and pervasive tone carries over considerable distances, which led to their use as signals, timekeepers and alarms. In addition, the sound of the bell is thought to have supernatural properties; it is believed, for example, that it can be heard in the underworld. The spiritual significance of means that they play an im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzu (bell)
are round, hollow Japanese Shinto bells that contains pellets that sound when agitated. They are somewhat like a jingle bell in form, though the materials produce a coarse, rolling sound. come in many sizes, ranging from tiny ones on good luck charms (called ) to large ones at shrine entrances. are, however, classified as small bells, since big bells are referred to as . The former is associated with Shinto and shrines while the latter is related to Buddhist temples and ceremonies. At Shinto shrines, large drape over entrances, as it is said that ringing them calls , allowing one to acquire positive power and authority, while repelling evil. Handheld clustered , similar to jingle bells, are used musically at Shinto ceremonies. There are ceremonies, for instance, where female performers dance with bells such as those with some sort of short blade at their center. The bell's cool tinkles are also considered psychological air-conditioning for the summer since their clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Musical Instruments
Traditional Japanese musical instruments, known as in Japanese, are musical instruments used in the traditional folk music of Japan. They comprise a range of string, wind, and percussion instruments. Percussion instruments *; also spelled – clapper made from wooden slats connected by a rope or cord * – wooden or bamboo clappers * – pellet drum, used as a children's toy * – small, ornately decorated hourglass-shaped drum * – hand-held bell tree with three tiers of pellet bells * – small drum used in * – small flat gong * – a pair of sticks which are beaten together slowly and rhythmically * (also called ) – clapper made from a pair of flat wooden sticks * – woodblock carved in the shape of a fish, struck with a wooden stick; often used in Buddhist chanting * – hand drum * or () – singing bowls used by Buddhist monks in religious practice or rituals * – hourglass-shaped double-headed drum; struck only on one side * – clapper made from wooden slats conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bells (percussion)
Bells may refer to: * Bell, a musical instrument Places * Bells, North Carolina * Bells, Tennessee * Bells, Texas * Bells Beach, Victoria, an internationally famous surf beach in Australia * Bells Corners, Ontario Music * Bells, directly struck percussion instruments * Glockenspiel, also known as bells * The Bells (band), a Canadian rock band from the 1970s * ''Bells'' (album), an album by Albert Ayler * ''The Bells'' (Lou Reed album), an album by Lou Reed * The Bells (symphony), or in Russian "Kolokola," a choral work by Rachmaninov based on the poem by Edgar Allan Poe *"Bells", a song by Fred Wesley and Horny Horns from the album '' The Final Blow'' Film and television * "Bells" (''Blackadder''), an episode of the British sitcom ''Blackadder II'' * "Bells", an episode of ''New Girl'' * ''Bells'', a 1982 Canadian-American film also known as ''Murder by Phone'' Brands and enterprises * Bell's Brewery, a brewery in Michigan, United States * Bell's whisky, a blended whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |