|
Kamarupa
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam. Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to 1140 CE, Davaka was absorbed by Kamarupa in the 5th century CE."As regards the eastern limits of the kingdom, Davaka was absorbed within Kamarupa under Kalyanavarman and the outlying regions were brought under subjugation by Mahendravarman." Ruled by three dynasties from their capitals in present-day Guwahati, North Guwahati and Tezpur, Kamarupa at its height covered the entire Brahmaputra Valley, North Bengal, Bhutan and northern part of Bangladesh, and at times portions of what is now West Bengal, Bihar and Sylhet. Though the historical kingdom disappeared by the 12th century to be replaced by smaller political entities, the notion of Kamarupa persisted and ancient and medieval chroniclers continued to call a part of this kingdom Kamrup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamarupi Prakrit
Kamarupi Prakrit is the postulated Middle Indo-Aryan (MIA) Prakrit language used in ancient Kamarupa (5th–13th century). This language is the historical ancestor of the Kamatapuri lects and the modern Assamese language;"In this study I refer to the western dialect of Asamiya as ''Kamrupi'', and the historical ancestor of proto-Kamata and proto-Asamiya as ''proto-Kamrupa''." and can be dated prior to 1250 CE, when the proto-Kamta language, the parent of the Kamatapuri lects, began to develop. Though not substantially proven, the existence of the language that predated the Kamatapuri lects and modern Assamese is widely believed. The evidence of this MIA exist in systematic errors in the Sanskrit language used in the Kamarupa inscriptions. A distinguishing characteristic of Kamarupa inscriptions is the replacement of ''ś'' and ''ṣ'' by ''s'', which is contrary to Vararuci's rule, the main characteristic of Magadhi Prakrit, which warrants that ''ṣ'' and ''s'' are repla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamrup Region
Kamrup is the modern region situated between two rivers, the Manas and the Barnadi in Western Assam, with the same territorial extent as the Colonial and post-Colonial "Undivided Kamrup district". It was the capital region of two of the three dynasties of Kamarupa and Guwahati, the current political center of Assam, is situated here. It is characterized by its cultural artifacts. Etymology The origin of name is attributed to a legend in the Kalika Purana which mentions that it is in this region that Kamadeva regained his form. Ancient Kamrup (350–1140) The history of the Kamrup region dates back to the 4th century under Kamarupa Kingdom. The kingdom was successively ruled by three dynasties - the Varman, the Mlechchha (Mech) and the Pala dynasties. Among these, the capitals of the Varman Dynasty and the Pala Dynasty, called Pragjyotishpura and Durjaya respectively, were in Kamrup, whereas the capital of the Mlechchha dynasty was in Tezpur outside the Kamrup region. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
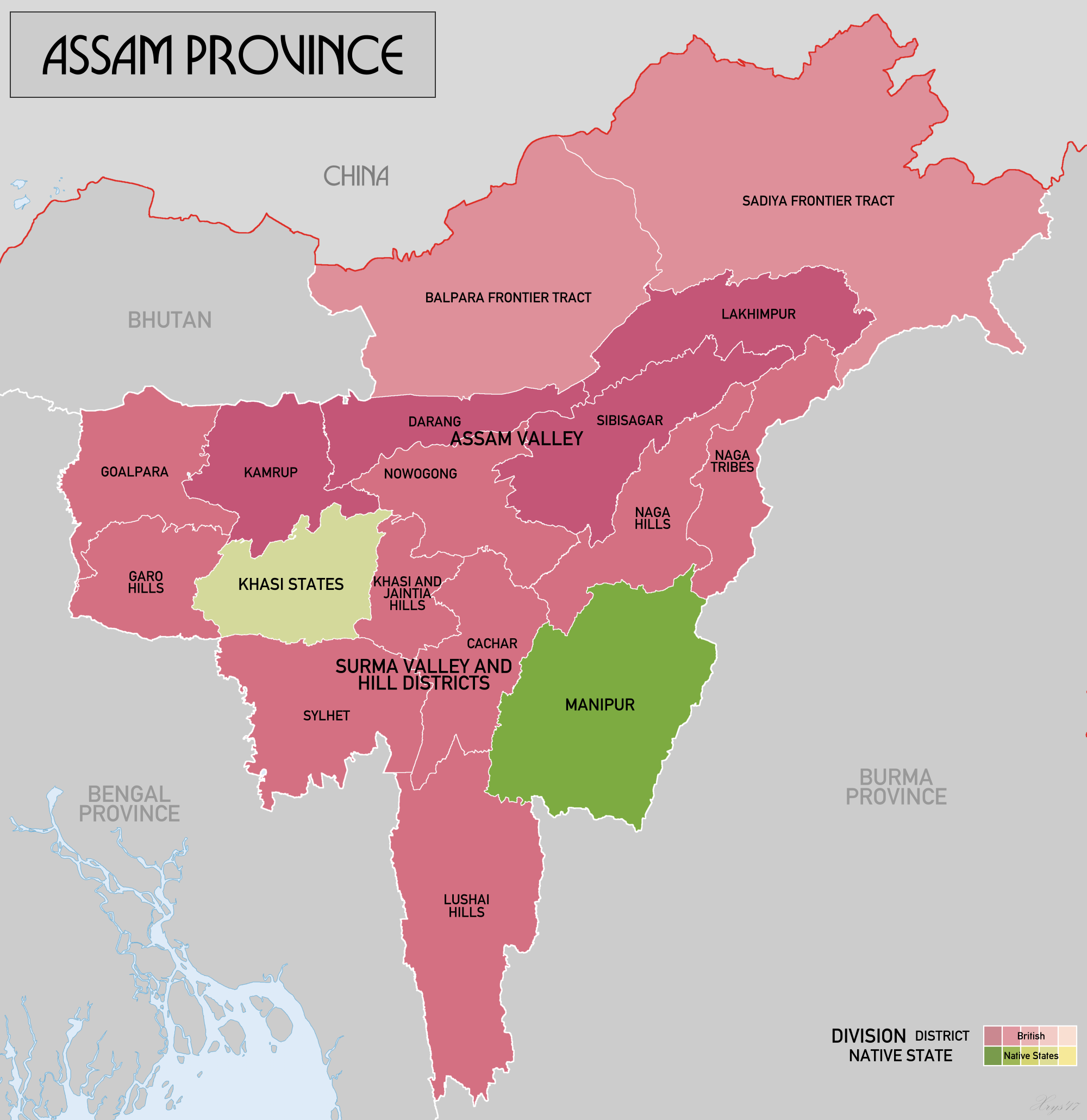
Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a wide strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese and Boro are the official languages of Assam, while Bengali is an additional official language in the Barak Valley. Assam is known for Assam tea and Assam silk. The state was the first site for oil drilling in Asia. Assam is home to the one-horned Indian rhinoceros, along with the wild water buffalo, pygmy hog, tiger and various species of Asiatic birds, and provides one of the last wild habitats for the Asian elephant. The Assamese economy is aided by wildlife tourism to Kaziranga National Park and Manas National Park, which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical India
The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 200 BCE to 1200 CE. The period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, starting with Simuka, from 230 BCE. The "middle" period lasted for about 1,500 years and ended in 1200 CE, with the rise of the Delhi Sultanate, founded in 1206, and the end of the Later Cholas (Rajendra Chola III, who died in 1279 CE). This period encompasses two eras: Classical India, from the Maurya Empire up until the end of the Gupta Empire in 500 CE, and early Medieval India from 500 CE onwards. It also encompasses the era of classical Hinduism, which is dated from 200 BCE to 1100 CE. From 1 CE until 1000 CE, India's economy is estimated to have been the largest in the world, having between one-third and one-quarter of the world's wealth. It is followed by the late Medieval period in the 13th century. The Northwest During the 2nd century BCE, the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Kingdoms Of India
The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 200 BCE to 1200 CE. The period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, starting with Simuka, from 230 BCE. The "middle" period lasted for about 1,500 years and ended in 1200 CE, with the rise of the Delhi Sultanate, founded in 1206, and the end of the Later Cholas (Rajendra Chola III, who died in 1279 CE). This period encompasses two eras: Classical India, from the Maurya Empire up until the end of the Gupta Empire in 500 CE, and early Medieval India from 500 CE onwards. It also encompasses the era of classical Hinduism, which is dated from 200 BCE to 1100 CE. From 1 CE until 1000 CE, India's economy is estimated to have been the largest in the world, having between one-third and one-quarter of the world's wealth. It is followed by the late Medieval period in the 13th century. The Northwest During the 2nd century BCE, the Maur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragjyotishpura
Pragjyotishpura () or Pragjyotisapura, now deemed to be a region within modern Guwahati, was an ancient city and capital of the Varman dynasty (350 - 650 A.D). Though the earliest mention of Pragjyotisha in local sources come from the 7th century, the form was changed to ''Pragjyotishpura'' in the 9th century which describes it as the city of Naraka within Kamarupa. In Puranas, Puranic text like the Ramayana, Pragjyotishpura is described as the fortress of Narakasura on mount Varaha located in the north-west of the Indian subcontinent in what is modern-day Punjab and Sindh. Etymology The Pragjyotishpura is derived from Sanskrit. Prag means former or eastern and 'jyotisha' a 'star', 'astrology', 'shining', 'pura' a city thus meaning ' city of eastern light ' otherwise 'city of eastern astrology'. Location of Pragjyotishpura No inscription up to the 12th century, when the kingdom of Kamarupa came to an end, give an indication of the location of Pragjyotishpura, and the exact loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guwahati
Guwahati (, ; formerly rendered Gauhati, ) is the biggest city of the Indian state of Assam and also the largest metropolis in northeastern India. Dispur, the capital of Assam, is in the circuit city region located within Guwahati and is the seat of the Government of Assam. A major riverine port city along with hills, and one of the fastest growing cities in India, Guwahati is situated on the south bank of the Brahmaputra. It is called the ''Gateway to North East India''. The ancient cities of Pragjyotishpura and Durjaya (North Guwahati) were the capitals of the ancient state of Kamarupa. Many ancient Hindu temples like the Kamakhya Temple, Ugratara Devalaya, Ugratara Temple, Basistha Temple, Doul Govinda Temple, Umananda Temple, Navagraha temples#Navagraha Temple in Assam, Navagraha Temple, Sukreswar Temple, Rudreswar Temple, Manikarneswar Temple, Aswaklanta Temple, Dirgheshwari temple, Dirgheshwari Temple, Asvakranta Temple, Lankeshwar Temple, Bhubaneswari Temple, Shree Gane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davaka
Davaka was a kingdom of ancient Indian subcontinent, located in current central region of Assam state. The references to it comes from the 4th century Allahabad pillar inscription of Samudragupta, where it is mentioned as one of five frontier kingdoms of the Gupta Empire. Other references are the Shung-Shu History of the Liu Song dynasty, where the kingdom is named ''Kapili'' (now the name of a river); the Gachtal stone pillar inscription written in Kamrupi Prakrit. N. K. Bhattasali has identified it with Dabaka in modern Hojai district, with the kingdom associated with the Kopili-Kolong river valley. Historians such as B. N. Puri (1968) and P. C. Choudhury (1959) claim that it was absorbed much earlier in the first half of the 5th century during the reign of Kalyana Varman (422–446). Its capital was located near Kopili river. In the year 428 AD, an ambassador was sent to China by Davaka king, whose name according to Chinese sources is Yuegnai or Yu Chai. Gatchal Stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Guwahati
North Guwahati is northern part of the city of Guwahati and a town area committee in Kamrup Rural district in the Indian state of Assam.This town abounds in historical places and picnic spots. National Highway 27 passes through North Guwahati. Amingaon neighbourhood is district headquarter of Kamrup Rural district. History North Guwahati is also known as Durjaya, was capital of the ancient state of Kamarupa under Pala dynasty. In early medieval times, the area was known as Kamarupa Nagara. North Guwahati possesses temples, roads, bridges, fortifications, and moats which are of ancient origin. There are two temples on the Aswakranta hill. The upper temple contains the image of Vishnu lying on Ananta-Sajya. It is one of the finest specimens of sculptural skill in Kamarupa about the beginning of the twelfth century. The western part of the town is called Sil-Sako because it still contains a small stone-built bridge over a stream. The eastern part is known as Raja-duar (king's gat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durjaya
Durjaya, now North Guwahati, was capital of Kamarupa kingdom under the Pala Dynasty for the period 900 to 1100 C.E. Pala rulers built their capital on the banks of the Brahmaputra and surrounded it with a rampart and a strong palisade, whence they named it Durjaya (=impregnable). Many wealthy merchants lived there in safety and it boasted of many plastered turrets. Encouraged by the King, the learned men, religious preceptors, and poets made it a place of resort. See also * Varman Dynasty The Varman dynasty (350–650) was the first historical dynasty of the Kamarupa kingdom. It was established by Pushyavarman, a contemporary of Samudragupta. The earlier Varmans were subordinates of the Gupta Empire, but as the power of the Gup ... References {{Reflist2Gayajidham Guwahati Kamarupa (former kingdom) Pala dynasty (Kamarupa) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibeto-Burman Languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylhet Division
Sylhet Division ( bn, সিলেট বিভাগ) is the northeastern division of Bangladesh. It is bordered by the Indian states of Meghalaya, Assam and Tripura to the north, east and south respectively, and by the Bangladeshi divisions of Chittagong to the southwest and Dhaka and Mymensingh to the west. Prior to 1947, it included the subdivision of Karimganj (presently in Barak Valley, India). However, Karimganj (including the thanas of Badarpur, Patharkandi and Ratabari) was inexplicably severed from Sylhet by the Radcliffe Boundary Commission. According to Niharranjan Ray, it was partly due to a plea from a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar. Etymology and names The name ''Sylhet'' is an anglicisation of ''Shilhot'' (শিলহট). Its origins seem to come from the Sanskrit words শিলা ''śilā'' (meaning 'stone') and হট্ট ''haṭṭa'' (meaning 'marketplace'). These words match the landscape and topography of the hilly region. The shila stones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |