|
Jet Nozzle
A propelling nozzle is a nozzle that converts the internal energy of a working gas into propulsive force; it is the nozzle, which forms a jet, that separates a gas turbine, or gas generator, from a jet engine. Propelling nozzles accelerate the available gas to subsonic, transonic, or supersonic velocities depending on the power setting of the engine, their internal shape and the pressures at entry to, and exit from, the nozzle. The internal shape may be convergent or convergent-divergent (C-D). C-D nozzles can accelerate the jet to supersonic velocities within the divergent section, whereas a convergent nozzle cannot accelerate the jet beyond sonic speed. Propelling nozzles may have a fixed geometry, or they may have variable geometry to give different exit areas to control the operation of the engine when equipped with an afterburner or a reheat system. When afterburning engines are equipped with a C-D nozzle the throat area is variable. Nozzles for supersonic flight speeds, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nozzle
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow (specially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe. A nozzle is often a pipe or tube of varying cross sectional area, and it can be used to direct or modify the flow of a fluid (liquid or gas). Nozzles are frequently used to control the rate of flow, speed, direction, mass, shape, and/or the pressure of the stream that emerges from them. In a nozzle, the velocity of fluid increases at the expense of its pressure energy. Types Jet A gas jet, fluid jet, or hydro jet is a nozzle intended to eject gas or fluid in a coherent stream into a surrounding medium. Gas jets are commonly found in gas stoves, ovens, or barbecues. Gas jets were commonly used for light before the development of electric light. Other types of fluid jets are found in carburetors, where smooth calibrated orifices are used to regulate the flow of fuel into an engine, and in jacuzzis or spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-33
The Klimov RD-33 is a turbofan jet engine for a lightweight fighter jet that is the primary engine for the Mikoyan MiG-29 and CAC/PAC JF-17 Thunder. It was developed in OKB-117 led by S. P. Izotov (now OAO Klimov) from 1968 with production starting in 1981. Previous generations of Russian supersonic fighters such as the MiG-21 and MiG-23 used turbojets, but western fighters such as the F-111 and F-4K introduced the use of afterburning turbofans in the 1960s which were more efficient. The RD-33 was the first afterburning turbofan engine produced by the Klimov company of Russia in the thrust class. It features a modular twin-shaft design with individual parts that can be replaced separately. Variants In early 1970s the RD-33 was selected for new light fighter jet, later becoming Mikoyan MiG-29, the other option was Tumansky R-67-300. Years of development has built an extensive engine family. A newly designed thrust vectoring nozzle (TVN) is now available. New models of the RD-33 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
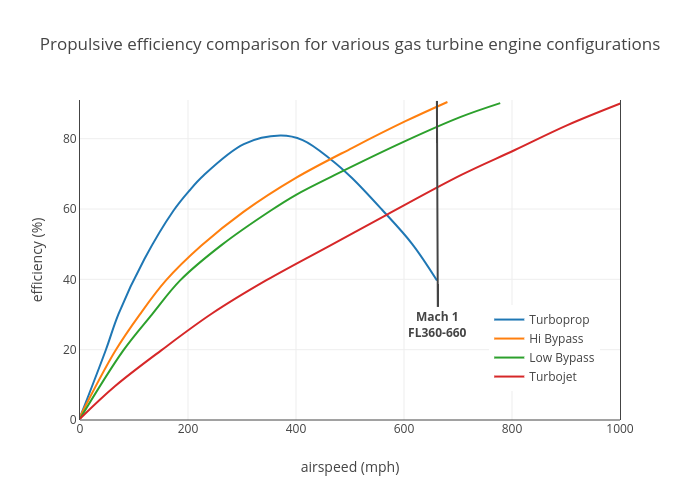
SR-71
The Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a Range (aeronautics), long-range, high-altitude, Mach number, Mach 3+ military strategy, strategic reconnaissance aircraft developed and manufactured by the American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation. It was operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and NASA. The SR-71 was developed as a black project from the Lockheed A-12 reconnaissance aircraft during the 1960s by Lockheed's Skunk Works division. American aerospace engineer Kelly Johnson (engineer), Clarence "Kelly" Johnson was responsible for many of the aircraft's innovative concepts. The shape of the SR-71 was based on that of the A-12, which was one of the first aircraft to be designed with a reduced radar cross-section. Initially, a strategic bomber, bomber variant of the A-12 was requested by Curtis LeMay, before the program was focused solely on reconnaissance. Mission equipment for the reconnaissance role included signals intelligence sensors, side looking airborne r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
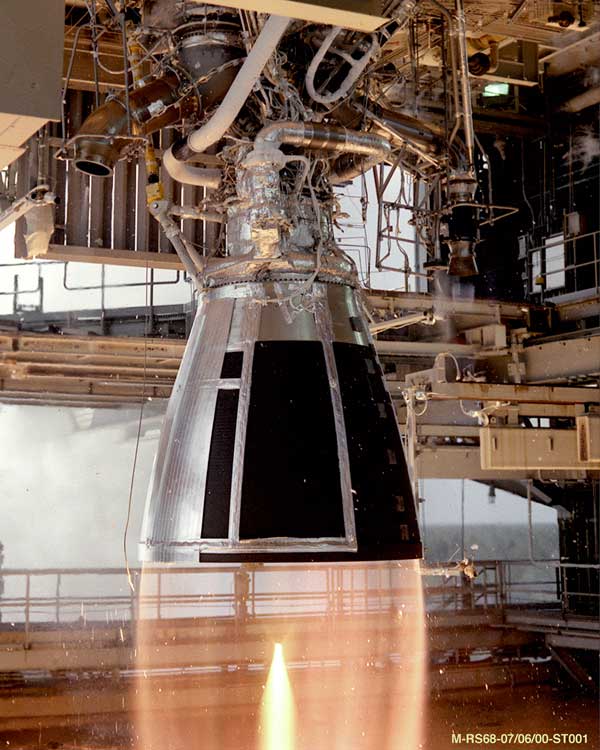
Rocket Motor
A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, in accordance with Newton's third law. Most rocket engines use the combustion of reactive chemicals to supply the necessary energy, but non-combusting forms such as cold gas thrusters and nuclear thermal rockets also exist. Vehicles propelled by rocket engines are commonly called rockets. Rocket vehicles carry their own oxidiser, unlike most combustion engines, so rocket engines can be used in a vacuum to propel spacecraft and ballistic missiles. Compared to other types of jet engine, rocket engines are the lightest and have the highest thrust, but are the least propellant-efficient (they have the lowest specific impulse). The ideal exhaust is hydrogen, the lightest of all elements, but chemical rockets produce a mix of heavier species, reducing the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Nozzle V2
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from rocket propellant, propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with Airbreathing jet engine, airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, Reaction control system, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, Reaction wheel, momentum wheels, Thrust vectoring, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, Spin-stabilisati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbofan
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft engine, aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the ''turbo'' portion refers to a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and the ''fan'', a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to force air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the combustion chamber and turbines, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses these components. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust. The ratio of the mass-flow of air bypassing the engine core to the mass-flow of air passing through the core is referred to as the bypass ratio. The engine produces thrust through a combination of these two portions working together; engines that use more Propelling nozzle, jet thrust relative to fan thrust are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bypass Ratio
The bypass ratio (BPR) of a turbofan engine is the ratio between the mass flow rate of the bypass stream to the mass flow rate entering the core. A 10:1 bypass ratio, for example, means that 10 kg of air passes through the bypass duct for every 1 kg of air passing through the core. Turbofan engines are usually described in terms of BPR, which together with engine pressure ratio, turbine inlet temperature and fan pressure ratio are important design parameters. In addition, BPR is quoted for turboprop and unducted fan installations because their high propulsive efficiency gives them the overall efficiency characteristics of very high bypass turbofans. This allows them to be shown together with turbofans on plots which show trends of reducing specific fuel consumption (SFC) with increasing BPR. BPR is also quoted for lift fan installations where the fan airflow is remote from the engine and doesn't physically touch the engine core. Bypass provides a lower fuel consumption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concorde
The Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde () is a retired Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation (later Aérospatiale) and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC). Studies started in 1954, and France and the UK signed a treaty establishing the development project on 29 November 1962, as the programme cost was estimated at £70 million (£ in ). Construction of the six prototypes began in February 1965, and the first flight took off from Toulouse on 2 March 1969. The market was predicted for 350 aircraft, and the manufacturers received up to 100 option orders from many major airlines. On 9 October 1975, it received its French Certificate of Airworthiness, and from the UK CAA on 5 December. Concorde is a tailless aircraft design with a narrow fuselage permitting a 4-abreast seating for 92 to 128 passengers, an ogival delta wing and a droop nose for landing visibility. It is powered by four Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 turbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
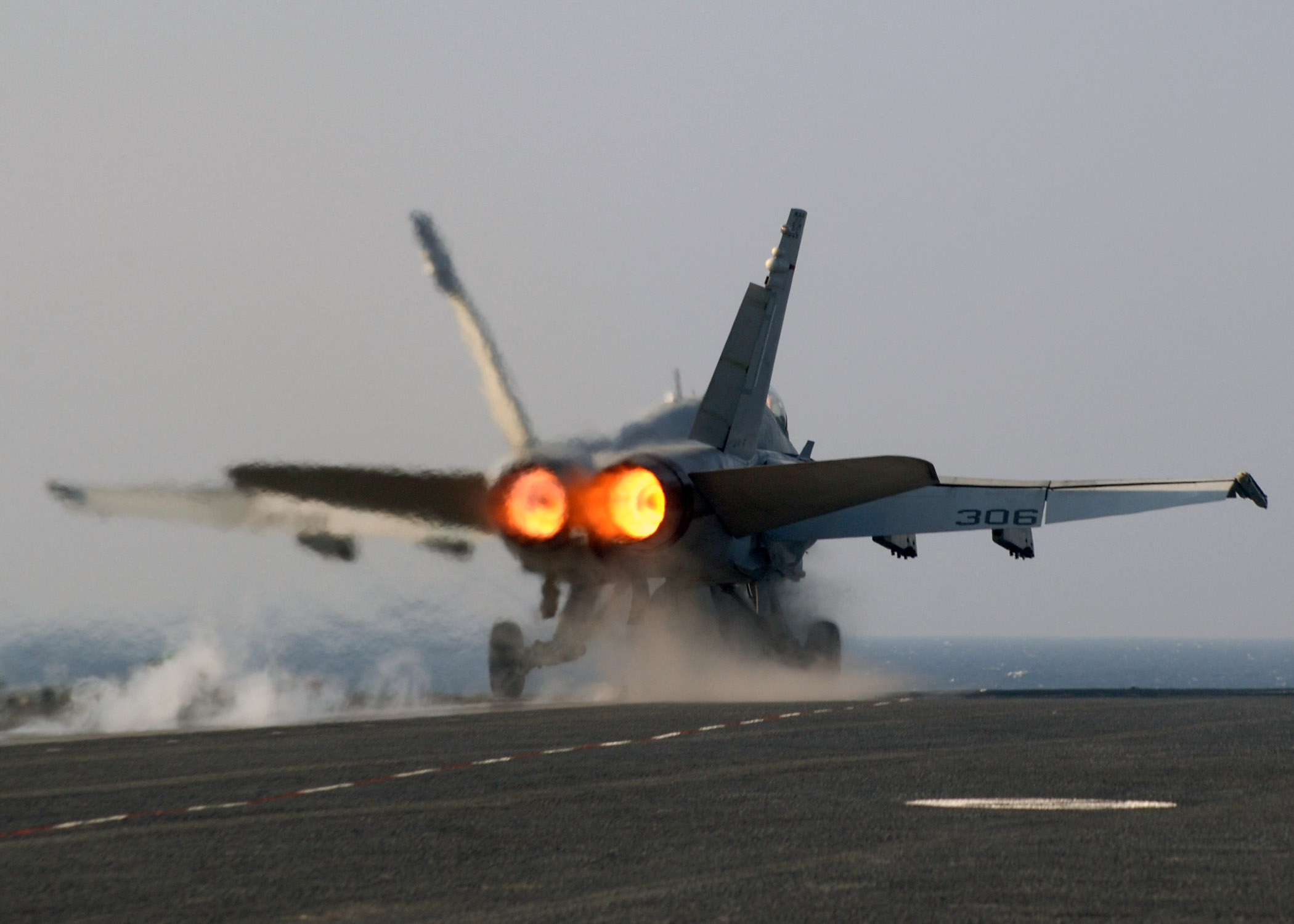
Afterburner
An afterburner (or reheat in British English) is an additional combustion component used on some jet engines, mostly those on military supersonic aircraft. Its purpose is to increase thrust, usually for supersonic flight, takeoff, and combat. The afterburning process injects additional fuel into a combustor in the jet pipe behind (''i.e.'', "after") the turbine, "reheating" the exhaust gas. Afterburning significantly increases thrust as an alternative to using a bigger engine with its attendant weight penalty, but at the cost of increased fuel consumption (decreased fuel efficiency) which limits its use to short periods. This aircraft application of "reheat" contrasts with the meaning and implementation of "reheat" applicable to gas turbines driving electrical generators and which reduces fuel consumption. Jet engines are referred to as operating ''wet'' when afterburning and ''dry'' when not. An engine producing maximum thrust wet is at ''maximum power,'' while an engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
With Low Area Ratio , a ...
With or WITH may refer to: * With, a preposition in English * Carl Johannes With (1877–1923), Danish doctor and arachnologist * With (character), a character in ''D. N. Angel'' * ''With'' (novel), a novel by Donald Harrington * ''With'' (album), a 2014 album by TVXQ * ''With'' (EP), a 2021 EP by Nam Woo-hyun Radio stations * WITH (FM), a radio station (90.1 FM) licensed to Ithaca, New York, United States * WRBS (AM), a radio station (1230 AM) licensed to Baltimore, Maryland, United States, which used the call sign WITH from 1941 until 2006 * WZFT, a radio station (104.3 FM) licensed to Baltimore, Maryland, United States, which used the call sign WITH-FM from 1949 until 1974 Places * Woodlands Integrated Transport Hub Woodlands Bus Interchange (formerly Woodlands Regional Bus Interchange) is a bus interchange in Singapore. Located at Woodlands, the interchange is linked to Woodlands MRT station and adjacent to Causeway Point shopping mall. It is the larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Engine Nozzles
A rocket engine nozzle is a propelling nozzle (usually of the de Laval type) used in a rocket engine to expand and accelerate combustion products to high supersonic velocities. Simply: propellants pressurized by either pumps or high pressure ullage gas to anywhere between two to several hundred atmospheres are injected into a combustion chamber to burn, and the combustion chamber leads into a nozzle which converts the energy contained in high pressure, high temperature combustion products into kinetic energy by accelerating the gas to high velocity and near-ambient pressure. History Simple bell-shaped nozzles were developed in the 1500s. The de Laval nozzle was originally developed in the 19th century by Gustaf de Laval for use in steam turbines. It was first used in an early rocket engine developed by Robert Goddard, one of the fathers of modern rocketry. It has since been used in almost all rocket engines, including Walter Thiel's implementation, which made possible German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choked Flow
Choked flow is a compressible flow effect. The parameter that becomes "choked" or "limited" is the fluid velocity. Choked flow is a fluid dynamic condition associated with the venturi effect. When a flowing fluid at a given pressure and temperature passes through a constriction (such as the throat of a convergent-divergent nozzle or a valve in a pipe) into a lower pressure environment the fluid velocity increases. At initially subsonic upstream conditions, the conservation of energy principle requires the fluid velocity to increase as it flows through the smaller cross-sectional area of the constriction. At the same time, the venturi effect causes the static pressure, and therefore the density, to decrease at the constriction. Choked flow is a limiting condition where the mass flow will not increase with a further decrease in the downstream pressure environment for a fixed upstream pressure and temperature. For homogeneous fluids, the physical point at which the choking occurs f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |