|
Invariant Measure
In mathematics, an invariant measure is a measure that is preserved by some function. The function may be a geometric transformation. For examples, circular angle is invariant under rotation, hyperbolic angle is invariant under squeeze mapping, and a difference of slopes is invariant under shear mapping. Ergodic theory is the study of invariant measures in dynamical systems. The Krylov–Bogolyubov theorem proves the existence of invariant measures under certain conditions on the function and space under consideration. Definition Let (X, \Sigma) be a measurable space and let f : X \to X be a measurable function from X to itself. A measure \mu on (X, \Sigma) is said to be invariant under f if, for every measurable set A in \Sigma, \mu\left(f^(A)\right) = \mu(A). In terms of the pushforward measure, this states that f_*(\mu) = \mu. The collection of measures (usually probability measures) on X that are invariant under f is sometimes denoted M_f(X). The collection of ergodic meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
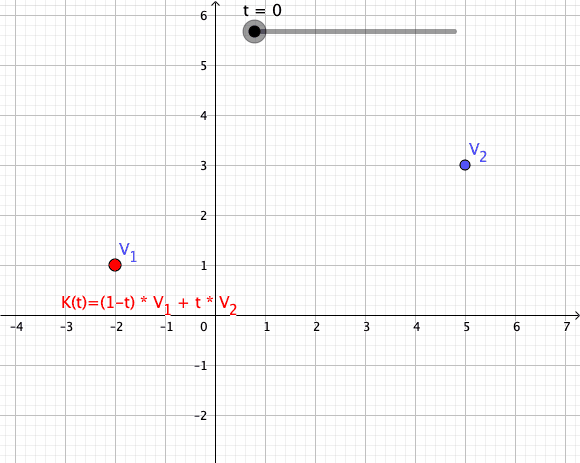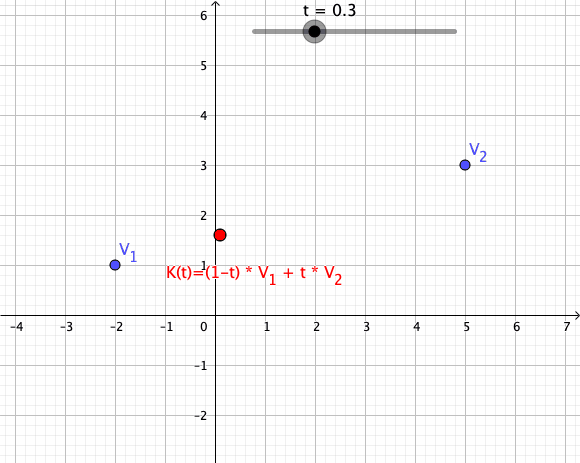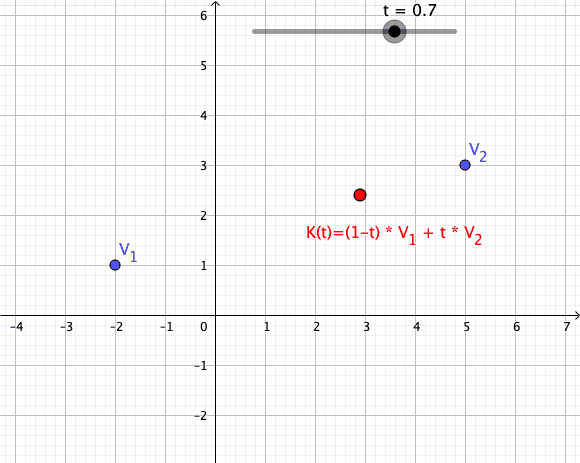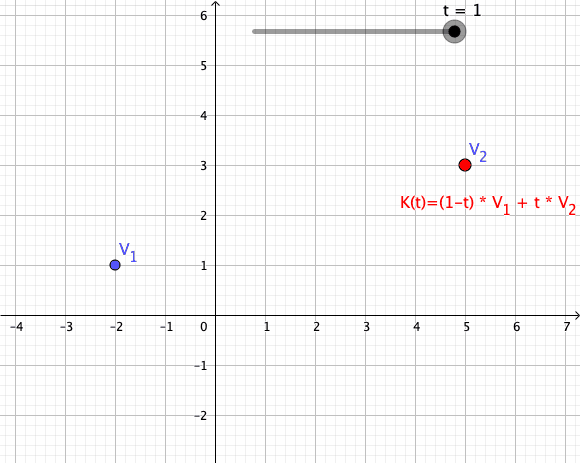
Convex Combination
In convex geometry and vector algebra, a convex combination is a linear combination of points (which can be vectors, scalars, or more generally points in an affine space) where all coefficients are non-negative and sum to 1. In other words, the operation is equivalent to a standard weighted average, but whose weights are expressed as a percent of the total weight, instead of as a fraction of the ''count'' of the weights as in a standard weighted average. More formally, given a finite number of points x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n in a real vector space, a convex combination of these points is a point of the form :\alpha_1x_1+\alpha_2x_2+\cdots+\alpha_nx_n where the real numbers \alpha_i satisfy \alpha_i\ge 0 and \alpha_1+\alpha_2+\cdots+\alpha_n=1. As a particular example, every convex combination of two points lies on the line segment between the points. A set is convex if it contains all convex combinations of its points. The convex hull of a given set of points is identical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebesgue Measure
In measure theory, a branch of mathematics, the Lebesgue measure, named after French mathematician Henri Lebesgue, is the standard way of assigning a measure to subsets of ''n''-dimensional Euclidean space. For ''n'' = 1, 2, or 3, it coincides with the standard measure of length, area, or volume. In general, it is also called ''n''-dimensional volume, ''n''-volume, or simply volume. It is used throughout real analysis, in particular to define Lebesgue integration. Sets that can be assigned a Lebesgue measure are called Lebesgue-measurable; the measure of the Lebesgue-measurable set ''A'' is here denoted by ''λ''(''A''). Henri Lebesgue described this measure in the year 1901, followed the next year by his description of the Lebesgue integral. Both were published as part of his dissertation in 1902. Definition For any interval I = ,b/math>, or I = (a, b), in the set \mathbb of real numbers, let \ell(I)= b - a denote its length. For any subset E\subseteq\mathbb, the Lebesgue oute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borel Sigma Algebra
In mathematics, a Borel set is any set in a topological space that can be formed from open sets (or, equivalently, from closed sets) through the operations of countable union, countable intersection, and relative complement. Borel sets are named after Émile Borel. For a topological space ''X'', the collection of all Borel sets on ''X'' forms a σ-algebra, known as the Borel algebra or Borel σ-algebra. The Borel algebra on ''X'' is the smallest σ-algebra containing all open sets (or, equivalently, all closed sets). Borel sets are important in measure theory, since any measure defined on the open sets of a space, or on the closed sets of a space, must also be defined on all Borel sets of that space. Any measure defined on the Borel sets is called a Borel measure. Borel sets and the associated Borel hierarchy also play a fundamental role in descriptive set theory. In some contexts, Borel sets are defined to be generated by the compact sets of the topological space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Line
In elementary mathematics, a number line is a picture of a graduated straight line (geometry), line that serves as visual representation of the real numbers. Every point of a number line is assumed to correspond to a real number, and every real number to a point. The integers are often shown as specially-marked points evenly spaced on the line. Although the image only shows the integers from –3 to 3, the line includes all real numbers, continuing forever in each direction, and also numbers that are between the integers. It is often used as an aid in teaching simple addition and subtraction, especially involving negative numbers. In advanced mathematics, the number line can be called as a real line or real number line, formally defined as the set (mathematics), set of all real numbers, viewed as a geometry, geometric space (mathematics), space, namely the Euclidean space of dimension one. It can be thought of as a vector space (or affine space), a metric space, a topological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Sector Squeeze Mapping
Hyperbolic is an adjective describing something that resembles or pertains to a hyperbola (a curve), to hyperbole (an overstatement or exaggeration), or to hyperbolic geometry. The following phenomena are described as ''hyperbolic'' because they manifest hyperbolas, not because something about them is exaggerated. * Hyperbolic angle, an unbounded variable referring to a hyperbola instead of a circle * Hyperbolic coordinates, location by geometric mean and hyperbolic angle in quadrant I *Hyperbolic distribution, a probability distribution characterized by the logarithm of the probability density function being a hyperbola * Hyperbolic equilibrium point, a fixed point that does not have any center manifolds * Hyperbolic function, an analog of an ordinary trigonometric or circular function * Hyperbolic geometric graph, a random network generated by connecting nearby points sprinkled in a hyperbolic space * Hyperbolic geometry, a non-Euclidean geometry * Hyperbolic group, a finitely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Operator
Transfer may refer to: Arts and media * ''Transfer'' (2010 film), a German science-fiction movie directed by Damir Lukacevic and starring Zana Marjanović * ''Transfer'' (1966 film), a short film * ''Transfer'' (journal), in management studies * "The Transfer" (''Smash''), a television episode *''The Transfer'', a novel by Silvano Ceccherini Finance * Transfer payment, a redistribution of income and wealth by means of the government making a payment * Balance transfer, transfer of the balance (either of money or credit) in an account to another account * Money transfer (other) ** Wire transfer, an international expedited bank-to-bank funds transfer Science and technology Learning and psychology * Transfer (propaganda), a method of psychological manipulation * Knowledge transfer, within organizations * Language transfer, in which native-language grammar and pronunciation influence the learning and use of a second language * Transfer of learning, in education Mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Differential Equation
A stochastic differential equation (SDE) is a differential equation in which one or more of the terms is a stochastic process, resulting in a solution which is also a stochastic process. SDEs are used to model various phenomena such as stock prices or physical systems subject to thermal fluctuations. Typically, SDEs contain a variable which represents random white noise calculated as the derivative of Brownian motion or the Wiener process. However, other types of random behaviour are possible, such as jump processes. Random differential equations are conjugate to stochastic differential equations. Background Stochastic differential equations originated in the theory of Brownian motion, in the work of Albert Einstein and Smoluchowski. These early examples were linear stochastic differential equations, also called 'Langevin' equations after French physicist Langevin, describing the motion of a harmonic oscillator subject to a random force. The mathematical theory of stochasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markov Chain
A Markov chain or Markov process is a stochastic model describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. Informally, this may be thought of as, "What happens next depends only on the state of affairs ''now''." A countably infinite sequence, in which the chain moves state at discrete time steps, gives a discrete-time Markov chain (DTMC). A continuous-time process is called a continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC). It is named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov. Markov chains have many applications as statistical models of real-world processes, such as studying cruise control systems in motor vehicles, queues or lines of customers arriving at an airport, currency exchange rates and animal population dynamics. Markov processes are the basis for general stochastic simulation methods known as Markov chain Monte Carlo, which are used for simulating sampling from complex probability dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the possible upper sides of a flipped coin such as heads H and tails T) in a sample space (e.g., the set \) to a measurable space, often the real numbers (e.g., \ in which 1 corresponding to H and -1 corresponding to T). Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice; it may also represent uncertainty, such as measurement error. However, the interpretation of probability is philosophically complicated, and even in specific cases is not always straightforward. The purely mathematical analysis of random variables is independent of such interpretational difficulties, and can be based upon a rigorous axiomatic setup. In the formal mathematical language of measure theory, a random var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
If And Only If
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" (shortened as "iff") is a biconditional logical connective between statements, where either both statements are true or both are false. The connective is biconditional (a statement of material equivalence), and can be likened to the standard material conditional ("only if", equal to "if ... then") combined with its reverse ("if"); hence the name. The result is that the truth of either one of the connected statements requires the truth of the other (i.e. either both statements are true, or both are false), though it is controversial whether the connective thus defined is properly rendered by the English "if and only if"—with its pre-existing meaning. For example, ''P if and only if Q'' means that ''P'' is true whenever ''Q'' is true, and the only case in which ''P'' is true is if ''Q'' is also true, whereas in the case of ''P if Q'', there could be other scenarios where ''P'' is true and ''Q'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |