|
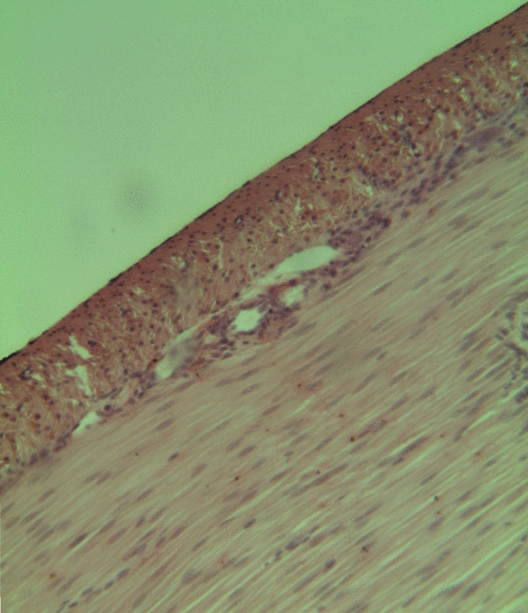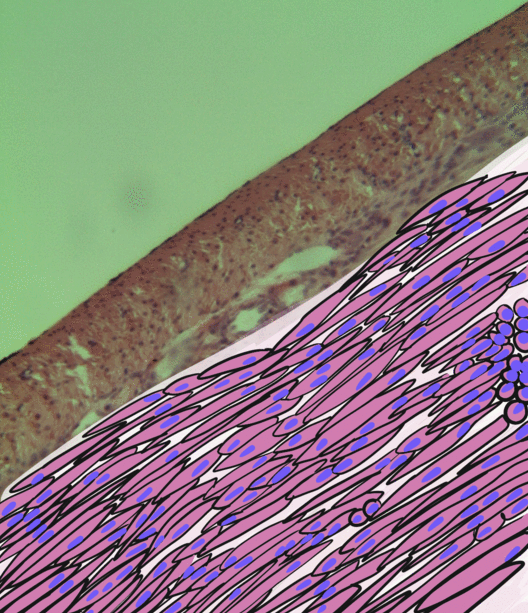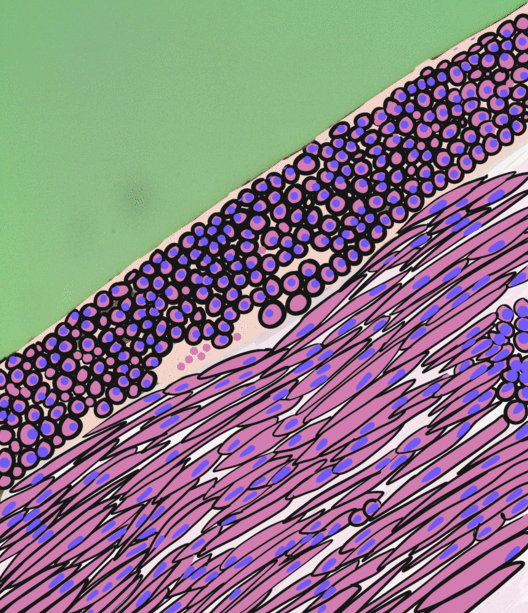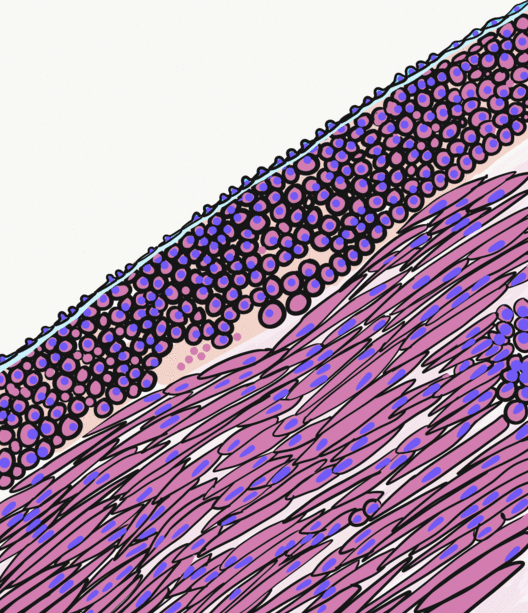
Internal Elastic Lamina
The internal elastic lamina or internal elastic lamella is a layer of elastic tissue that forms the outermost part of the tunica intima of blood vessels. It separates tunica intima from tunica media. Histology It is readily visualized with light microscopy in sections of muscular arteries, where it is thick and prominent, and arterioles, where it is slightly less prominent and often incomplete. It is very thin in veins and venules. In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present.http://www.ouhsc.edu/histology/text%20sections/cardiovascular.html There is small amount of subendothelial connective tissue between basement membrane of endothelial cells and internal elastic lamina. Reduplication of internal elastic lamina can be seen in elderly individuals due to intimal fib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
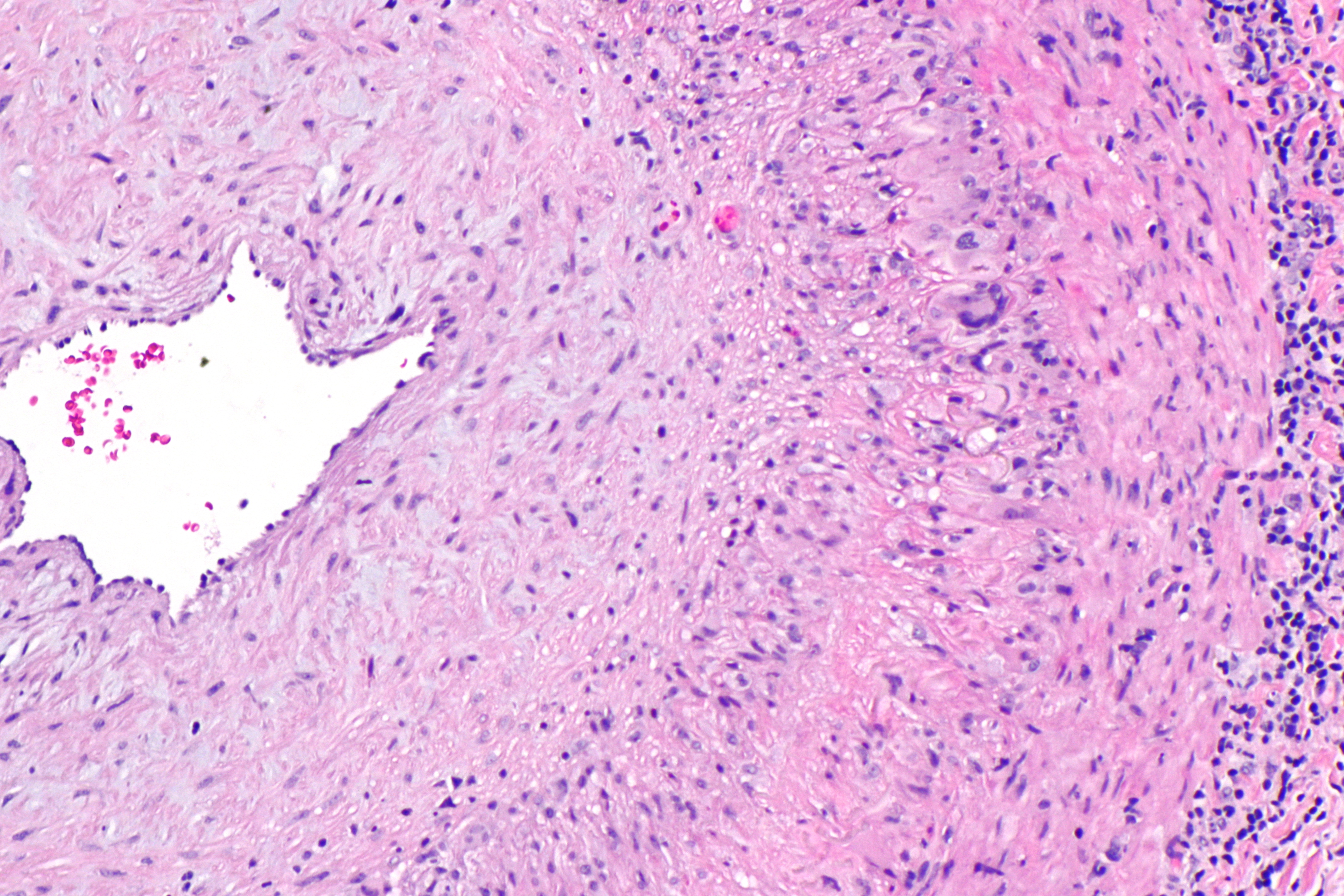
Cholesterol Embolus - Very High Mag
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Intima
The tunica intima (New Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic arteries – A single layer of Endothelial and a supporting layer of elastin-rich collagen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Media
The tunica media (New Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. Artery Tunica media is made up of smooth muscle cells, elastic tissue and collagen. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. The middle coat (tunica media) is distinguished from the inner (tunica intima) by its color and by the transverse arrangement of its fibers. * In the ''smaller arteries'' it consists principally of smooth muscle fibers in fine bundles, arranged in lamellæ and disposed circularly around the vessel. These lamellæ vary in number according to the size of the vessel; the smallest arteries having only a single layer, and those slightly larger three or four layers - up to a maximum of six layers. It is to this coat that the thickness of the wall of the artery is mainly due. * In the ''larger arteries'', as the ilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributing Artery
A muscular artery (or distributing artery) is a medium-sized artery that draws blood from an elastic artery and branches into "resistance vessels" including small arteries and arterioles. Their walls contain larger number of smooth muscles, allowing them to contract and expand depending on peripheral blood demand. This contrasts to the mechanism of elastic arteries, which use their elastic properties to store the energy generated by the heart's contraction for a brief moment (elastic recoil). Under the microscope, muscular arteries can be identified by their clearly defined internal elastic lamina. In constricted vessels, the elastic lamina of muscular arteries appears thick and kinky. The elastic lamina is best visualized using Verhoeff's stain, but can be easily detected in specimens stained using other techniques as a well-defined negative staining region. Examples of muscular arteries include the radial artery, femoral artery and the splenic artery In human anatomy, the spl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterioles
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries.This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure Microanatomy In a healthy vascular system the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of nitric oxide by the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conducting Artery
An elastic artery (conducting artery or conduit artery) is an artery with many collagen and elastin filaments in the tunica media, which gives it the ability to stretch in response to each pulse. This elasticity also gives rise to the Windkessel effect, which helps to maintain a relatively constant pressure in the arteries despite the pulsating nature of the blood flow. Elastic arteries include the largest arteries in the body, those closest to the heart. They give rise to medium-sized vessels known as distributing arteries (or ''muscular arteries''). The pulmonary arteries, the aorta, and its branches together comprise the body's system of elastic arteries. Elastic arteries receive their own blood supply by the vasa vasorum unlike smaller blood vessels, which are supplied by diffusion Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between Epithelium, epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The Electron microscope, electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an underlying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intimal Fibroplasia
The tunica intima (New Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic arteries – A single layer of Endothelial and a supporting layer of elastin-rich coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aging
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have ceased dividing, or to the population of a species. In humans, ageing represents the accumulation of changes in a human being over time and can encompass physical, psychological, and social changes. Reaction time, for example, may slow with age, while memories and general knowledge typically increase. Ageing increases the risk of human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke and many more. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Current ageing theories are assigned to the damage concept, whereby the accumulation of damage (such as DNA ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Gieson
Van Gieson's stain is a mixture of picric acid and acid fuchsin. It is the simplest method of differential staining of collagen and other connective tissue. It was introduced to histology by American neuropsychiatrist and pathologist Ira Van Gieson. HvG stain generally refers to the combination of hematoxylin and ''Van Gieson's stain'', but can possibly refer to a combination of hibiscus extract-iron solution and ''Van Gieson's stain''. Other dyes Other dyes used in connection with Van Gieson staining include: * Alcian blue * Amido black 10B * Verhoeff's stain Verhoeff's stain, also known as Verhoeff's elastic stain (VEG) or Verhoeff–Van Gieson stain (VVG), is a staining protocol used in histology, developed by American ophthalmic surgeon and pathologist Frederick Herman Verhoeff (1874–1968) in 1908 ... References Histology Staining {{Biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Cell Arteritis
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), also called temporal arteritis, is an inflammatory autoimmune disease of large blood vessels. Symptoms may include headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, and difficulty opening the mouth. Complication can include blockage of the artery to the eye with resulting blindness, as well as aortic dissection, and aortic aneurysm. GCA is frequently associated with polymyalgia rheumatica. The cause is unknown. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the small blood vessels that supply the walls of larger arteries. This mainly affects arteries around the head and neck, though some in the chest may also be affected. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms, blood tests, and medical imaging, and confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery. However, in about 10% of people the temporal artery is normal. Treatment is typical with high doses of steroids such as prednisone or prednisolone. Once symptoms have resolved, the dose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |