|
Intersection (aviation)
In aviation, an intersection is a virtual navigational fix that helps aircraft maintain their flight plan. It is usually defined as the intersection (in the geometrical sense) of two VOR radials. They are usually identified as major airway intersections where aircraft, operating under instrument flight rules, often change direction of flight while en route. According to the Federal Aviation Regulations, some intersections are designated as mandatory reporting points for pilots who are not in radar contact with air traffic control. Intersections also play an important role in departure and approach procedures. All intersections have an alphabetical or alphanumeric designation. Near major airports, the intersection designation code typically consists of three letters followed by the runway number. Most other intersection designations consist of five-letter combinations that are either pronounceable or chosen for their mnemonic value, since either air traffic control Air t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ktso INTERSECTIONS
KTSO (100.9 FM) is a radio station licensed to Sapulpa, Oklahoma that serves the greater Tulsa area broadcasting an oldies-leaning soft adult contemporary format. It is part of the Stephens Media Group (no relation to the newspaper owner) and has been on the air since 1977. Its studios are located at the CityPlex Towers in South Tulsa. Radio tower KTSO broadcasts from a tower between Glenpool and Sapulpa, off Highway 75. The tower was constructed in 2014, while the station was still KXOJ-FM, and was part of an FCC granted class C3 upgrade, increasing the station to an ERP of 19,000 watts. The new signal also includes an HD signal that covers the Tulsa metro area. Previously, KXOJ operated from a 361-foot tower near Sapulpa, operating at only 5,000 watts. Several inner-ring Tulsa suburbs such as Broken Arrow, Claremore and Okmulgee only got a grade B signal. History Before August 16, 2016, 100.9 FM's call sign was KXOJ-FM. Every morning between 6 and 10am KXOJ-FM's on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Aviation Regulations
The Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs) are rules prescribed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) governing all aviation activities in the United States. The FARs comprise Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). A wide variety of activities are regulated, such as aircraft design and maintenance, typical airline flights, pilot training activities, hot-air ballooning, lighter-than-air aircraft, man-made structure heights, obstruction lighting and marking, model rocket launches, commercial space operations, model aircraft operations, Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) and kite flying. The rules are designed to promote safe aviation, protecting pilots, flight attendants, passengers and the general public from unnecessary risk. FAR vs. 14 CFR Since 1958, these rules have typically been referred to as "FARs", short for Federal Aviation Regulations. However, another set of regulations (Title 48) is titled "Federal Acquisitions Regulations", and this has led to con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercept Method
In astronomical navigation, the intercept method, also known as Marcq St. Hilaire method, is a method of calculating an observer's position on earth (geopositioning). It was originally called the ''azimuth intercept'' method because the process involves drawing a line which intercepts the azimuth line. This name was shortened to ''intercept'' method and the ''intercept distance'' was shortened to 'intercept'. The method yields a line of position (LOP) on which the observer is situated. The intersection of two or more such lines will define the observer's position, called a "fix". Sights may be taken at short intervals, usually during hours of twilight, or they may be taken at an interval of an hour or more (as in observing the Sun during the day). In either case, the lines of position, if taken at different times, must be advanced or retired to correct for the movement of the ship during the interval between observations. If observations are taken at short intervals, a few minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Position Line
A position line or line of position (LOP) is a line (or, on the surface of the earth, a curve) that can be both identified on a chart (nautical chart or aeronautical chart) and translated to the surface of the earth. The intersection of a minimum of two position lines is a fix that is used in position fixing to identify a navigator's location. There are several types of position line: * Compass bearing – the angle between north and the line passing through the compass and the point of interest * Transit – a line passing through the observer and two other reference points * Leading line – the line passing through two marks indicating a safe channel * Leading lights – the line passing through two beacons indicating a safe channel * Sector lights – the lines created by masked colored lights that indicate a safe channel See also * Coordinate line * Intersection (aeronautics) * Navigation * Position circle A position circle is a circle that can be measured both from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviator
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators, because they are involved in operating the aircraft's navigation and engine systems. Other aircrew members, such as drone operators, flight attendants, mechanics and ground crew, are not classified as aviators. In recognition of the pilots' qualifications and responsibilities, most militaries and many airlines worldwide award aviator badges to their pilots. History The first recorded use of the term ''aviator'' (''aviateur'' in French) was in 1887, as a variation of ''aviation'', from the Latin ''avis'' (meaning ''bird''), coined in 1863 by in ''Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne'' ("Aviation or Air Navigation"). The term ''aviatrix'' (''aviatrice'' in French), now archaic, was formerly used for a female aviator. These terms were used more in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding. Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imagery as specific tools to encode information in a way that allows for efficient storage and retrieval. Mnemonics aid original information in becoming associated with something more accessible or meaningful—which, in turn, provides better retention of the information. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often used for lists and in auditory form, such as short poems, acronyms, initialisms, or memorable phrases, but mnemonics can also be used for other types of information and in visual or kinesthetic forms. Their use is based on the observation that the human mind more easily remembers spatial, personal, surprising, physical, sexual, humorous, or otherwise "relatable" information, rather than more abstract or impersonal forms of informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
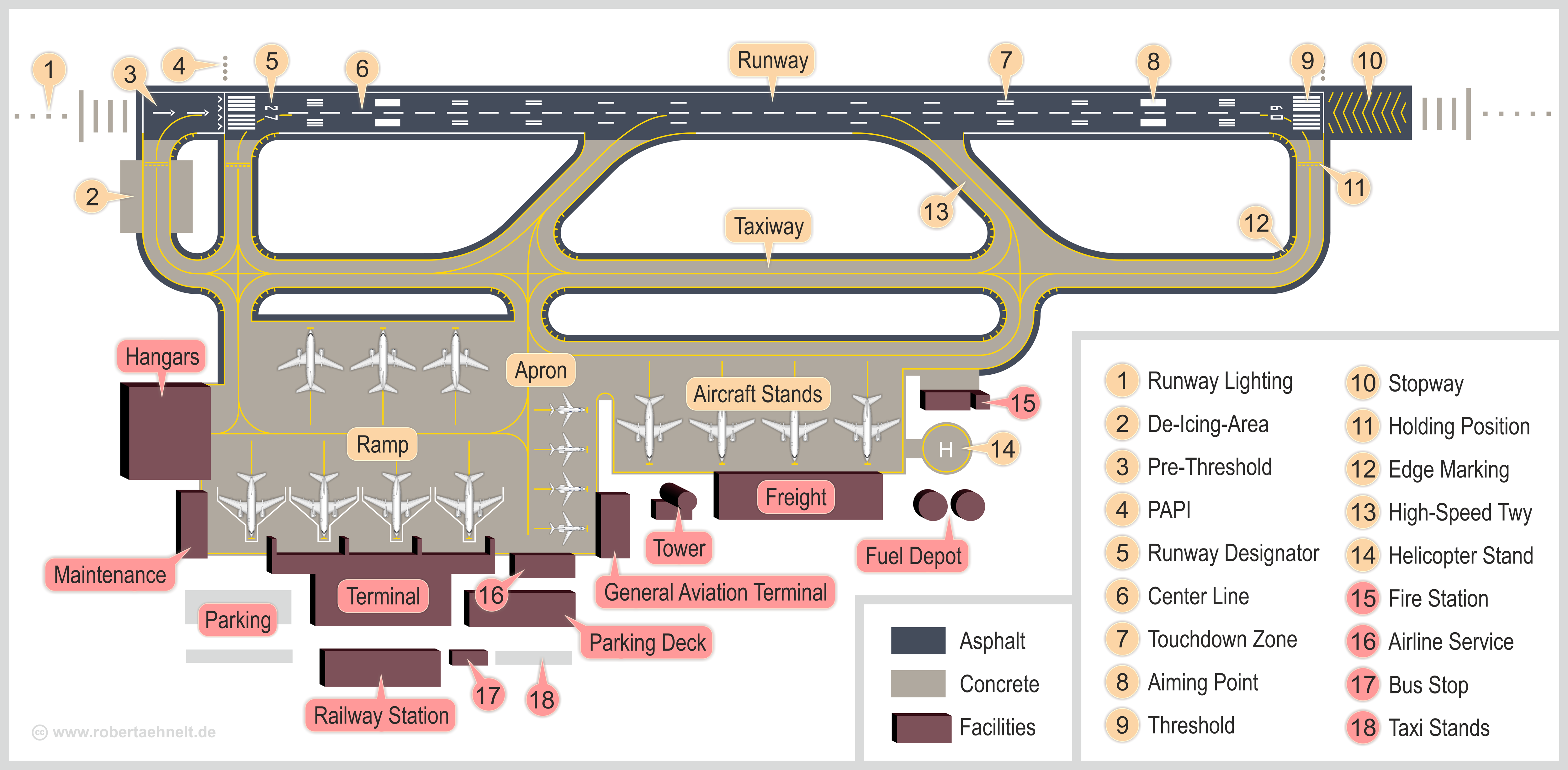
Runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, grass, soil, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or road salt, salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and Airport apron, ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using Tarmacadam, tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now International Civil Aviation Organization#Use of the International System of Units, commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphanumeric
Alphanumericals or alphanumeric characters are a combination of alphabetical and numerical characters. More specifically, they are the collection of Latin letters and Arabic digits. An alphanumeric code is an identifier made of alphanumeric characters. Merriam-Webster suggests that the term "alphanumeric" may often additionally refer to other symbols, such as punctuation and mathematical symbols. In the POSIX/C locale, there are either 36 (A–Z and 0–9, case insensitive) or 62 (A–Z, a–z and 0–9, case-sensitive) alphanumeric characters. Subsets of alphanumeric used in human interfaces When a string of mixed alphabets and numerals is presented for human interpretation, ambiguities arise. The most obvious is the similarity of the letters I, O and Q to the numbers 1 and 0. Therefore, depending on the application, various subsets of the alphanumeric were adopted to avoid misinterpretation by humans. In passenger aircraft, aircraft seat maps and seats were designated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first fully phonemic script, the Proto-Sinaitic script, later known as the Phoenician alphabet, is considered to be the first alphabet and is the ancestor of most modern alphabets, including Arabic, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Latin, and possibly Brahmic. It was created by Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in the Sinai Peninsula (as the Proto-Sinaitic script), by selecting a small number of hieroglyphs commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values of the Canaanite languages. However, Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Traffic Control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airspace. The primary purpose of ATC worldwide is to prevent collisions, organize and expedite the flow of air traffic, and provide information and other support for pilots. Air traffic controllers monitor the location of aircraft in their assigned airspace by radar and communicate with the pilots by radio. To prevent collisions, ATC enforces Separation (air traffic control), traffic separation rules, which ensure each aircraft maintains a minimum amount of empty space around it at all times. In many countries, ATC provides services to all private, military, and commercial aircraft operating within its airspace. Depending on the type of flight and the class of airspace, ATC may issue ''instructions'' that pilots are required to obey, or ''advis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be achieved by generating aerodynamic lift associated with gliding or propulsive thrust, aerostatically using buoyancy, or by ballistic movement. Many things can fly, from animal aviators such as birds, bats and insects, to natural gliders/parachuters such as patagial animals, anemochorous seeds and ballistospores, to human inventions like aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, airships, balloons, etc.) and rockets which may propel spacecraft and spaceplanes. The engineering aspects of flight are the purview of aerospace engineering which is subdivided into aeronautics, the study of vehicles that travel through the atmosphere, and astronautics, the study of vehicles that travel through space, and ballistics, the study of the flight of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_Ystad-2020.jpg)


