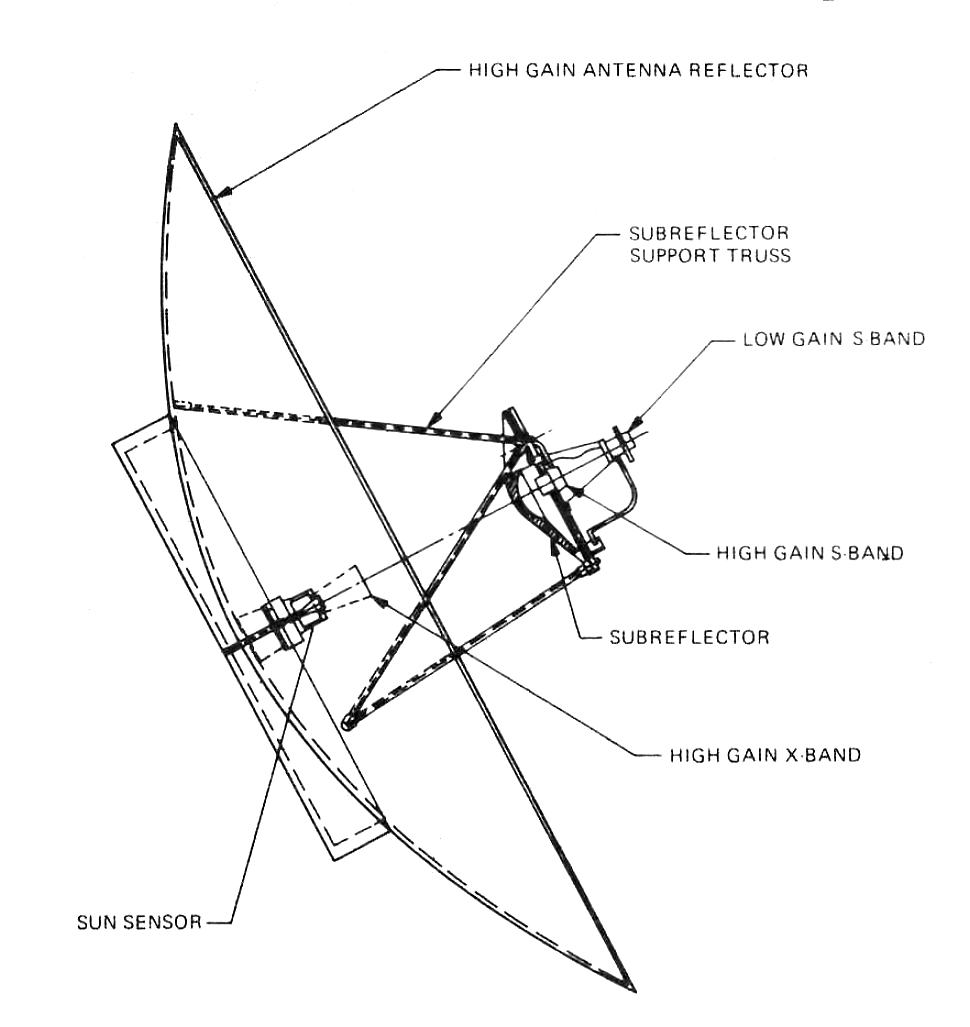
|
Inner Satellite
In astronomy, an inner moon or inner natural satellite is a natural satellite following a prograde, low-inclination orbit inwards of the large satellites of the parent planet. They are generally thought to have been formed ''in situ'' at the same time as the coalescence of the original planet. Neptune's moons are an exception, as they are likely reaggregates of the pieces of the original bodies, which were disrupted after the capture of the large moon Triton. Inner satellites are distinguished from other regular satellites by their proximity to the parent planet, their short orbital periods (usually under a day), their low mass, small size, and irregular shapes. Discovery Thirty inner satellites are currently known, found orbiting around all four of the giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune). Because of their small size, and glare from the nearby planet, they can be very difficult to observe from Earth. Some, such as Pan and Daphnis at Saturn, have only ever been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Emerson Barnard
Edward Emerson Barnard (December 16, 1857 – February 6, 1923) was an American astronomer. He was commonly known as E. E. Barnard, and was recognized as a gifted observational astronomer. He is best known for his discovery of the high proper motion of Barnard's Star in 1916, which is named in his honor. Early life Barnard was born in Nashville, Tennessee, to Reuben Barnard and Elizabeth Jane Barnard (''née'' Haywood), and had one brother. His father died three months before his birth, so he grew up in an impoverished family and did not receive much in the way of formal education. His first interest was in the field of photography, and he became a photographer's assistant at the age of nine. He later developed an interest in astronomy. In 1876 he purchased a refractor telescope, and in 1881 he discovered his first comet, but failed to announce his discovery. He found his second comet later the same year and a third in 1882. While he was still working at a photography studio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
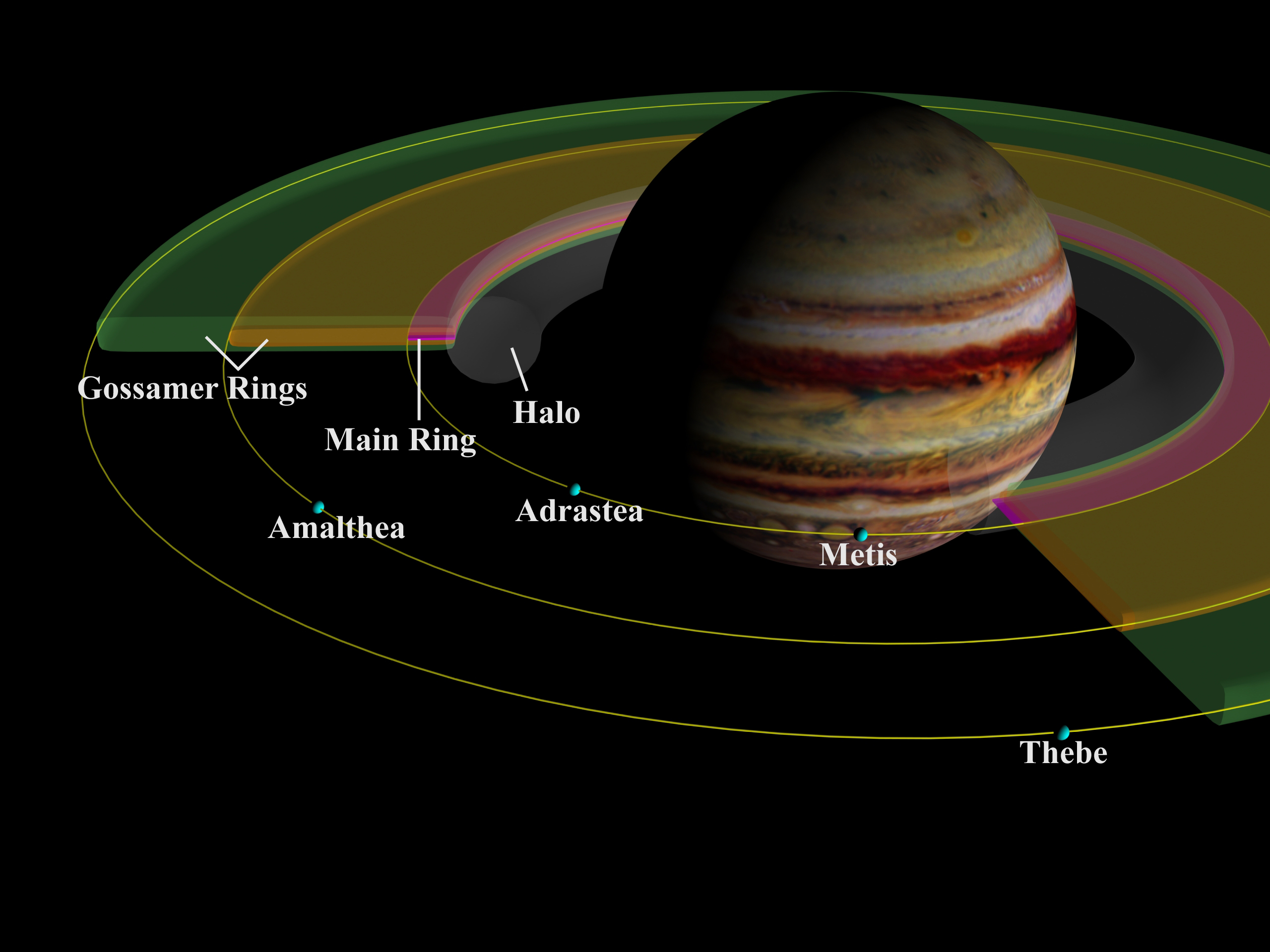
Metis (moon)
Metis , also known as , is the innermost known moon of Jupiter. It was discovered in 1979 in images taken by ''Voyager 1'', and was named in 1983 after the first wife of Zeus, Metis. Additional observations made between early 1996 and September 2003 by the ''Galileo'' spacecraft allowed its surface to be imaged. Metis is tidally locked to Jupiter, and its shape is strongly asymmetrical, with one of the diameters being almost twice as large as the smallest one. It is also one of the two moons known to orbit Jupiter in less than the length of Jupiter's day, the other being Adrastea. It orbits within the main ring of Jupiter, and is thought to be a major contributor of material to the rings. Discovery and observations Metis was discovered in 1979 by Stephen P. Synnott in images taken by the ''Voyager 1'' probe and was provisionally designated as . In 1983, it was officially named after the mythological Metis, a Titaness who was the first wife of Zeus (the Greek equivalen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Deceleration
Tidal acceleration is an effect of the tidal forces between an orbiting natural satellite (e.g. the Moon) and the primary planet that it orbits (e.g. Earth). The acceleration causes a gradual recession of a satellite in a prograde orbit away from the primary, and a corresponding slowdown of the primary's rotation. The process eventually leads to tidal locking, usually of the smaller body first, and later the larger body (e.g. theoretically with Earth in 50 billion years). The Earth–Moon system is the best-studied case. The similar process of tidal deceleration occurs for satellites that have an orbital period that is shorter than the primary's rotational period, or that orbit in a retrograde direction. The naming is somewhat confusing, because the average speed of the satellite relative to the body it orbits is ''decreased'' as a result of tidal acceleration, and ''increased'' as a result of tidal deceleration. This conundrum occurs because a positive acceleration at one instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naiad (moon)
Naiad , (also known as Neptune III and previously designated as S/1989 N 6) named after the naiads of Greek legend, is the innermost satellite of Neptune and the nearest to the center of any gas giant with moons with a distance of 48,224 km from the planet's center. Its orbital period is less than a Neptunian day, resulting in tidal dissipation that will cause its orbit to decay. Eventually it will either crash into Neptune's atmosphere or break up to become a new ring. History Naiad was discovered sometime before mid-September 1989 from the images taken by the ''Voyager 2'' probe. The last moon to be discovered during the flyby, it was designated S/1989 N 6. The discovery was announced on 29 September 1989, in the IAU Circular No. 4867, and mentions "25 frames taken over 11 days", implying a discovery date of sometime before 18 September. The name was given on 16 September 1991. Physical characteristics Naiad is irregularly shaped. It is likely that it is a ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roche Limit
In celestial mechanics, the Roche limit, also called Roche radius, is the distance from a celestial body within which a second celestial body, held together only by its own force of gravity, will disintegrate because the first body's tidal forces exceed the second body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings, whereas outside the limit, material tends to coalesce. The Roche radius depends on the radius of the first body and on the ratio of the bodies' densities. The term is named after Édouard Roche (, ), the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848. Explanation The Roche limit typically applies to a satellite's disintegrating due to tidal forces induced by its ''primary'', the body around which it orbits. Parts of the satellite that are closer to the primary are attracted more strongly by gravity from the primary than parts that are farther away; this disparity effectively pulls the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebe (moon)
Thebe , also known as , is the fourth of Jupiter's moons by distance from the planet. It was discovered by Stephen P. Synnott in images from the ''Voyager 1'' space probe taken on March 5, 1979, while making its flyby of Jupiter. In 1983, it was officially named after the mythological nymph Thebe. The second largest of the inner satellites of Jupiter, Thebe orbits within the outer edge of the Thebe gossamer ring that is formed from dust ejected from its surface. It is irregularly shaped and reddish in colour, and is thought like Amalthea to consist of porous water ice with unknown amounts of other materials. Its surface features include large craters and high mountains—some of them are comparable to the size of the moon itself. Thebe was photographed in 1979 by the ''Voyager 1'' and ''2'' spacecraft, and later, in more detail, by the ''Galileo'' orbiter in the 1990s. Discovery and observations Thebe was discovered by Stephen P. Synnott in images from the ''Voyager 1'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of a "typical" value. Median income, for example, may be a better way to suggest what a "typical" income is, because income distribution can be very skewed. The median is of central importance in robust statistics, as it is the most resistant statistic, having a breakdown point of 50%: so long as no more than half the data are contaminated, the median is not an arbitrarily large or small result. Finite data set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune. ''Voyager 2'' remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets. ''Voyager 2'' was the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System. ''Voyager 2'' successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989. The spacecraft is now in its extended mission of studying interstellar space. It has been operating for as of ; , it has reached a distance of from Earth. The probe entered interstellar space on November 5, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voyager 1'' has been operating for as of . It communicates through NASA's Deep Space Network to receive routine commands and to transmit data to Earth. Real-time distance and velocity data is provided by NASA and JPL. At a distance of from Earth , it is the most distant human-made object from Earth. The probe made flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's largest moon, Titan. NASA had a choice of either doing a Pluto or Titan flyby; exploration of the moon took priority because it was known to have a substantial atmosphere. ''Voyager 1'' studied the weather, magnetic fields, and rings of the two gas giants and was the first probe to provide detailed images of their moons. As part of the Voyager program and like its sister craft ''Voyager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)