|
IWarp
iWARP is a computer networking protocol that implements remote direct memory access (RDMA) for efficient data transfer over Internet Protocol networks. Contrary to some accounts, iWARP is not an acronym. Because iWARP is layered on Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)-standard congestion-aware protocols such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP), it makes few requirements on the network, and can be successfully deployed in a broad range of environments. History In 2007, the IETF published five Request for Comments (RFCs) that define iWARP: # RFC 5040 ''A Remote Direct Memory Access Protocol Specification'' is layered over Direct Data Placement Protocol (DDP). It defines how RDMA Send, Read, and Write operations are encoded using DDP into headers on the network. # RFC 5041 ''Direct Data Placement over Reliable Transports'' is layered over MPA/TCP or SCTP. It defines how received data can be directly placed into an upper layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Networking Protocol
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses pre-determined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenFabrics Alliance
The OpenFabrics Alliance is a non-profit organization that promotes remote direct memory access (RDMA) switched fabric technologies for server and storage connectivity. These high-speed data-transport technologies are used in high-performance computing facilities, in research and various industries. The OpenFabrics Alliance aims to develop open-source software that supports the three major RDMA fabric technologies: InfiniBand, RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) and iWARP. The software includes two packages, one that runs on Linux and FreeBSD and one that runs on Microsoft Windows. The alliance worked with two large Linux distributors—SUSE and Red Hat—as well as Microsoft on compatibility with their operating systems. History Founded in June 2004 as the OpenIB Alliance, the organization originally developed an InfiniBand software stack for Linux. Initial funding for the Alliance was provided by the United States Department of Energy. The alliance released the first vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
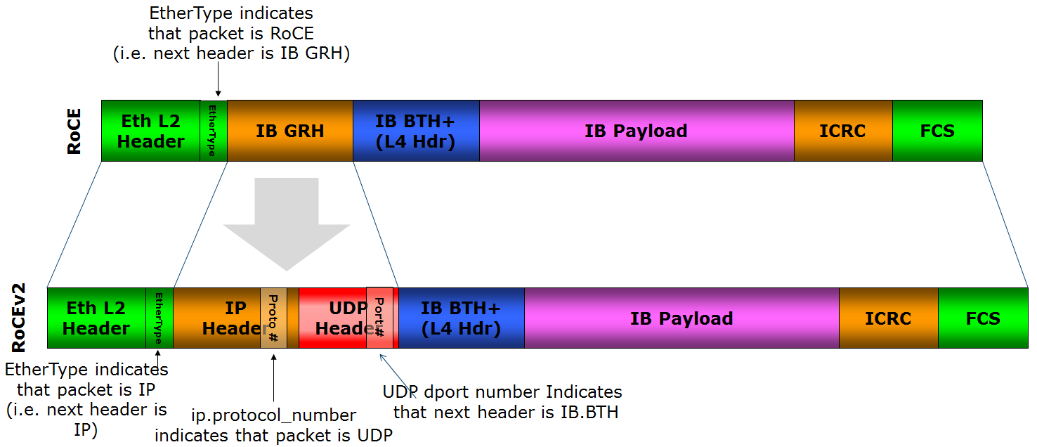
RDMA Over Converged Ethernet
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) or InfiniBand over Ethernet (IBoE) is a network protocol that allows remote direct memory access (RDMA) over an Ethernet network. It does this by encapsulating an InfiniBand (IB) transport packet over Ethernet. There are two RoCE versions, RoCE v1 and RoCE v2. RoCE v1 is an Ethernet link layer protocol and hence allows communication between any two hosts in the same Ethernet broadcast domain. RoCE v2 is an internet layer protocol which means that RoCE v2 packets can be routed. Although the RoCE protocol benefits from the characteristics of a converged Ethernet network, the protocol can also be used on a traditional or non-converged Ethernet network. Background Network-intensive applications like networked storage or cluster computing need a network infrastructure with a high bandwidth and low latency. The advantages of RDMA over other network application programming interfaces such as Berkeley sockets are lower latency, lower CPU load and highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvell Technology, Inc
Marvell may refer to: * Marvell, Arkansas, a small city in the United States * Marvell Technology Group, American semiconductor company People * Andrew Marvell (1621–1678), English metaphysical poet and politician * Marcus Marvell (born 1970), English cricketer * Marjorie Marvell (born 1938), Australian cricket player * William Marvell, 18th century English executioner * Marvell Scott (born 1973), American sports reporter and physician * Marvell Tell (born 1996), American football player * Marvell Thomas (1941–2017), American keyboardist * Marvell Wynne (baseball) (born 1959), American baseball player * Marvell Wynne (soccer) (born 1986), American soccer player, son of the baseball player See also * Captain Marvel (Mar-Vell), a Marvel Comics character * Marvel (other) Marvel may refer to: Business * Marvel Entertainment, an American entertainment company ** Marvel Comics, the primary imprint of Marvel Entertainment ** Marvel Universe, a fictional shared uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelsio Communications
Chelsio Communications is a privately held technology company headquartered in Sunnyvale, California with a design center in Bangalore, India. Early venture capital funding came from Horizons Ventures, Invesco, Investor Growth Capital, NTT Finance, Vendanta Capital, Abacus Capital Group, Pacesetter Capital Group, and New Enterprise Associates. A third round of funding raised $25 million in late 2004. LSI Corporation was added as investor in 2006 in the series D round. By January 2008, a $25M financing round was announced as series E. In 2009, an additional $17M was raised from previous investors plus Mobile Internet Capital. Chelsio sells hardware and software solutions including protocol acceleration technology, Unified Wire Ethernet network adapter cards, unified storage software, high performance storage gateways, unified management software, bypass cards, and other solutions. Chelsio was an early vendor of 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology, announcing a product in 2004, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network File System
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol. Versions and variations Sun used version 1 only for in-house experimental purposes. When the development team added substantial changes to NFS version 1 and released it outside of Sun, they decided to release the new version as v2, so that version interoperation and RPC version fallback could be tested. NFSv2 Version 2 of the protocol (defined in RFC 1094, March 1989) originally operated only over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Its designers meant to keep the server side stateless, with locking (for example) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI RDMA Protocol
In computing the SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) is a protocol that allows one computer to access SCSI devices attached to another computer via remote direct memory access (RDMA).ANSI T10 SRPr16a, www.t10.org ANSI T10 SRPr16a, web.archive.org /ref> The SRP protocol is also known as the SCSI Remote Protocol. The use of RDMA makes higher throughput and lower latency possible than what is generally available through e.g. the TCP/IP communication protocol. Though the SRP protocol has been designed to use RDMA networks efficiently, it is also possible to implement the SRP protocol over networks that do not support RDMA.
|
Sockets Direct Protocol
The Sockets Direct Protocol (SDP) is a transport-agnostic protocol to support stream sockets over remote direct memory access (RDMA) network fabrics. SDP was originally defined by the Software Working Group (SWG) of the InfiniBand Trade Association. Originally designed for InfiniBand (IB), SDP is currently maintained by the OpenFabrics Alliance. Protocol SDP defines a standard wire protocol over an RDMA fabric to support stream sockets (SOCK_STREAM). SDP uses various RDMA network features for high-performance zero-copy data transfers. SDP is a pure wire-protocol level specification and does not go into any socket API or implementation specifics. The purpose of the Sockets Direct Protocol is to provide an RDMA-accelerated alternative to the Transmission Control Protocol, TCP protocol on Internet Protocol, IP. The goal is to do this in a manner which is transparent to the application. Solaris 10 and Solaris 11 Express include support for SDP. Several other Unix operating system var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Server Message Block
Server Message Block (SMB) is a communication protocol originally developed in 1983 by Barry A. Feigenbaum at IBM and intended to provide shared access to files and printers across nodes on a network of systems running IBM's OS/2. It also provides an authenticated inter-process communication (IPC) mechanism. In 1987, Microsoft and 3Com implemented SMB in LAN Manager for OS/2, at which time SMB used the NetBIOS service atop the NetBIOS Frames protocol as its underlying transport. Later, Microsoft implemented SMB in Windows NT 3.1 and has been updating it ever since, adapting it to work with newer underlying transports: TCP/IP and NetBT. SMB implementation consists of two vaguely named Windows services: "Server" (ID: LanmanServer) and "Workstation" (ID: LanmanWorkstation). It uses NTLM or Kerberos protocols for user authentication. In 1996, Microsoft published a version of SMB 1.0 with minor modifications under the Common Internet File System (CIFS ) moniker. CIFS was compatible w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |