|
Hysterotomy Abortion
Hysterotomy abortion is a surgical procedure that removes an intact fetus from the uterus in a process similar to a cesarean section. The procedure is generally used after another method of termination has failed, or when such a procedure would be medically inadvisable, such as in the case of placenta accreta.Roche, Natalie E. (June 16, 2006)Surgical Management of Abortion Retrieved July 1, 2007. In 2016, this method made up less than 0.01% of all abortions in the United States, with the CDC reporting only 51 having occurred due to the invasive and complex nature of the procedure, and the availability of much simpler and safer methods. In 2022, scholars reported that in the aftermath of the overturning of ''Roe v. Wade'' and the subsequent limitations on elective induced abortion in Texas, providers were performing hysterotomy abortions again, under the view that it may not be technically considered an abortion under existing law. Indications As with other abortion procedures, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
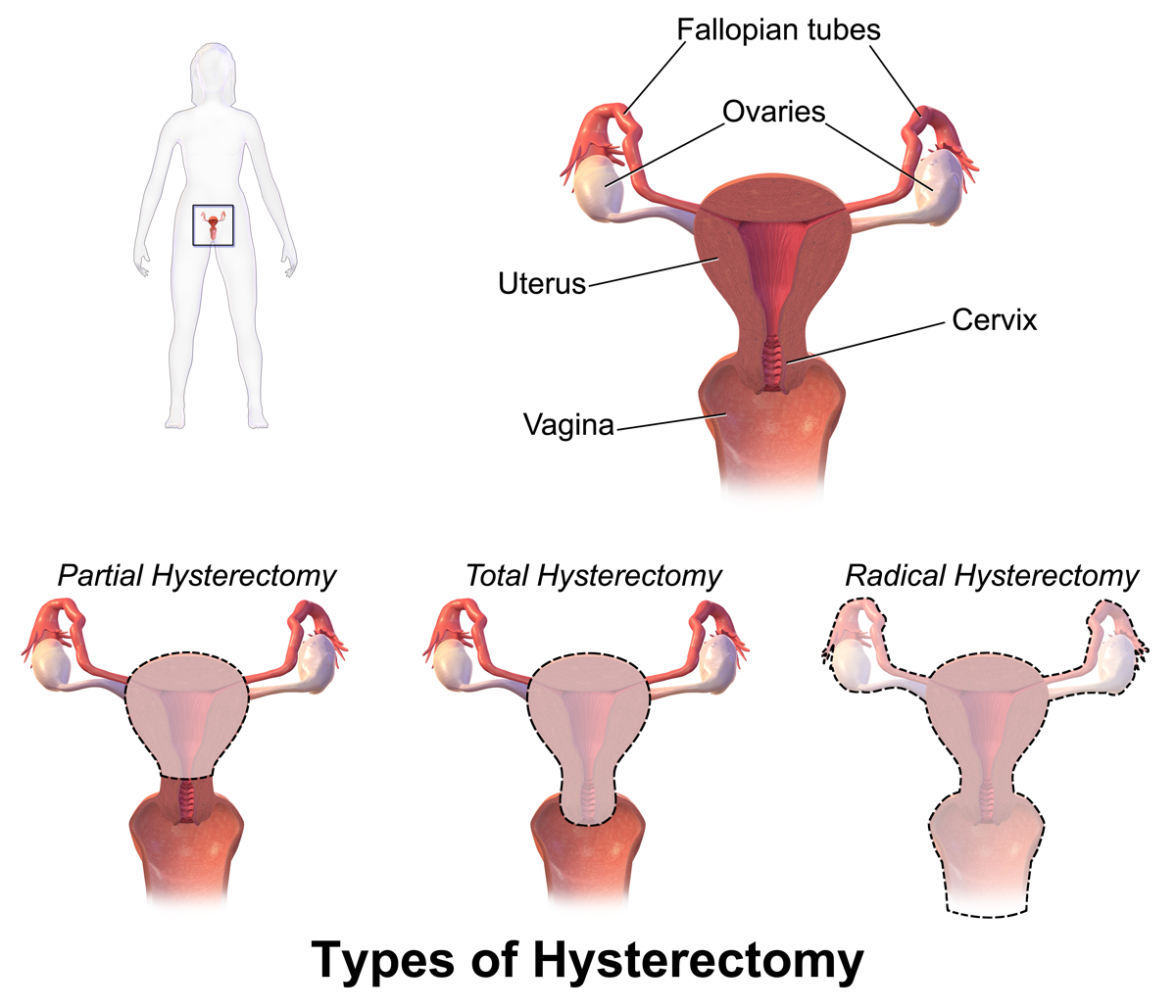
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries (oophorectomy), Fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. Usually performed by a gynecologist, a hysterectomy may be total (removing the body, fundus, and cervix of the uterus; often called "complete") or partial (removal of the uterine body while leaving the cervix intact; also called "supracervical"). Removal of the uterus renders the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as endometriosis, irregular bleeding, and uterine fibroids. It is expected that the frequency of hysterectom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Surgery
The term abdominal surgery broadly covers Surgery, surgical procedures that involve opening the abdomen (laparotomy). Surgery of each abdominal organ is dealt with separately in connection with the description of that organ (see stomach, kidney, liver, etc.) Diseases affecting the abdominal cavity are dealt with generally under their own names (e.g. appendicitis). Types The most common abdominal surgeries are described below. *Appendectomy: surgical opening of the abdominal cavity and removal of the vermiform appendix, appendix. Typically performed as definitive treatment for appendicitis, although sometimes the appendix is Preventive healthcare, prophylactically removed incidental to another abdominal procedure. *Caesarean section (also known as C-section): a surgical procedure in which one or more incisions are made through a mother's abdomen (laparotomy) and uterus (hysterotomy) to deliver one or more babies, or, rarely, to remove a dead fetus. *Inguinal hernia surgery: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain death is sometimes used as a legal definition of death. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose shortly after death. Death is an inevitable process that eventually occurs in almost all organisms. Death is generally applied to whole organisms; the similar process seen in individual components of an organism, such as cells or tissues, is necrosis. Something that is not considered an organism, such as a virus, can be physically destroyed but is not said to die. As of the early 21st century, over 150,000 humans die each day, with ageing being by far the most common cause of death. Many cultures and religions have the idea of an afterlife, and also may hold the idea of judgement of good and bad deeds in one's life ( h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York (state)
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area. With 20.2 million people, it is the fourth-most-populous state in the United States as of 2021, with approximately 44% living in New York City, including 25% of the state's population within Brooklyn and Queens, and another 15% on the remainder of Long Island, the most populous island in the United States. The state is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont to the east; it has a maritime border with Rhode Island, east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the north and Ontario to the northwest. New York City (NYC) is the most populous city in the United States, and around two-thirds of the state's popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care provider. Etymology The word patient originally meant 'one who suffers'. This English noun comes from the Latin word ', the present participle of the deponent verb, ', meaning 'I am suffering,' and akin to the Greek verb (', to suffer) and its cognate noun (). This language has been construed as meaning that the role of patients is to passively accept and tolerate the suffering and treatments prescribed by the healthcare providers, without engaging in shared decision-making about their care. Outpatients and inpatients An outpatient (or out-patient) is a patient who attends an outpatient clinic with no plan to stay beyond the duration of the visit. Even if the patient will not be formally admitted with a note as an outpatient, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt-like taste. Potassium chloride can be obtained from ancient dried lake deposits. KCl is used as a fertilizer, in medicine, in scientific applications, domestic water softeners (as a substitute for sodium chloride salt), and in food processing, where it may be known as E number additive E508. It occurs naturally as the mineral sylvite, and in combination with sodium chloride as sylvinite. Uses Fertilizer The majority of the potassium chloride produced is used for making fertilizer, called potash, since the growth of many plants is limited by potassium availability. Potassium chloride sold as fertilizer is known as muriate of potash (MOP). The vast majority of potash fertilizer worldwide is sold as MOP. Medical use Potassium is vital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxin
Digoxin (better known as Digitalis), sold under the brand name Lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. Digoxin is one of the oldest medications used in the field of cardiology. It works by increasing myocardial contractility, increasing stroke volume and blood pressure, reducing heart rate, and somewhat extending the time frame of the contraction. Digoxin is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Digoxin has a half life of approximately 36 hours given at average doses in patients with normal renal function. It is excreted mostly unchanged in the urine. Common side effects include breast enlargement with other side effects generally due to an excessive dose. These side effects may include loss of appetite, nausea, trouble seeing, confusion, and an irregular heartbeat. Greater care is required in older people and those with poor kidney function. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foeticide
Foeticide (British English), or feticide (American and Canadian English), is the act of killing a fetus, or causing a miscarriage. Etymology Foeticide derives from two constituent Latin roots. ''Foetus'', meaning child, is an alternate form of ''fetus'' coming from the writings of Isidorus, who preferred ''oe'' due to its association with ''foveo'' "I cherish" as opposed to ''feo'' "I beget". ''Foetus'' is compounded with the suffix ''-cide'', from '' caedere'', "to cut down, to kill." Also see homicide, genocide, infanticide, matricide, and regicide. Fetal homicide Laws in the United States In the U.S., most crimes of violence are covered by state law, not federal law. 38 states currently recognize the unborn child (the term usually used) or fetus as a homicide victim, and 29 of those states apply this principle throughout the period of pre-natal development. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
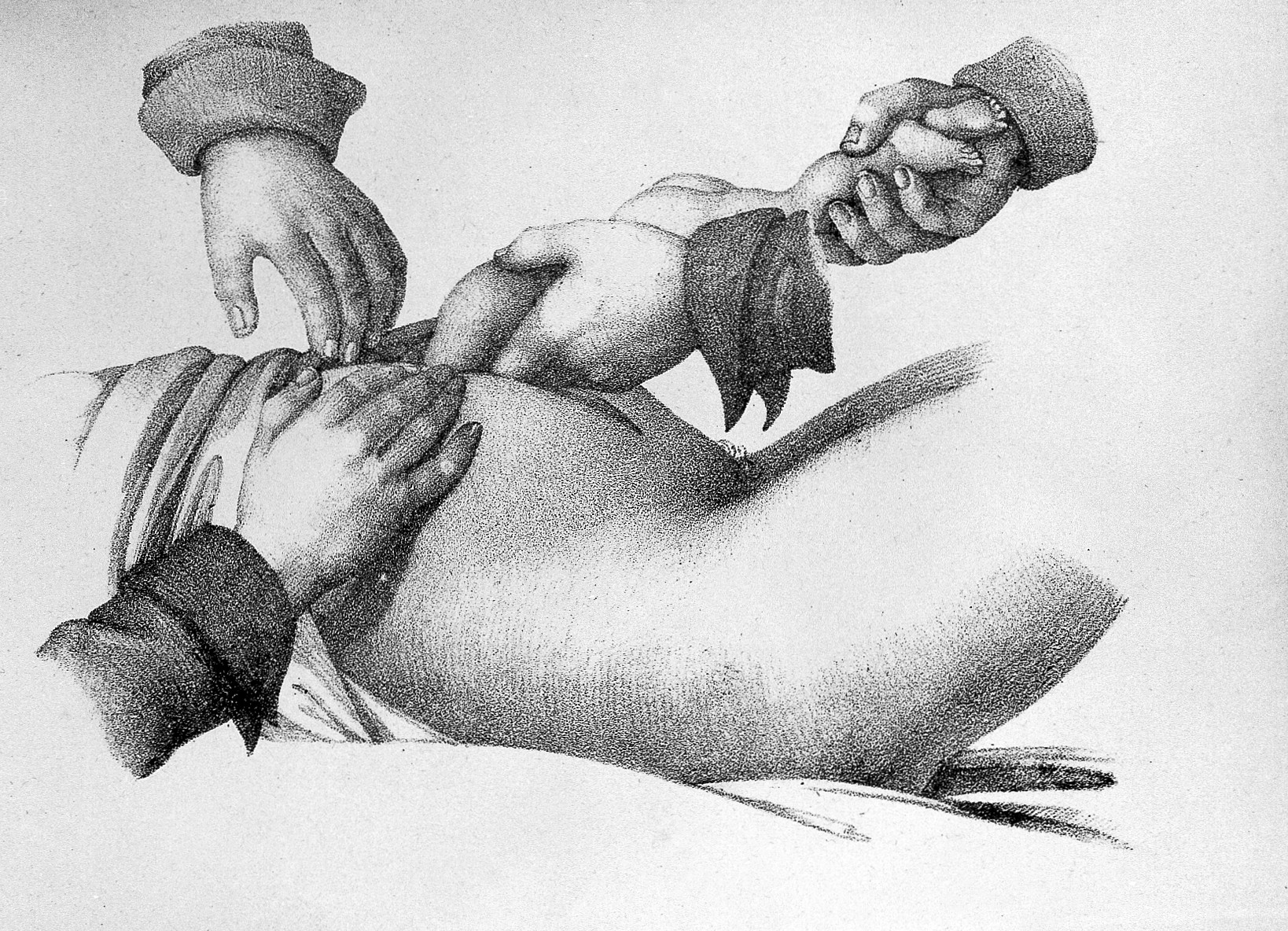
Hysterotomy
A hysterotomy is an incision made in the uterus. This surgical incision is used in several medical procedures, including during termination of pregnancy in the second trimester (or abortion) and delivering the fetus during caesarean section. It is also used to gain access and perform surgery on a fetus during pregnancy to correct birth defects, and it is an option to achieve resuscitation if cardiac arrest occurs during pregnancy and it is necessary to remove the fetus from the uterus. There are several types of incisions that can be made, including a midline vertical incision and a low transverse incision. The incision is made using a scalpel and is about 1-2 cm long, but it can be longer depending on the procedure that is performed. Other types of incisions are low transverse incision with T-extension in the midline, low transverse incision with J-extension, and low transverse incision with U-extension. These are used when low transverse incisions do not provide enough space in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New England Journal Of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one. History In September 1811, John Collins Warren, a Boston physician, along with James Jackson, submitted a formal prospectus to establish the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and Collateral Branches of Science'' as a medical and philosophical journal. Subsequently, the first issue of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' was published in January 1812. The journal was published quarterly. In 1823, another publication, the ''Boston Medical Intelligencer'', appeared under the editorship of Jerome V. C. Smith. The editors of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' purchased the weekly ''Intelligencer'' for $600 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)