|
Haplogroup CF (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup CF, also known as CF-P143 and CT(xDE), is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. This paternal lineage is defined by the SNP P143. The clade's existence and distribution are inferred from the fact that haplogroups descended from CF include most human male lineages in Eurasia, Oceania and The Americas. CF is an immediate descendant of the Haplogroup CT (CT-M168), and is the sibling of Haplogroup DE (DE-YAP). It is the immediate ancestor of both Haplogroup C and Haplogroup F. There are, as yet, no confirmed cases of living individuals or human remains belonging to the basal, undivergent haplogroup CF*. In the year 2017, C-M217 (C2) & C-M130 were reported among males belonging to the Shan people The Shan people ( shn, တႆး; , my, ရှမ်းလူမျိုး; ), also known as the Tai Long, or Tai Yai are a Tai ethnic group of Southeast Asia. The Shan are the biggest minority of Burma (Myanmar) and primarily live in th ...s, who are concentrated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian Highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and partly the Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. Western Asia covers an area of , with a pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup C-M216 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup C-M210 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup C-M208 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single kinship, line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a Hierarchy#Nested hierarchy, nest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup C-M130 (Y-DNA)
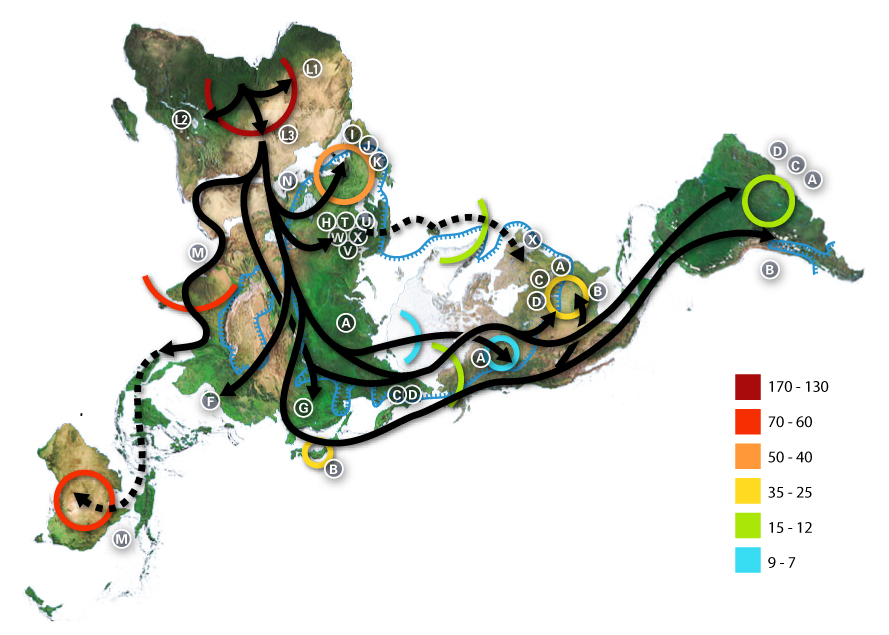
Haplogroup C is a major Y-chromosome haplogroup, defined by UEPs M130/RPS4Y711, P184, P255, and P260, which are all SNP mutations. It is one of two primary branches of Haplogroup CF alongside Haplogroup F. Haplogroup C is found in ancient populations on every continent except Africa and is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among males belonging to many peoples indigenous to East Asia, Central Asia, Siberia, North America and Australia as well as a some populations in Europe, the Levant, and later Japan.崎谷満『DNA・考古・言語の学際研究が示す新・日本列島史』(勉誠出版 2009年)(in Japanese) The haplogroup is also found with moderate to low frequency among many present-day populations of Southeast Asia, South Asia, and Southwest Asia. In addition to the basal paragroup C*, this haplogroup now has two major branches: C1 (F3393/Z1426; previously CxC3, i.e. old C1, old C2, old C4, old C5 and old C6) and C2 (M217; the former C3). Origins Haplog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-DNA Haplogroups In Populations Of Oceania ...
Listed here are notable ethnic groups and native populations from the Oceania (Pacific Islands and Australia) and East Indonesia by human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups based on relevant studies. See also *Oceania **Languages of Oceania **Demographics of Oceania **List of Oceanian countries by population Notes References External linksY-DNA Ethnographic and Genographic Atlas and Open-Source Data Compilation {{Y-chromosome haplogroups by population Oceania Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-DNA Haplogroups In Populations Of East And Southeast Asia
The tables below provide statistics on the human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups most commonly found among ethnolinguistic groups and populations from East and South-East Asia. ST means Sino-Tibetan languages. Main table Austronesian and Tai-Kadai The following is a table of Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup frequencies of Austro-Tai peoples (i.e., Tai-Kadai peoples and Austronesian peoples).Li, Hui, et al. (2008).Paternal genetic affinity between western Austronesians and Daic populations" ''BMC Evolutionary Biology'' 2008, 8:146. Tibeto-Burman branch of Sino-Tibetan The following table of Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup frequencies of Tibeto-Burman-speaking peoples of western and southwestern China is from Wen, et al. (2004). See also *Y-DNA haplogroups by group **Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of South Asia **Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Central and North Asia **Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Oceania **Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of the Near East **Y-DNA haplog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-DNA Haplogroups By Ethnic Group
The various ethnolinguistic groups found in the Caucasus, Central Asia, Europe, the Middle East, North Africa and/or South Asia demonstrate differing rates of particular Y-DNA haplogroups. In the table below, the first two columns identify ethnolinguistic groups. Subsequent columns represent the sample size (''n'') of the study or studies cited, and the percentage of each haplogroup found in that particular sample. (Data from studies conducted before 2004 may be inaccurate or a broad estimate, due to obsolete haplogroup naming systems – e.g. the former ''Haplogroup 2'' included members of the relatively unrelated haplogroups known later as Haplogroup G and macrohaplogroup IJ hich comprises haplogroups I and J) See also * Genetics ** Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroups ** Human genome ** Genetic genealogy ** Genealogical DNA testing ** Race and genetics * Genetic history * Timeline of human evolution ** Recent African origin of modern humans ** Genetic history of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-chromosome Haplogroups In Populations Of The World
The following articles are lists of human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups found in populations around the world. * Y-DNA haplogroups by ethnic group *Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Europe * Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of the Near East *Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of North Africa * Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Sub-Saharan Africa * Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of the Caucasus *Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of South Asia *Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of East and Southeast Asia * Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Central and North Asia *Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Oceania * Y-DNA haplogroups in indigenous peoples of the Americas * List of haplogroups of historic people See also *Recent African origin of modern humans *Genetic history of the Middle East *Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia * Genetic history of Europe *Genetic history of Italy *Genetic history of North Africa * Genetic history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas *Genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
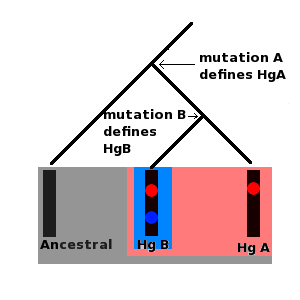
Subclade
In genetics, a subclade is a subgroup of a haplogroup. Naming convention Although human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and Y chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) haplogroups and subclades are named in a similar manner, their names belong to completely separate systems. mtDNA mtDNA haplogroups are defined by the presence of a series of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers in the hypervariable regions and the coding region of mitochondrial DNA. They are named with the capital letters A through Z, with further subclades named using numbers and lower case letters. Y-DNA Y-DNA haplogroups are defined by the presence of a series of SNP markers on the Y chromosome. Subclades are defined by a ''terminal SNP'', the SNP furthest down in the Y chromosome phylogenetic tree. Human Y-DNA The Y Chromosome Consortium (YCC) developed a system of naming major human Y-DNA haplogroups with the capital letters A through T, with further subclades named using numbers and lower case letters (YCC longhand nomenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paragroup
Paragroup is a term used in population genetics to describe lineages within a haplogroup that are not defined by any additional unique markers. In human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups, paragroups are typically represented by an asterisk (*) placed after the main haplogroup. The term "paragroup" is a portmanteau of the terms paraphyletic haplogroup indicating that paragroups form paraphyletic subclades. Apart from the mutations that define the parent haplogroup, paragroups may not possess any additional unique markers. Alternatively paragroups may possess unique markers that have not been discovered. If a unique marker is discovered within a paragroup, the specific lineage is given a unique name and is moved out of the paragroup to form an independent subclade. For example, the paragroup of human Y-DNA Haplogroup DE is DE*. A member of DE* has the marker that defines DE, but not the markers that define DE's only known immediate subclades, haplogroups D and E. Likewise, haplog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |