|
Half-Jew
The term Halbjude (English: Half-Jew) is a derogatory term for people with a non-Jewish and a Jewish parent. The overwhelming majority of the so-called half-Jews were legally classified as " first-degree Jewish hybrids" during the era of Nazi Germany. Occasionally, the term was used even before the Nazi era. Within Judaism the term half Jew is unusual, since it does not recognize any partial degrees of Judaism; one can either be Jewish or not. Situation within the German Reich During the Nazi era, half-Jews was not a legal term. The term was not used in the Nuremberg Race Laws and the related ordinances. In 1941 the word half-Jew was included in the Duden for the first time: the group of " Jewish half-breeds" was further divided into "Jewish half-breeds of the first degree" with two Jewish grandparents and "Jewish half-breeds of the second degree" with one Jewish grandparent. However, first-degree hybrids were classified in different categories, despite the assumption of the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mischling
(; " mix-ling"; plural: ) was a pejorative legal term used in Nazi Germany to denote persons of mixed "Aryan" and non-Aryan, such as Jewish, ancestry as codified in the Nuremberg racial laws of 1935. In German, the word has the general denotation of hybrid, mongrel, or half-breed. Outside its use in official Nazi terminology, the term ''Mischlingskinder'' ("mixed children") was later used to refer to war babies born to non-white soldiers and German mothers in the aftermath of World War II. Nazi definitions of Mischling Since the Nazis were unable to find a racial definition of a "Jew", they instead relied on one's ancestors' religious backgrounds to determine whether someone was of "German or related blood" ("Aryan") or a "Jew" ("non-Aryan"). Thus, the Nuremberg Laws in 1935 defined a "full Jew" (''Istjude'' or ''Volljude'' in Nazi terminology) as a person – regardless of religious affiliation or self-identification – who had at least three grandparents who had been enro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
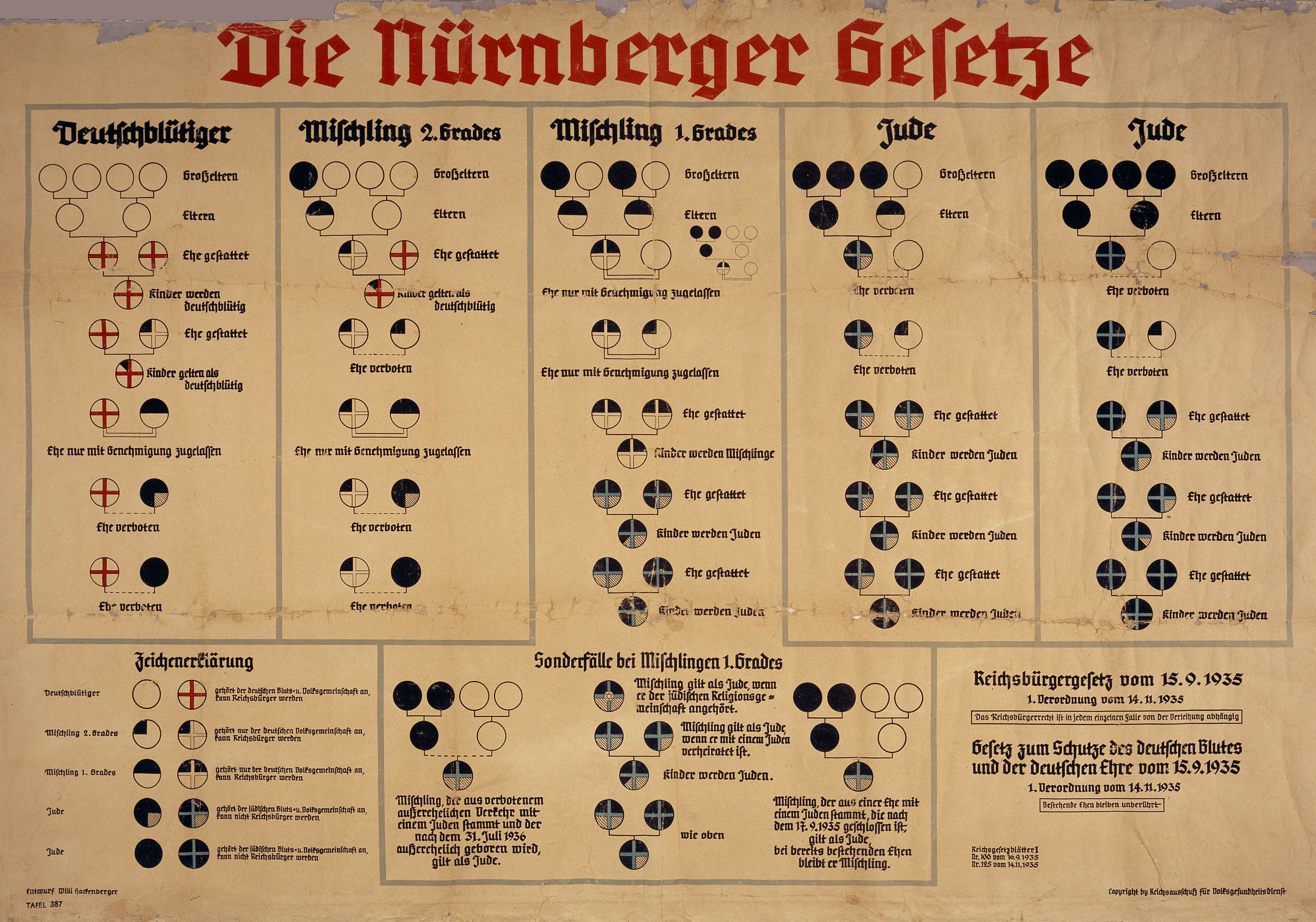
Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of the Nazi Party. The two laws were the Law for the Protection of German Blood and German Honour, which forbade marriages and extramarital intercourse between Jews and Germans and the employment of German females under 45 in Jewish households; and the Reich Citizenship Law, which declared that only those of German or related blood were eligible to be Reich citizens. The remainder were classed as state subjects without any citizenship rights. A supplementary decree outlining the definition of who was Jewish was passed on 14 November, and the Reich Citizenship Law officially came into force on that date. The laws were expanded on 26 November 1935 to include Romani and Black people. This supplementary decree defined Romanis as "enemies of the rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Eichmann
Otto Adolf Eichmann ( , ''''. ; 19 March 1906 – 1 June 1962) was a German-Austrian SS-'''' and one of the major organisers of – the so-called " |
Eugen Dühring
Eugen Karl Dühring (12 January 1833, Berlin21 September 1921, Nowawes in modern-day Potsdam-Babelsberg) was a German philosopher, positivist, economist, and socialist who was a strong critic of Marxism. Life and works Dühring was born in Berlin, Prussia. After a legal education he practised at Berlin as a lawyer until 1859. A weakness of the eyes, ending in total blindness, occasioned his taking up the studies with which his name is now connected. In 1864, he became docent of the University of Berlin, but, in consequence of a quarrel with the professoriate, was deprived of his licence to teach in 1874. Among his works are (1865); (1865); (1865); (1869); (1872), one of his most successful works; (1873); (1875), entitled in a later edition ; (1878); and (1883). He also published (1881, ''The Jewish Question as a Racial, Moral, and Cultural Question''). He published his autobiography in 1882 under the title ; the mention of ('enemies') is characteristic. Dühring's ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edom
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.Negev & Gibson (ed.), 2001, ''Edom; Edomites'', pp. 149–150 Most of its former territory is now divided between present-day southern Israel and Jordan. Edom appears in written sources relating to the late Bronze Age and to the Iron Age in the Levant. Edomites are related in several ancient sources including the Tanakh, a list of the Egyptian pharaoh Seti I from c. 1215 BC as well as in the chronicle of a campaign by Ramesses III (r. 1186–1155 BC). Archaeological investigation has shown that the nation flourished between the 13th and the 8th century BC and was destroyed after a period of decline in the 6th century BC by the Babylonians. After the fall of the kingdom of Edom, the Edomites were pushed westward towards southern Judah by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herod The Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renovation of the Second Temple in Jerusalem and the expansion of the Temple Mount towards its north, the enclosure around the Cave of the Patriarchs in Hebron, the construction of the port at Caesarea Maritima, the fortress at Masada, and Herodium. Vital details of his life are recorded in the works of the 1st century CE Roman–Jewish historian Josephus. Herod also appears in the Christian Gospel of Matthew as the ruler of Judea who orders the Massacre of the Innocents at the time of the birth of Jesus, although most Herod biographers do not believe that this event occurred. Despite his successes, including singlehandedly forging a new aristocracy from practically nothing, he has still been criticised by various historians. His reign pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halakha
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandments ('' mitzvot''), subsequent Talmudic and rabbinic laws, and the customs and traditions which were compiled in the many books such as the ''Shulchan Aruch''. ''Halakha'' is often translated as "Jewish law", although a more literal translation of it might be "the way to behave" or "the way of walking". The word is derived from the root which means "to behave" (also "to go" or "to walk"). ''Halakha'' not only guides religious practices and beliefs, it also guides numerous aspects of day-to-day life. Historically, in the Jewish diaspora, ''halakha'' served many Jewish communities as an enforceable avenue of law – both civil and religious, since no differentiation of them exists in classical Judaism. Since the Jewish Enlightenment (''Hask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Burnier
Andreas Burnier, born Catharina Irma Dessaur (3 July 1931 – 18 September 2002) was a Dutch writer. Burnier has published poetry, lectures, books and articles, many of which address homosexuality, in order to emphasize women's problems in a male-dominated society. Literary debut Burnier debuted in the literary magazine ''Tirade'' with her story ''Verschrikkingen van het Noorden''. Along with assuming a new name as a writer, Burnier also assumed the opposite gender. In 1965, she published her first novel, ''Een tevreden lach'' (the title of which translates as something like "A Contented Laugh"). In it she wrote about her homosexuality, a topic that had previously not been widely discussed in Dutch literature. She did not mean to publish this novel at first as she wrote it for herself due to the need of reflection, and she deemed it unfit for publication, but after coming into contact with a manager who worked at Querido, who wanted to read it, it became published. ''Een tevrede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignatz Bubis
Ignatz Bubis (12 January 1927 – 13 August 1999), German Jewish leader, was the influential chairman (and later president) of the Central Council of Jews in Germany (''Zentralrat der Juden in Deutschland'') from 1992 to 1999. In this capacity he led a public campaign against German antisemitism. Bubis's high profile both in Frankfurt and nationwide involved him in a number of public controversies. Life Born in the formerly German city of Breslau (today Wrocław, Poland), Bubis moved with his family to Dęblin, Poland in 1935.Richard S. Levy (2005)Antisemitism: A Historical Encyclopedia of Prejudice and Persecution, Volume 1.ABC-CLIO. p. 88. . During the Nazi occupation of Dęblin, Bubis lived in the Dęblin–Irena Ghetto before deportation to the HASAG labor camp in Częstochowa in 1944. After liberation, he moved to Dresden and later West Germany as the political situation in the Soviet zone of occupation deteriorated. He established himself in the precious metal industry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Seyss-Inquart
Arthur Seyss-Inquart (German: Seyß-Inquart, ; 22 July 1892 16 October 1946) was an Austrian Austrian National Socialism, Nazi politician who served as Chancellor of Austria in 1938 for two days before the ''Anschluss''. His positions in Nazi Germany included "deputy governor to Hans Frank in the Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), General Government of Occupied Poland, and ''Reichskommissar, Reich commissioner'' for the German-occupied Netherlands" including shared responsibility "for the The Holocaust in the Netherlands, deportation of Dutch Jews and the shooting of hostages". During World War I, Seyss-Inquart fought for the Austro-Hungarian Army with distinction. After the war he became a successful lawyer, and went on to join the governments of Chancellor of Austria, Chancellors Engelbert Dollfuss and Kurt Schuschnigg. In 1938, Schuschnigg resigned in the face of a German invasion, and Seyss-Inquart was appointed his successor. The newly installed Nazis proceeded to transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deportation
Deportation is the expulsion of a person or group of people from a place or country. The term ''expulsion'' is often used as a synonym for deportation, though expulsion is more often used in the context of international law, while deportation is more used in national (municipal) law. Forced displacement or forced migration of an individual or a group may be caused by deportation, for example ethnic cleansing, and other reasons. A person who has been deported or is under sentence of deportation is called a ''deportee''. Definition Definitions of deportation apply equally to nationals and foreigners. Nonetheless, in the common usage the expulsion of foreign nationals is usually called deportation, whereas the expulsion of nationals is called extradition, banishment, exile, or penal transportation. For example, in the United States: "Strictly speaking, transportation, extradition, and deportation, although each has the effect of removing a person from the country, are differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)