|
Helium Mass Spectrometer
A helium mass spectrometer is an instrument commonly used to detect and locate small leaks. It was initially developed in the Manhattan Project during World War II to find extremely small leaks in the gas diffusion process of uranium enrichment plants. It typically uses a vacuum chamber in which a sealed container filled with helium is placed. Helium leaks out of the container, and the rate of the leak is detected by a mass spectrometer. Detection technique Helium is used as a tracer because it penetrates small leaks rapidly. Helium also has the properties of being non-toxic, chemically inert and present in the atmosphere only in minute quantities (5 ppm). Typically a helium leak detector will be used to measure leaks in the range of 10 to 10 Pa· m· s. A flow of 10 Pa·m·s is about 0.006 ml per minute at standard conditions for temperature and pressure (STP). A flow of 10 Pa·m·s is about 0.003 ml per century at STP. Types of leaks Typically there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the actual bombs. The Army component of the project was designated the Manhattan District as its first headquarters were in Manhattan; the placename gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. Along the way, the project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys. The Manhattan Project began modestly in 1939, but grew to employ more than 130,000 people and cost nearly US$2 billion (equivalent to about $ billion in ). Over 90 percent of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, https://www.ashrae.org/technical-resources/free-resources/ashrae-terminology Refrigeration can be considered an artificial, or human-made, cooling method. Refrigeration refers to the process by which energy, in the form of heat, is removed from a low-temperature medium and transferred to a high-temperature medium. This work of energy transfer is traditionally driven by mechanical means, but can also be driven by heat, magnetism, electricity, laser, or other means. Refrigeration has many applications, including household refrigerators, industrial freezers, cryogenics, and air conditioning. Heat pumps may use the heat output of the refrigeration process, and also may be designed to be reversible, but are otherwise similar to air conditioning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leak Noise Correlator
A leak noise correlator is an electronic device used for Leak Detection and as a leak locator to find leaks in pressurized water or gas lines. Typically, microphones or acoustic sound sensors are placed in contact with the pipe, at two or more points, to record the sound emitted by a leak (e.g. a hissing noise) somewhere between the points. The sound data is processed through a mathematical algorithm which compares or Correlation, correlates the two recordings to determine the difference in the times it takes noise to travel from the site of the leak to each of the sensors. If the distance between the sensors is known in advance, this timing information can be used to determine the location of the leak., The cross correlation signal of one continuous function, f, with another, g, is defined as: :(f \star g)(t)\ \stackrel \int_^ f^*(\tau)\ g(t+\tau)\,d\tau, where f * denotes the complex conjugate of f. If f and g are two sound recordings of the noise produced by the leak, delayed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracer-gas Leak Testing
A tracer-gas leak testing method is a nondestructive testing method that detects gas leaks. A variety of methods with different sensitivities exist. Tracer-gas leak testing is used in the petrochemical industry, the automotive industry, and in the manufacture of semiconductors, among other uses. Types Several tracer-gas leak testing methods exist, including: * Detection of leaks using helium mass spectrometer, which provides high sensitivity * Hydrogen leak testing, which provides the best mobility * Refrigerant gas leak detection, for refrigeration applications Method selection Typical leakage rates The nature of the product or the process and the process gases will set the leak rate requirement: Sensitivity of methods Based on the target leak rate, the table below will help to choose the most suitable method. Applications Typical applications of tracer-gas leak testing include: * In Petrochemical plant, petrochemical plants, Cracking (chemistry), hydrocracking, vapoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
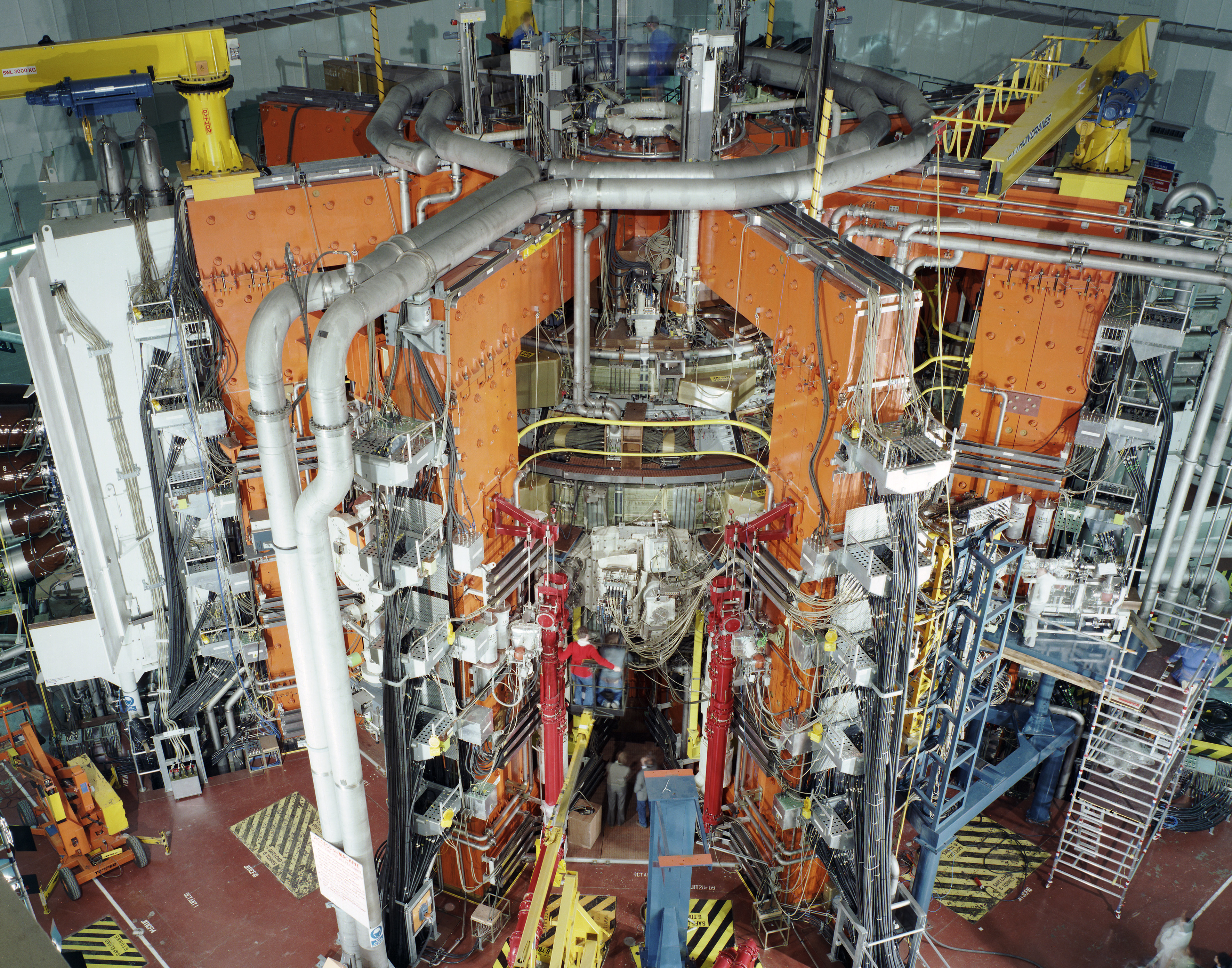
Wendelstein 7-X
The Wendelstein 7-X (abbreviated W7-X) reactor is an experimental stellarator built in Greifswald, Germany, by the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP), and completed in October 2015.Introduction – the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator Retrieved 5 November 2014. Its purpose is to advance stellarator technology: though this experimental reactor will not produce electricity, it is used to evaluate the main components of a future plant; it was developed based on the predecessor experimental reactor. , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion, nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an Inertial confinement fusion, inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma (physics), plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressure by around 20%. But hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
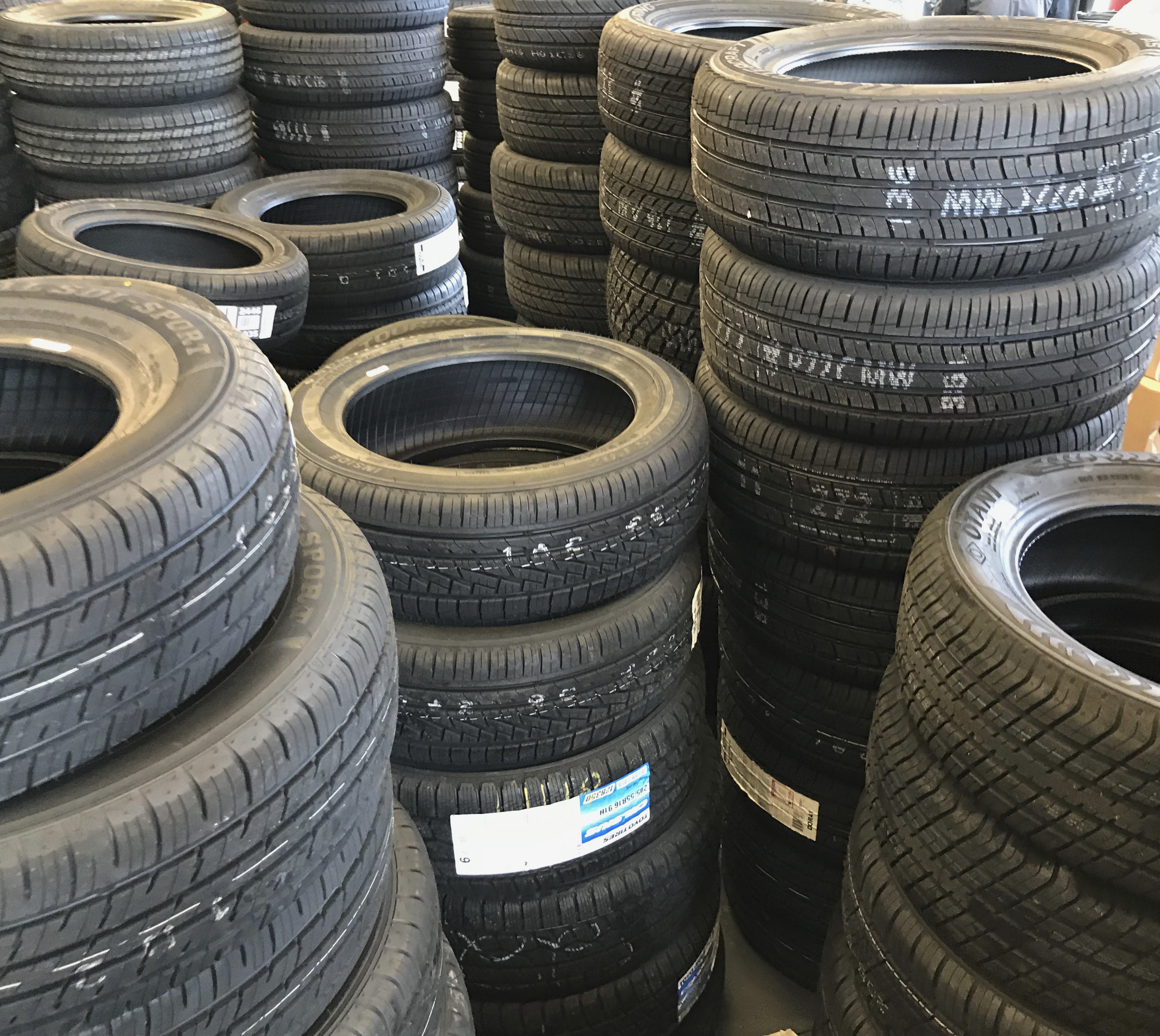
Tire
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a Rim (wheel), wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide Traction (engineering), traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, which also provide a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, that is designed to match the weight of the vehicle with the bearing strength of the surface that it rolls over by providing a bearing pressure that will not deform the surface excessively. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tire tread, tread and a body. The tread provides Traction (engineering), traction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Extinguisher
A fire extinguisher is a handheld active fire protection device usually filled with a dry or wet chemical used to extinguish or control small fires, often in emergencies. It is not intended for use on an out-of-control fire, such as one which has reached the ceiling, endangers the user (i.e., no escape route, smoke, explosion hazard, etc.), or otherwise requires the equipment, personnel, resources, and/or expertise of a fire brigade. Typically, a fire extinguisher consists of a hand-held cylindrical pressure vessel containing an agent that can be discharged to extinguish a fire. Fire extinguishers manufactured with non-cylindrical pressure vessels also exist but are less common. There are two main types of fire extinguishers: stored-pressure and cartridge-operated. In stored pressure units, the expellant is stored in the same chamber as the firefighting agent itself. Depending on the agent used, different propellants are used. With dry chemical extinguishers, nitrogen is typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Bottle
Bottled gas is a term used for substances which are gaseous at standard temperature and pressure (STP) and have been compressed and stored in carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or composite material, composite bottles known as gas cylinders. Gas state in cylinders There are four cases: either the substance remains a gas at standard temperature but increased pressure, the substance liquefies at standard temperature but increased pressure, the substance is dissolved in a solvent, or the substance is liquefied at reduced temperature and increased pressure. In the last case the bottle is constructed with an inner and outer shell separated by a vacuum (dewar flask) so that the low temperature can be maintained by evaporative cooling. Case I The substance remains a ''gas'' at ''standard temperature'' and ''increased pressure'', its critical temperature being below standard temperature. Examples include: * air * argon * fluorine * helium * hydrogen * krypton * nitrogen * oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosol Spray
Aerosol spray is a type of dispensing system which creates an aerosol mist of liquid particles. It comprises a can or bottle that contains a payload, and a propellant under pressure. When the container's valve is opened, the payload is forced out of a small opening and emerges as an aerosol or mist. History The concepts of aerosol probably go as far back as 1790.Bellis, MarThe History of Aerosol Spray Cans/ref> The first aerosol spray can patent was granted in Oslo in 1927 to Erik Rotheim, a Norwegian chemical engineer,Norwegian Patent No. 46613, issued on November 23, 1926 and a United States patent was granted for the invention in 1931. — Method and Means for the Atomizing or Distribution of Liquid or Semiliquid Materials, issued April 7, 1931 The patent rights were sold to a United States company for 100,000 Norwegian kroner. The Norwegian Postal Service, Posten Norge, celebrated the invention by issuing a stamp in 1998. In 1939, American Julian S. Kahn received a pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)