|
Hand Of Fatima
The ''hamsa'' ( ar, خمسة, khamsa) is a palm-shaped amulet popular throughout North Africa and in the Middle East and commonly used in jewellery and wall hangings.Bernasek et al., 2008p. 12Sonbol, 2005pp. 355–359 Depicting the open right hand, an image recognized and used as a sign of protection in many times throughout history, the ''hamsa'' has been traditionally believed to provide defense against the evil eye. ''Khamsah'' is an Arabic word that means "five", but also refers to images of "the five fingers of the hand".Zenner, 1988p. 284World Institute for Advanced Phenomenological Research and Learning (Belmont, Estados Unidos), 1991p. 219Drazin, 2009p. 268 In Jewish culture, the ''hamsa'' is associated with the number five because of the five fingers depicted on the hand, and because the word ''khamsa'' is cognate to the Hebrew ''ḥamishah'' (חֲמִישָׁה), which also means "five." The ''Hamsa'' has also been known as the Hand of Fatima after the daughter of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khamsa
Khamsa (Arabic, lit. "five") may refer to: * Hamsa, a popular amulet in the Middle East and North Africa, also romanized as ''khamsa'' * Al Khamsa, a bloodline for Arabian horses that traces back to five mares * Al Khamsa (organization), a nonprofit organization in the United States that supports the breeding of Al Khamsa bloodline horses * Khamseh, a tribal people of Iran * Khamsa (film), ''Khamsa'' (film), a 2008 film * Khamsa of Nizami, a quintet of five long Persian poems, such as those of Nizami Ganjavi. See also * Khamsa of Nizami (British Library, Or. 12208), the manuscript of the five poems of Nezami Ganjavi * Melikdoms of Karabakh, also known as ''Khamsa Melikdoms'', the five Armenian Melikdoms of Karabakh, from the Middle Ages to the Early Modern Age. * Hamsa (other) * Khansa (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalah
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and Jewish theology, school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The definition of Kabbalah varies according to the tradition and aims of those following it, from its origin in medieval Judaism to its later adaptations in Western esotericism (Christian Kabbalah and Hermetic Qabalah). Jewish Kabbalah is a set of esoteric teachings meant to explain the relationship between the unchanging, eternal God in Judaism, God—the mysterious ''Ein Sof'' (, ''"The Infinite"'')—and the mortal, finite universe (God's Genesis creation narrative, creation). It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed their own transmission of Primary texts of Kabbalah, sacred texts within the realm of Jewish traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefarditas or Hispanic Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the Iberian Peninsula. The term, which is derived from the Hebrew ''Sepharad'' (), can also refer to the Mizrahi Jews of Western Asia and North Africa, who were also influenced by Sephardic law and customs. Many Iberian Jewish exiles also later sought refuge in Mizrahi Jewish communities, resulting in integration with those communities. The Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula prospered for centuries under the Muslim reign of Al-Andalus following the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, but their fortunes began to decline with the Christian ''Reconquista'' campaign to retake Spain. In 1492, the Alhambra Decree by the Catholic Monarchs of Spain called for the expulsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Of Horus
The Eye of Horus, ''wedjat'' eye or ''udjat'' eye is a concept and symbol in ancient Egyptian religion that represents well-being, healing, and protection. It derives from the mythical conflict between the god Horus with his rival Set, in which Set tore out or destroyed one or both of Horus's eyes and the eye was subsequently healed or returned to Horus with the assistance of another deity, such as Thoth. Horus subsequently offered the eye to his deceased father Osiris, and its revitalizing power sustained Osiris in the afterlife. The Eye of Horus was thus equated with funerary offerings, as well as with all the offerings given to deities in temple ritual. It could also represent other concepts, such as the moon, whose waxing and waning was likened to the injury and restoration of the eye. The Eye of Horus symbol, a stylized eye with distinctive markings, was believed to have protective magical power and appeared frequently in ancient Egyptian art. It was one of the most com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apotropaic Magic
Apotropaic magic (from Greek "to ward off") or protective magic is a type of magic intended to turn away harm or evil influences, as in deflecting misfortune or averting the evil eye. Apotropaic observances may also be practiced out of superstition or out of tradition, as in good luck charms (perhaps some token on a charm bracelet), amulets, or gestures such as crossed fingers or knocking on wood. Many different objects and charms were used for protection throughout history. Symbols and objects Ancient Egyptian Apotropaic magical rituals were practiced throughout the ancient Near East and ancient Egypt. Fearsome deities were invoked via ritual in order to protect individuals by warding away evil spirits. In ancient Egypt, these household rituals (performed in the home, not in state-run temples) were embodied by the deity who personified magic itself, Heka. The two gods most frequently invoked in these rituals were the hippopotamus-formed fertility goddess, Taweret, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno Barbatti
Bruno Barbatti (September 27, 1926 – March 31, 2020) was a Swiss scholar and writer. He was born in Zurich to an Italian father and a German mother. He studied at the universities of Fribourg, Paris (Sorbonne), Florence and Zurich, where he obtained a doctorate in German. For 35 years, he taught at the Kantonsschule Rämibühl, where he was once a student. Barbatti is best known for his book ''Berber Carpets of Morocco''. He did extensive field work in Morocco, especially Marrakech, where his wife Dominique was a high school teacher for several years. The couple built up an extensive collection of carpets over the years. Some were exhibited at Museum Bellerive A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these ... in Zurich in 1996. He married the French writer and teacher Dominiqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
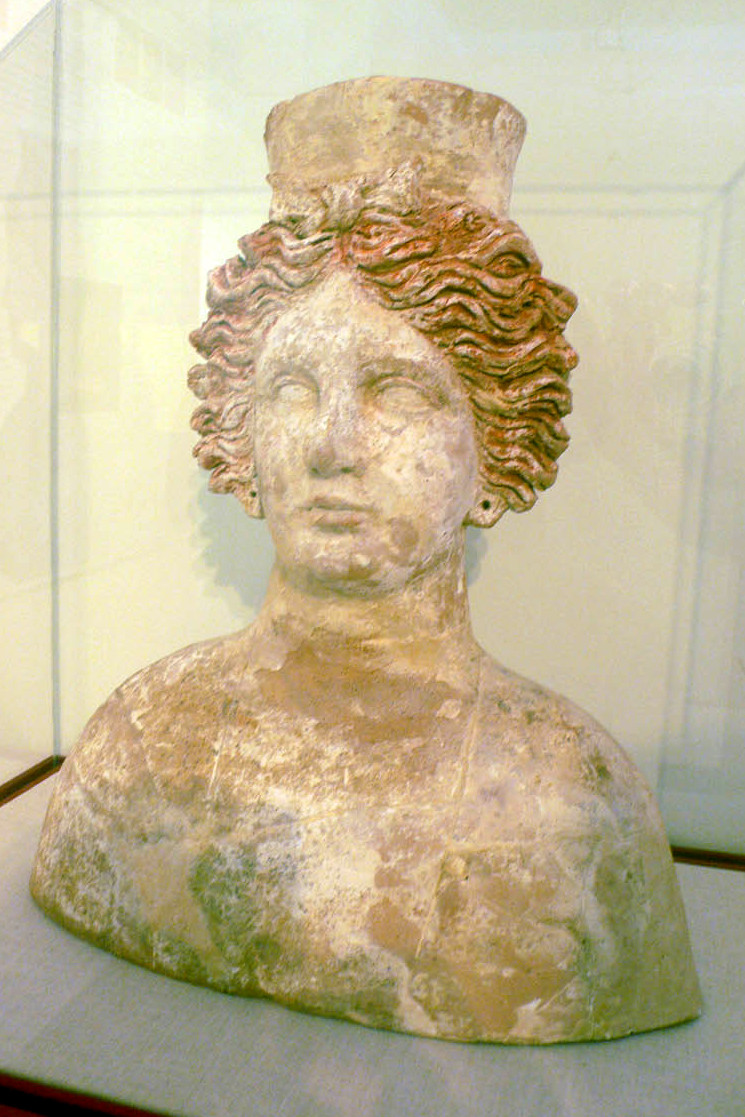
Tanit
Tanit ( Punic: 𐤕𐤍𐤕 ''Tīnīt'') was a Punic goddess. She was the chief deity of Carthage alongside her consort Baal-Hamon. Tanit is also called Tinnit. The name appears to have originated in Carthage (modern day Tunisia), though it does not appear in local theophorous names. She was equivalent to the war goddess Astarte, and later worshipped in Roman Carthage in her Romanized form as Dea Caelestis, Juno Caelestis, or simply Caelestis. In modern-day Tunisian Arabic, it is customary to invoke or ('Mother Tannou' or 'Mother Tangou', depending on the region), in years of drought to bring rain. Similarly, Algerian, Tunisian and many other spoken forms of Arabic refer to " farming" to refer to non-irrigated agriculture. Such usage is attested in Hebrew, a Canaanite language sister to Phoenician, already in the 2nd century CE Mishnah. Tanit or Tinnīt? Until 1955 the name of the goddess was only known in Phoenician characters, as TNT (written without vowels). It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
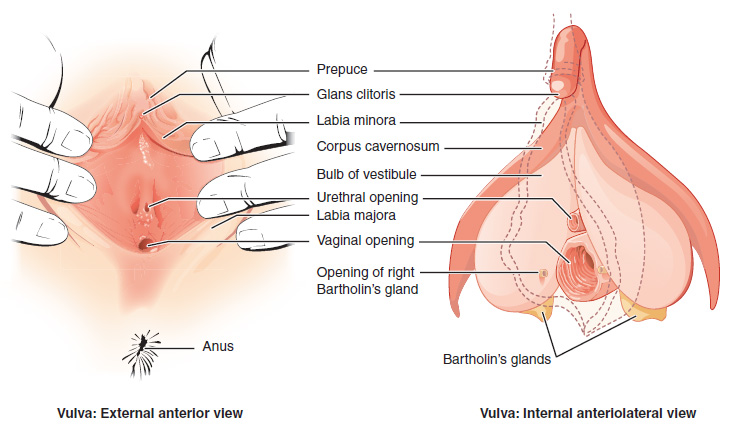
Vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external sex organ, female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horus
Horus or Heru, Hor, Har in Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as god of kingship and the sky. He was worshipped from at least the late prehistoric Egypt until the Ptolemaic Kingdom and Roman Egypt. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history, and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists."The Oxford Guide: Essential Guide to Egyptian Mythology", Edited by Donald B. Redford, Horus: by Edmund S. Meltzer, pp. 164–168, Berkley, 2003, . These various forms may be different manifestations of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality. He was most often depicted as a falcon, most likely a lanner falcon or peregrine falcon, or as a man with a falcon head. The earliest recorded form of Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother, Set cut him up into pieces after killing him, Osiris' wife Isis found all the pieces and wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was widely worshipped until the decline of ancient Egyptian religion during the rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut, as well as being brother and husband of Isis, and brother of Set, Nephthys, and Horus the Elder, with Horus the Younger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |